Cytoskeleton II - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
advertisement

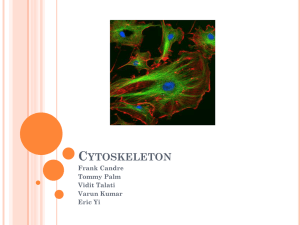
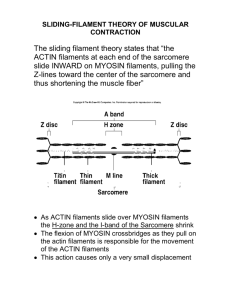
Cytoskeleton II Chapter 16 Tubulin heterodimer is the microtubule subunit Microtubule structure Growing and shrinking microtubules Growing and shrinking microtubules Structure of actin Actin binds to many different proteins Intermediate filaments Model of intermediate filament structure Model of intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments can withstand high levels of deforming force Keratin filaments in an epithelial cell Blistering of the skin caused by a mutant keratin gene Normal skin Blistering of the skin caused by a mutant keratin gene Skin with mutated keratin gene Blistering of the skin caused by a mutant keratin gene Cells rupture between the nucleus and the hemidesmosomes Polymerization of tubulin is nucleated by the γtubulin ring Electron micrograph of purified γ-tubulin complexes Single microtubules nucleated from the γ-tubulin ring The centrosome is the major microtubule organizing center of animal cells and contain γ-tubulin ring complexes Centriole surrounded by centrosome matrix figure 09-08a.jpg figure 09-08a.jpg figure 09-09.jpg Figure 9.9 Figure 9.9 spindle figure 09-08b.jpg Leading edge of cell nucleates actin filaments all actin filaments Newly formed actin filaments Model for actin filament nucleation by ARP complex ARP complex nucleates more efficiently when bound to preexisting actin filament Electron micrograph of branched actin filaments Thymosin inhibition Profilin recruitment Stathmin sequesters free tubulin Monomer concentration and capping protein determine growth or shrinkage rate Stabilization and destabilization of microtubules Capping proteins direct microtubules to specific locations in the cell