Chapter 13: Chemical Reactions
advertisement

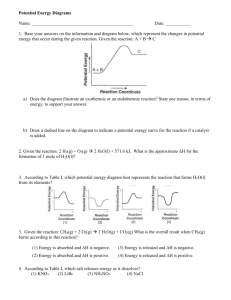
Chemical Reactions (Chapter 13) coefficients reactants products Student Learning Objectives • Utilize chemical equations to determine the amounts of reactants, products, and energy change. • Characterize acids and bases. • Describe reactions involving oxygen. How is a chemical equation balanced? A chemical reaction is the process of forming new substances. Atoms are combined to form molecules. Molecules separate into atoms. The chemical equation shows definite proportions of each substance. (same numbers of atoms on each side) Al + Br2 Al2Br6 Practice 1) Pb 2) C3H8 3) Al 4) BaO + PbO2 + + + + H2SO4 PbSO4 O2 CO2 + H2O HCL AlCl3 + H2 H2O Ba(OH)2 + H2O There are always 6.022 x 1023 atoms or molecules in 1 mole of a substance. Avogadro’s Number 6.022 x 1023 particles mole Hydrogen & Water Practice 1) Calculate the amount of grams and number of particles in one mole. a) Gold b) NaCl c) Cu(NO3)2 2) Calculate the number of moles, and the number of molecules, in 2 grams of carbon dioxide. More Practice 3) How many grams of each reactant are needed and how many grams of product are produced in the reaction? Al + Br2 Al2Br3 What are exothermic and endothermic reactions? The amount of chemical potential energy may change during a chemical reaction. Exothermic Reaction Endothermic Reaction Energy released Reactants → higher PE Energy absorbed Products → higher PE Activation Energy A spike of energy is needed to break existing bonds. H2 + Cl2 2HCl Bond Strength Bond Energy is the energy required to break 1 mole of bonds. (Same energy released when bond forms) Bond Energy to Break = Bond Energy Released The net bond energy indicates whether the process was exothermic or endothermic. Examples 1) N2 + H2 N2H4 2) H4C2 + O2 CO2 + H2O What can cause reaction rates to vary? 1. Temperature 2. Concentration 3. Surface area 4. Catalysts What is this? Catalysts A catalyst accelerates the reaction. Provides different pathway Lowers activation energy Reappears as a product Progression of Reaction With catalyst Practice 1) Why are there warnings on some medications not to break, crush, or chew the pill? 2) Why do you think some laundry soaps contain enzymes? 3) Why are photographic prints processed in the dark? What is an acid? What is a base? Acids contain H+ and H30+ ions, and are substances that donate hydrogen ions. Proton Donor Bases contain hydroxide (OH−) ions, or are substances that accept a hydrogen ions. Proton Acceptor Examples 1) Baking soda (NaHCO3) 2) HCl + NaHCO3 H2CO3 + NaCl Practice Identify the acid substances and the base substances. CH3CO2H + H2O CH3CO2- + H3O+ Strong Acids & Bases Strong acids and bases completely ionize in water. Some Strong Acids HNO3 HCl H2SO4 nitric acid hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid Some Strong Bases LiOH NaOH KOH lithium hydroxide sodium hydroxide potassium hydroxide The neutralization reaction of an acid and a base produces water and a salt. Acid Base Water Salt HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl HBr + KOH H2O + KBr pH A substance that has an equal number of acid and base ions is neutral. (pH balanced) pH 1 to 6 7 8 to 14 Solution Acidic Neutral Basic Substance pH Battery Acid Stomach Acid Cola Orange Juice Coffee Milk Human Blood Hand Soap Ammonia Bleach 0.5 1.5 – 2.0 2.5 3.5 5.0 6.5 7.34 – 7.45 9.0 – 10.0 11.5 12.5 Practice 1) If the water you drink has a pH of 6.8, is it acidic, basic, or neutral? 2) Blood has buffers to help control the natural pH your body needs. The amount of CO2 in the blood stream can change pH. What do we do naturally that can change the pH of blood? What is “acid rain”? Acid Rain is moisture that has a pH of less than 5. Rain, snow, sleet, or fog Rainwater normally has a pH of 5.6 to 6.2 Acids may combine with dust (dry deposition) Water naturally reacts with CO2 in the atmosphere, forming a weak acid. water + carbon dioxide carbonic acid (H2CO3) Strong Acids in Our Atmosphere Human-produced exhaust emissions of sulfur and nitrogen oxides form strong acids. sulfates + water sulfuric acid (H2SO4) nitrates + water nitric acid (HNO3) Location Question Where would you expect a higher level of acidity in the atmosphere, WY or CA? Why? What are the factors? Trees killed by acid rain Czech Republic Image Credit Simon Fraser/Science Photo Library What is an oxidation-reduction reaction? Redox reactions involve a transfer of electrons, and often the addition or subtraction of oxygen. Oxidation Reduction Reactant loses electrons Reactant gains electrons Oxygen Added Oxygen Removed Redox Reactions Corrosion is a redox reaction between a metal and oxygen (O2). Combustion is a redox reaction between a non-metal and oxygen (O2). Redox Examples Corrosion is a redox reaction between a metal and oxygen (O2). Combustion is a redox reaction between a non-metal and oxygen (O2). Practice 1) Which element is oxidized and which is reduced? a) HgS + O2 Hg + SO2 b) SnO2 + 2C Sn + 2CO2 2) Is the iron oxidized or reduced in the formation of rust? 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) 2Fe2O3(s) More Practice 3) Is a combustion reaction, like the combustion of methane, exothermic or endothermic? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) How do batteries and fuel cells work? Batteries have 2 diodes; one that is oxidized and one that is reduced. Acidic solution reacts with metals One metal is reduced (+ end) One metal is oxidized (– end) Reactions free electrons Battery Cathode (+) • Metal gains e− • Metal is reduced Battery Anode (–) • Metal loses e− • Metal is oxidized Fuel Cells A fuel cell uses a membrane to separate the reactants. Hydrogen gas is oxidized. Oxygen gas is reduced. Product is H2O vapor. Practice 1) Where do you store your batteries? Why? 2) What is the difference between a dry cell battery and an alkaline battery? 3) What is the primary difference between a battery and a fuel cell? Practice: Where do you store your batteries? Why? A fuel cell uses a membrane to separate the reactants. Hydrogen gas is oxidized. Oxygen gas is reduced. Product is pure water vapor. What is electrolysis? Electrolysis is the use of electric current to cause chemical change. Reverses chemical reactions Splits compounds Al2O3 + Energy Al2 + O2 What is electrolysis? Electrolysis is the use of electric current to cause chemical change. Reverses chemical reactions Splits compounds Example: Al2O3 + Energy Al2 + O2 Question: How do you recharge your cell phone battery? Practice 1) Is electrolysis an exothermic or endothermic process? 2) Describe the chemical process of recharging your mobile phone device. 3) What other devices operate in the same way? 4) Can you think of other examples of electrolysis?