Dexmedetomidine Drug Information: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects
advertisement

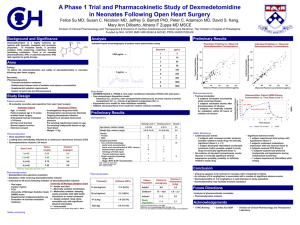
Dexmedetomidine Brand Names: Precedex - activation of receptors in brain and spinal cord inhibits neuronal firing (release of norepinephrine), causing hypotension, bradycardia, sedation, and analgesia - hypnotic and sedative effects: locus coeruleus is predominant noradrenergic nucleus in the brain - analgesic effects : alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord modulates pain transmission signals - blood pressure and heart rate: activation of the postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors inhibits the sympathetic activity decreases blood pressure and heart rate Background - alpha2 agonist with 7 to 8 times the alpha2 selectivity of clonidine - properties: sedation, anxiolysis, sympatholysis, some analgesic properties Dosing (adults) ICU sedation: I.V.: Initial: Loading infusion (optional) of 1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/hour; adjust rate to desired level of sedation Procedural sedation: I.V.: Initial: Loading infusion of 0.5-1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.6 mcg/kg/hour, titrate to desired effect; usual range: 0.2-1 mcg/kg/hour Fiberoptic intubation (awake): I.V. Initial: Loading infusion of 1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.7 mcg/kg/hour until endotracheal tube is secured. - supplied as 200 mcg/2 mL (100 mcg/mL) in a glass vial - to prepare the infusion, withdraw 2 mL of Precedex and add to 48 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride injection to a total of 50 mL to achieve concentration of 4 mcg/mL - incompatible when administered with the following drugs: amphotericin B, diazepam Indications - FDA approved for sedation only in adults undergoing mechanical ventilation for < 24 hours - off label uses: - adjunctive agent for sedation and analgesia in pediatric patients in ICU - pediatric procedural sedation - fiberoptic intubation - anesthesia for bariatric surgery, cardiac surgery, neurosurgical procedures requiring intraoperative active patient participation Advantages - enhances the anesthetic effect of intravenous & volatile agents as well as those used for regional block - does not cause respiratory depression - no evidence of cardiovascular rebound 24 h after abrupt cessation of infusion - allows intubated patients in ICU setting to be quickly aroused and oriented upon demand - does not require discontinuation prior to weaning from mechanical ventilation - ongoing sedation can be maintained with the use of dexmedetomidine during and following extubation - reduces the shivering in postoperative patients - one of side effects is dry mouth, which is an advantage during fiberoptic intubation Mechanism of Action Dosing (pediatrics) Loading dose: 0.5-1 mcg/kg; followed by a maintenance infusion of 0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/hour Pharmacokinetics - constant amount of drug eliminated per hour - onset: rapid - alpha2 half life: 6 minutes - elimination half life: 2 hours Metabolism - biotransformation by direct glucuronidation and cytochrome P450 metabolism in liver - majority of metabolites excreted in urine - no difference between healthy patients and those with renal impairment - clearance in adult patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment is decreased 53%, 64%, and 74% Side Effects - common: hypotension, bradycardia, sinus arrest, transient hypertension, dry mouth - effects of hypotension and bradycardia may be minimized by omitting or decreasing the loading dose References 1. Carollo, DS, Nossaman, BD, Ramadhyani, U. Dexmedetomidine: a review of clinical applications. Curr Opin Aneaesthesiol. 2008;21:457-461. 2. Phan, H and Nahata, MC. Clinical Uses of Dexmedetomidine in Pediatric Patients. Pediatr Drugs. 2008;10(1):49-69. 3. Haselman, MA. Dexmedetomidine: A Useful Adjunct to Consider in Some HighRisk Situations. AANA Journal. 2008;76(5):335-339. 4. Dexmedetomidine (drug information) on UptoDate.