Temple/Artesian Poster - The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
advertisement

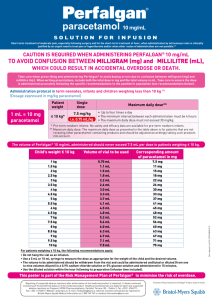
A Phase 1 Trial and Pharmacokinetic Study of Dexmedetomidine in Neonates Following Open Heart Surgery Felice Su MD, Susan C. Nicolson MD, Jeffrey S. Barrett PhD, Peter C. Adamson MD, David S. Kang, Mary Ann Diliberto, Athena F Zuppa MD MSCE Division of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics & Divisions of Cardiac Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine, The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Funded by NIH, GCRC #M01-RR-00240 & NICHD, PPRU #HD037255-09 C. C. Background and Significance Preliminary Results Analysis Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective α2agonist with hypnotic, analgesic and anxiolytic properties. In intubated adults, it provides sedation while preserving respiratory function facilitating extubation. There is no neonatal pharmacokinetic (PK) or pharmacodynamic (PD) data reported to guide therapy. Validated liquid chromatography & tandem mass spectrometry assay XIC of +MRM (2 pairs): 201.0/95.0 amu from Sample 12 (STD_9_1500 pg/ml) of Pt 3 & 4_111105.wiff (T... Population Predicted vs. Observed Dexmedetomidine Concentrations Max. 4.0e5 cps. 3.79 4.0e5 3.8e5 3.6e5 3.4e5 Standard pg/mL 1 5 2 10 3 25 4 50 5 100 6 250 7 500 8 1000 9 1500 1500 pg/mL I n t e n s it y , c p s 2.8e5 2.6e5 2.4e5 2.2e5 2.0e5 1.8e5 1.4e5 1.2e5 Aims 1.0e5 8.0e4 6.0e4 4.0e4 2.0e4 XIC of 0.0+MRM (2 pairs): 201.0/95.0 amu from Sample 4 (STD_1_5 pg/ml) of Pt 3 & 4_111105.wiff (Turb... 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 Time, min 2100 Primary •To define the pharmacokinetics and safety of dexmedetomidine in neonates following open heart surgery 4.0 4.5 Max. 2100.0 cps. 5.0 5.5 3.83 2000 1900 5 pg/mL 1800 1700 1600 1500 3.94 Patient population • 36 evaluable neonates post-operative from open heart surgery - - Exclusicon Criteria Investigational drug since birth Postoperative neuromuscular blockade Ongoing bloodstream infection Symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure Pre-existing hypotension based on age Pre-existing bradycardia based on age Heart block Weight < 2 kg 2.14 1200 1.21 1100 4.01 1000 Dose Level Infusion mcg/kg/hr 1 (n=9)* 0.25 0.2 2 (n=9)* 0.50 0.4 3 (n=9) 0.75 0.6 4 (n=9) 1.00 0.8 * Preliminary 2.43 1.91 900 2.84 2.91 3.24 1.80 800 5.37 4.13 3.43 5.11 4.36 700 1.70 600 1.30 500 400 300 200 100 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Time, min 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 Preliminary Results Pharmacodynamics • Tracheal extubation - 6 subjects extubated successfully while receiving infusion - 3 subjects extubated shortly after discontinuation of infusion - 5 subjects not medically suitable for extubation within 24 hours of initiation of infusion Demographics Dosing Level 1 Dosing Level 2 Overall Age (days), median (range) 3 (2-18) 4 (2-7) 3.5 Weight (kg), median (range) 3.5 (2.3-4.3) 3.4 (3.4-3.6) 3.5 Gender Female Male Surgical procedure Two ventricle physiology Aortic arch reconstruction Aortic arch reconstruction & VSD1 closure Arterial switch operation Tetralogy of Fallot repair Truncus arteriosus repair Single ventricle physiology Stage I BTS2 Stage I BTS2 & PA3 reconstruction 6 3 2 3 8 6 10 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 Observed Plasma Concentrations (pg/mL) Representative Patient UMSS-Plasma Concentration vs. Time (Dose Level 1) 400 4 350 300 3 250 200 2 150 100 1 50 0 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 3 5 40 Time (hours) Plasma Concentration Safety Monitoring • Cardiovascular events - 2 subjects with increased cardiac ischemia possibly related to study drug not clinically significant (Dose 2, n = 2) - 1 