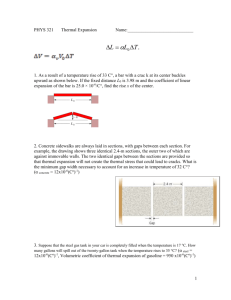
Physics & Electrical Engineering Study Sheet - Unit 1 Exam
advertisement
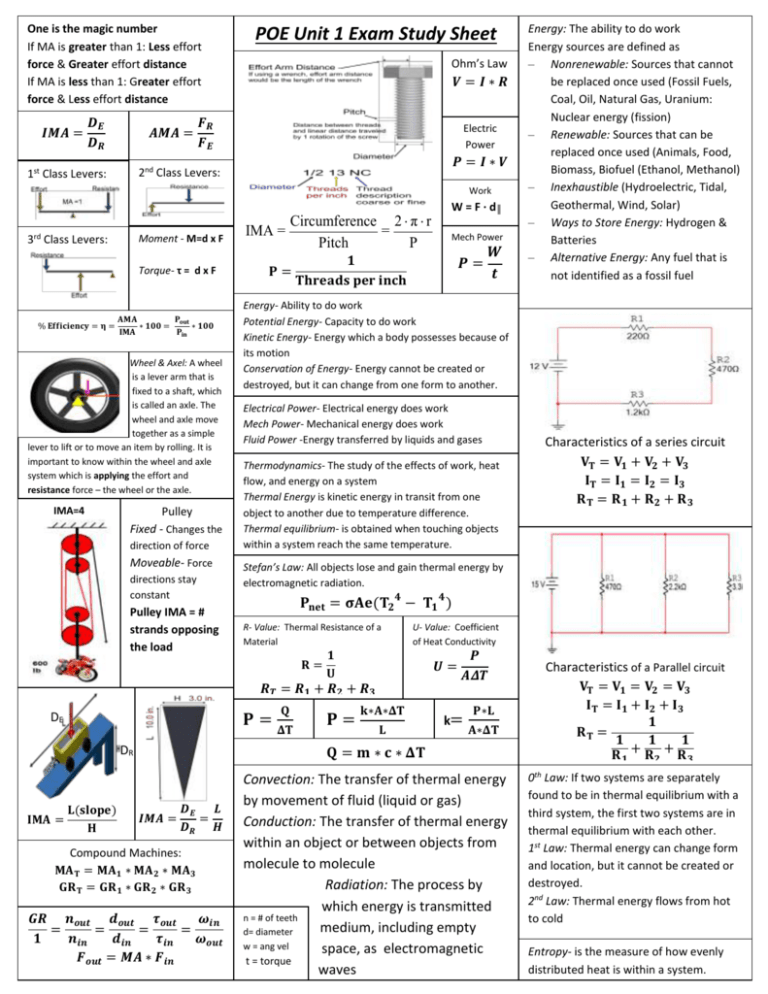
One is the magic number If MA is greater than 1: Less effort force & Greater effort distance If MA is less than 1: Greater effort force & Less effort distance 𝑰𝑴𝑨 = 𝑫𝑬 𝑫𝑹 𝑨𝑴𝑨 = POE Unit 1 Exam Study Sheet Ohm’s Law 𝑽=𝑰∗𝑹 𝑭𝑹 𝑭𝑬 Electric Power 𝑷=𝑰∗𝑽 2nd Class Levers: 1st Class Levers: Work 3rd Class Levers: Moment - M=d x F Torque- τ = d x F 𝐀𝐌𝐀 𝐏𝐨𝐮𝐭 % 𝐄𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐲 = 𝛈 = ∗ 𝟏𝟎𝟎 = ∗ 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝐈𝐌𝐀 𝐏𝐢𝐧 Wheel & Axel: A wheel is a lever arm that is fixed to a shaft, which is called an axle. The wheel and axle move together as a simple lever to lift or to move an item by rolling. It is important to know within the wheel and axle system which is applying the effort and resistance force – the wheel or the axle. IMA=4 Pulley Fixed - Changes the direction of force Moveable- Force directions stay constant Pulley IMA = # strands opposing the load Circumference 2 π r IMA = = Pitch P 𝐏= Mech Power 𝟏 𝐓𝐡𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐝𝐬 𝐩𝐞𝐫 𝐢𝐧𝐜𝐡 𝑷= 𝑾 𝒕 Energy- Ability to do work Potential Energy- Capacity to do work Kinetic Energy- Energy which a body possesses because of its motion Conservation of Energy- Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change from one form to another. Electrical Power- Electrical energy does work Mech Power- Mechanical energy does work Fluid Power -Energy transferred by liquids and gases Thermodynamics- The study of the effects of work, heat flow, and energy on a system Thermal Energy is kinetic energy in transit from one object to another due to temperature difference. Thermal equilibrium- is obtained when touching objects within a system reach the same temperature. 