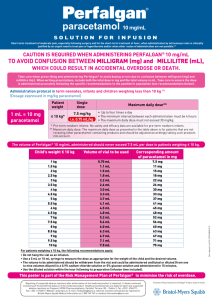
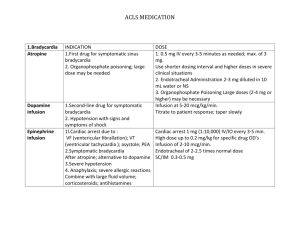
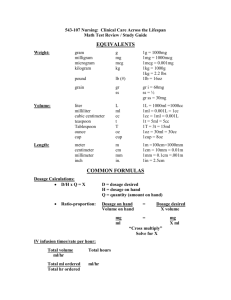
Recurrent Ventricular Tachycardia/Fibrillation Post
advertisement

Recurrent Ventricular Tachycardia/Fibrillation Post- CPB NB do not treat ectopic beats, couplets, triplets, non-sustained VT (<10 seconds) unless interfering with balloon pump Correct ischaemia / hypokalaemia / hypomagnesaemia / hypocalcaemia / hypoxia / acidosis / heart failure Perform 12 lead ECG to detect acute infarction / graft occlusion Ensure central line is not “irritating” the right ventricle Consider the possibility of proarrhythmia from any drug already used Consider inappropriate pacing (pace on T) because of poor pacemaker sensing Ventricular pacing (100-110 bpm) may prevent need for antiarrhythmic drugs If VT / VF is occurring infrequently it may be preferable to monitor and consult asthma? chronic airways disease? inotrope dependent? pulmonary oedema? yes no lignocaine 1mg/kg IVI & infusion3 sotalol2 ineffective? amiodarone1 1. Amiodarone dose: 300mg IVI over 120 minutes. Review when half of dose given – if hypotensive consider stopping infusion. Following the first dose give 450 mg over 12 hours. Se amiodarone infusion protocol Cardiology. 2. Sotalol dose: Oral: 80mg bd. Intravenous: 0.5 – 1.0mg/kg bd. Watch for hypotension/bradycardia. Dose must be adjusted with renal failure. 3. Lignocaine Dose: 1mg/kg IVI followed by infusion of 2-4mg/min according to Cardiology Lignocaine infusion protocol. N.B. lignocaine infusion dose must be reduced with hepatic impairment or cardiac failure.