Core Skills Framework
advertisement

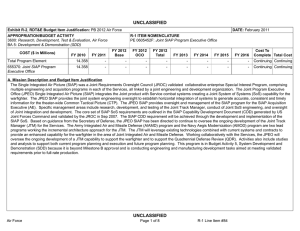
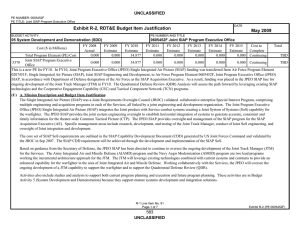
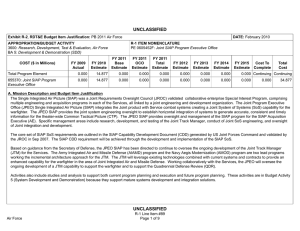
Workshop on Human Resource Management and Training in Statistical Offices 14 – 16 September 2010, Geneva, UNECE 5th Decade of Statistical Training for Development & Core Skills Framework Davaasuren Chultemjamts, Director, Statistical Institute for Asia and the Pacific UNESCAP 1 Outline • About SIAP • Core Skills Framework • 2009 Training Needs Survey 2 About SIAP 1970 : Established as the Asian Statistical Institute by the initiative of Government of Japan 1995 : Accorded the legal status as a subsidiary body of ESCAP 2010: The 40th Anniversary of SIAP SIAP is located in Japan 3 Goal of SIAP • The goal of the Institute is to ensure that: – Imparted knowledge and skills to the participants make significant contribution to proper policy and decision making in their respective countries. – Training capabilities of participating countries will be gradually improved and sustained thereby the effect of SIAP training is maximized. 4 Japan (MIC; JICA) 63 ESCAP Countries United Nations Statistical Institute for Asia and the Pacific Country Partner Institutions NSO/STI NSO/STI NSO/STI NSO/STI NSO/STI NSO/STI ESCAP Statistics Division International organizations Institutional Framework of SIAP 5 Resources Financial resources: Bulk (87%) of cash contributions derived from the Government of Japan Cash contributions from other members and associate members of ESCAP Non-financial resources: The Government of Japan: Administrative and infrastructure support Fellowships offered by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) Experts/resource persons 6 Resources (II) Non-financial resources: Members and associate members of ESCAP: Experts/resource persons Facilities and other support International organizations: Ad hoc funds for special projects Co-funding and other forms of cost-sharing of training courses Experts/resource persons 7 As of July 2010, 12,135 government statisticians from 126 countries have gone through the training course of SIAP. North and Central Asia 2% NonESCAP 2% Pacific 13% South and Southwest Asia 31% East and North-East Asia 16% SouthEast Asia 36% 8 More than 600 of SIAP alumni are holding influential positions at NSOs SIAP contributes to building a sense of community among official statisticians that facilitates: • dissemination of knowledge, • best practices and • exchange of expertise in developing official statistics 9 New Strategic Plan & New Strategies Results oriented strategic plan for AY 2010 – AY 2014 Strategies are: Training the trainers Reaching more people through distance training and providing e-learning resources Strengthening partnership with country partner institutes, international organizations, universities. 10 Results Framework Current practice: activity – based AY 2005 – AY 2009 Training Activities Resources e.g. human material financial & other resources Outputs e.g. Number of participants; Number of training materials etc. Results-based strategic management AY 2010 – AY 2014 Outcomes e.g. New knowledge; Increased skills; Change in attitude or value etc. Goal e.g. High quality & timely statistics support achievements of MDGs, sustainable development etc. 11 Training Programme for AY 2010 – AY 2014 I. II. Tokyo-based programme • SIAP-JICA courses • Short-term courses Outreach Ptogramme III. Management seminar for heads of NSOs Workshop on Statistical Quality Management and Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics Research based training programme Distance training and e-learning V. Regional, sub-regional courses/workshops/seminars Country courses Programme for managers of NSOs IV. VI. SIAP-JICA Distance training courses SIAP-JAXA* e-learning training E-training training resources Improved coordination of statistical training in the region A Forging partnerships seminar /workshop JAXA -Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency 12 Evolution of SIAP-JICA Courses Junior Level Statisticians Middle Level Statisticians Computer personnel Area Focused Courses 2-month Courses 10-month General Course 1970 - 1975 6-month Practical Course 1976 - 1998 Analysis & Interpretation of OS 1991 – 2004 Automatic Data Processing 1981 – 1995 Analysis, Interpretation & Dissemination of OS 2005 – 2009 Automatic Data Processing for Trainers 1996 – 1998 6-month Module Course 1999 – 2009 Analysis, Interpretation & Use of OS 2010-2014 Statistical Computing for Trainers 1999 – 2003 4-month course on MDGs 2010 - 2014 Application of ICT to Production & Dissemination for OS 2004 – 2009 Application of Information Management and Related ICT for OS 2010 – 2014 Courses on Country Specific Issues 1996 - 2001 Area Focused Course for Central Asian & Caucasus Countries 2001 - 2008 Area Focused Course for Central Asian Countries 2009 - 2011 13 Introduction of Core Skills Framework SIAP (Primary reason): to identify what skills SIAP should provide training on. NSO (Other uses): to identify which additional skills are needed by NSO staff to improve their organizational performance. Individual Staff of NSOs: to manage their own professional development and identify what skills they need to improve their job performance Descriptions in CSF can be used to decide on the skill requirement: for each Level for career path developments and for each subject area for training content/curriculum designing 14 Core Skills Framework Core skills framework was used to identify the skills required by NSO’s; grouped into 3 main types Core statistical skills Specialist statistical skills Statistical management skills Skills levels: Level 1: Clerical Support Level 2: Core skill –level 2 – (Compiler) Level 3: Core skill –level 3 – (Analyst) Level 4: Core skill –level 2 – (Senior Analyst) Level 5: Core skill –level 2 – (Supervisory) 15 CSF is not static and needs updating 16 2009 Training Needs Survey Conducted Training Needs Survey (TNS) in April 2009 Objective of TNS: To seek the views of heads of the NSO’s about their priorities for skills development in their organization their priorities for existing courses offered by SIAP how SIAP’s work could be improved and 17 What Are The Problems Which Need To Be Addressed? The need for training is greater than what can be supplied by SIAP Training programmes in single subject matter areas limits the improvement in capability of those being trained Training needed in new areas More training programmes for skills development at higher levels are needed 18 Strengthening Partnerships Country partner Institutes •Statistics Korea, Republic of Korea International Organizations •Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong, China •UN agencies Other organizations •SD-ESCAP ADB •UNECE ECO •UNSD IMF •UNDP ISI •Central Statistical Organization, India •Statistical Centre of Iran •BPS- Statistics Indonesia •Statistics Bureau, Japan •NSO Philippines • Other •UNESCO SPCI •UNFPA PARIS21 •ILO/SIMPOC WB • Other Training Institutes Universities 19 For more information please visit our website: http:www.unsiap.or.jp Thank you for your attention! 21