subject developed intermittent accelerated junctional rhythm possibly related to study drug not clinically significant (Dose 1) • No evidence of elevated transaminases, ocular dryness or clinically significant adrenal suppression possibly, probably or definitely related to study drug UMSS • Significant adverse events - 1 subject experienced atrial ectopy with hypotension (Dose 1) - 3 subjects underwent mediastinal exploration with clot removal (Dose 2) - 3 subjects received CPR (Dose 2) 2 subjects experienced profound bradycardia and hypotension during endotracheal suctioning 1 subject experienced intermittent atrial ectopy – Ventricular septal defect 2BTS – Blalock-Taussig shunt 3PA – Pulmonary artery 1VSD Conclusion results reflect dose level 1 and 2 Pharmacodynamics • Standardized intra-operative anesthetic • Extubation while receiving dexmedetomidine infusion • Collected for 48 hours following initiation of dexmedetomidine infusion: University of Michigan Sedation Scale - Vital signs 0 – Awake and alert - Cardiac rhythm 1 – Minimally sedated: tired/sleepy - FiO2 - University of Michigan Sedation Scale 2 – Moderately sedated: sleeping, easily arousable with light tactile (UMSS) score stimulation or verbal command - Supplemental analgesia/sedation use 3 – Deeply sedated: deep sleep, - Evaluation of tracheal extubation arousable only with significant readiness physical stimulation 4 – Unarousable Iselin-Chaves IA, et al. Anesth Analg 1998. 87: 949-55 Safety monitoring Observed Plasma Concentrations (pg/mL) 5.5 Base Model • NONMEM ADVAN 3, TRANS 4, first order conditional estimation (FOCE) with interaction • Two-compartment disposition model Clearance (CL, mL/min), inter-compartmental clearance (Q, mL/min) volume of central compartment (V1, L), volume of peripheral compartment (V2, L) • Exponential error model for inter-individual variability • Additive and proportional error model for random residual variability Pharmacokinetics • Dose escalation study B. A. immediately followed by a continuous intravenous B. • Loading dose infusion (CIVI) • Dexmedetomidine infusion ≤ 24 hours Bolus mcg/kg 2.23 UMSS Study Design 1300 Dexmedetomidine Plasma Concentration (pg/mL) Secondary •Pharmacodynamics - Tracheal extubation readiness - Relationship between level of sedation and plasma concentration - Supplemental sedation requirements - Impact on heart rate and blood pressure I n t e n s it y , c p s 1400 Individual Predicted Plasma Concentration (pg/mL) 3.0e5 Population Predicted Plasma Concentration (pg/mL) 3.2e5 1.6e5 Inclusion Criteria Age: ≤1 month Postconceptual age ≥ 37 weeks Isolated heart surgery Anticipated tracheal intubation < 24 hours Normal renal function Normal hepatic function Informed consent Individual Predicted vs. Observed Dexmedetomidine Concentrations Pharmacokinetics Parameter Cl (mL/kg/min) Q (mL/kg/min) V1 (L/kg) V2(L/kg) Estimate (SE%) 11.4 (8.2%) 2.2 (102%) 1.9 (25.3%) 0.4 (51.2%) Clearance (mL/kg/min) Volume of Distribution (L/kg) 9.0 1.6 13 – 16.8 1.8 – 2.3 Infants3 31.2 2.6 Study Population 11.4 2.2 Patient Population Adults1 Children2 • • • • Clearance appears to be reduced in neonates when compared to infants An infusion of 0.4 mcg/kg/hour is associated with a number of significant adverse events Dexmedetomidine at 0.2 mcg/kg/hour is well-tolerated in study population Dexmedetomidine may facilitate tracheal extubation Future Directions • Analysis of pharmacokinetic covariates • Pharmacodynamic analysis Acknowledgements 1Hospira, Precedex Product Label 2004 2Petroz GC, et al. Anesthesiology 2006. 105:1098–1110 3Su F, et al. The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Data not yet published. • CTRC Nursing • Cardiac ICU Staff • Division of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Laboratory