𝐏𝐧𝐞𝐭 = 𝛔𝐀𝐞(𝐓𝟐 𝟒 − 𝐓𝟏 𝟒 ) R- Value: Thermal Resistance of a Material U- Value: Coefficient of Heat Conductivity 𝟏 𝐔 𝑼= 𝑹𝑻 = 𝑹𝟏 + 𝑹𝟐 + 𝑹𝟑 𝐏= 𝐐 𝚫𝐓 𝐏= 𝐤∗𝐀∗𝚫𝐓 𝐋 𝑷 𝑨𝜟𝑻 k= 𝐏∗𝐋 𝐀∗𝚫𝐓 DR 𝐐 = 𝐦 ∗ 𝐜 ∗ 𝚫𝐓 Compound Machines: 𝐌𝐀 𝐓 = 𝐌𝐀 𝟏 ∗ 𝐌𝐀 𝟐 ∗ 𝐌𝐀𝟑 𝐆𝐑 𝐓 = 𝐆𝐑 𝟏 ∗ 𝐆𝐑 𝟐 ∗ 𝐆𝐑 𝟑 Convection: The transfer of thermal energy by movement of fluid (liquid or gas) Conduction: The transfer of thermal energy within an object or between objects from molecule to molecule Radiation: The process by which energy is transmitted n = # of teeth through medium, including empty d= diameter a w = ang vel space, as electromagnetic t = torque waves 𝐈𝐌𝐀 = 𝐋(𝐬𝐥𝐨𝐩𝐞) 𝐇 𝑰𝑴𝑨 = 𝑫𝑬 𝑳 = 𝑫𝑹 𝑯 𝑮𝑹 𝒏𝒐𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒐𝒖𝒕 𝝉𝒐𝒖𝒕 𝝎𝒊𝒏 = = = = 𝟏 𝒏𝒊𝒏 𝒅𝒊𝒏 𝝉𝒊𝒏 𝝎𝒐𝒖𝒕 𝑭𝒐𝒖𝒕 = 𝑴𝑨 ∗ 𝑭𝒊𝒏 Characteristics of a series circuit 𝐕𝐓 = 𝐕𝟏 + 𝐕𝟐 + 𝐕𝟑 𝐈𝐓 = 𝐈𝟏 = 𝐈𝟐 = 𝐈𝟑 𝐑𝐓 = 𝐑𝟏 + 𝐑𝟐 + 𝐑𝟑 Stefan’s Law: All objects lose and gain thermal energy by electromagnetic radiation. 𝐑= DE W = F · d║ Energy: The ability to do work Energy sources are defined as – Nonrenewable: Sources that cannot be replaced once used (Fossil Fuels, Coal, Oil, Natural Gas, Uranium: Nuclear energy (fission) – Renewable: Sources that can be replaced once used (Animals, Food, Biomass, Biofuel (Ethanol, Methanol) – Inexhaustible (Hydroelectric, Tidal, Geothermal, Wind, Solar) – Ways to Store Energy: Hydrogen & Batteries – Alternative Energy: Any fuel that is not identified as a fossil fuel Characteristics of a Parallel circuit 𝐕𝐓 = 𝐕𝟏 = 𝐕𝟐 = 𝐕𝟑 𝐈𝐓 = 𝐈𝟏 + 𝐈𝟐 + 𝐈𝟑 𝟏 𝐑𝐓 = 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝐑𝟏 + 𝐑𝟐 + 𝐑𝟑 0th Law: If two systems are separately found to be in thermal equilibrium with a third system, the first two systems are in thermal equilibrium with each other. 1st Law: Thermal energy can change form and location, but it cannot be created or destroyed. 2nd Law: Thermal energy flows from hot to cold Entropy- is the measure of how evenly distributed heat is within a system.