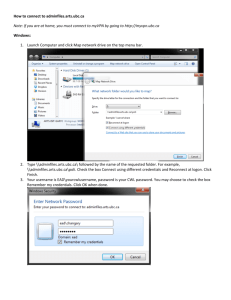
Interrupts & Timers
advertisement

UBC104
Embedded Systems
Review: Introduction to Microcontrollers
Processors
General purpose
processors:
80386
Pentium
Core Duo
Large number of pins
External memory
External peripherals
* Figure from Intel 386 DX Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
2
General Purpose Registers
Registers are dedicated for
moving data
EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX: general
purpose registers
EBP: Base pointer
ESP: Stack pointer
ESI, EDI: Index register
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
3
Microcontrollers
Support for peripherals inside uController
Limited number of pins
Dedicated purpose
Controlling devices, taking measurements
Controller families:
68H12: Motorola 68H11, 68HC12, …
8051: Intel 8051, 8052, 80251,…
PIC:
Microchip PIC16F628, 18F452, 16F877, …
AVR: Atmel ATmega128, ATtiny28L, AT90S8515,…
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
4
Rita51J
8051
128K of SRAM
128K FLASH ROM
Serial port
Digital I/O lines
* Figure from www.rigelcorp.com
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
5
Motes
Sensor nodes based on Atmel ATMega128
* Figures from CrossbowMPR-MIBUser Manual
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
6
Microcontroller Families
68H12: Motorola 68H11, 68HC12, …
8051: Intel 8051, 8052, 80251,…
PIC:
Microchip PIC16F628, 18F452, 16F877, …
AVR: Atmel ATmega128, ATtiny28L, AT90S8515,…
We are going to look at 8051s
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
7
Typical 8051s
32 input / output lines.
Internal data (RAM) memory - 256 bytes.
Up to 64 kbytes of ROM memory (usually flash)
Three 16-bit timers / counters
9 interrupts (2 external) with two priority levels.
Low-power Idle- and Power-down modes
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
8
Datasheets – Your New Friends!
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
9
Pin-Out of an 8051
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
10
8051 Components
Ports
RAM
Interrupt Controller
Timer
SPI Controller
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
11
8051 Internal RAM & SFRs
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
12
Special Function Registers (SFR)
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
13
Special Function Registers (SFR)
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
14
* Figure from Atmel AT89C51RD2 Datasheet
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
15
Ports
Driving low-power peripherals ie. LEDs, relays
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
16
Accessing Ports in C
void main (void) {
unsigned int i;
unsigned char j;
/* Delay var */
/* LED var */
while (1) {
for (j=0x01; j< 0x80; j<<=1) {
P1 = j;
for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
wait ();
}
}
for (j=0x80; j> 0x01; j>>=1) {
P1 = j;
for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
wait ();
}
}
/* Loop forever */
/* Blink LED 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 */
/* Output to LED Port */
/* Delay for 10000 Counts */
/* call wait function */
/* Blink LED 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 */
/* Output to LED Port */
/* Delay for 10000 Counts */
/* call wait function */
}
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
17
Summary
General information about 8051
Special Function Registers (SFRs)
Control of functionality of uController
Ports
Input/Output of uController
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
18
UBC104
Embedded Systems
Motivation for Next Topics
Tasks for Microcontroller
Controlling of processes (autonomic)
e.g. speed of vehicles, chemical processes
Control of devices through human operator
e.g. remote control, etc
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
20
Example: Controller Engineering
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
21
Topics for the Following Lectures
Interrupts & Timers
Communication
Analog to digital (A/D) conversation
Pulse Width Modulation
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
22
UBC104
Embedded Systems
Interrupts & Timers
Today’s Topics
Interrupts
Timers
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
24
Interrupts
Definition of ‘Interrupt’
Event that disrupts the normal execution of a
program and causes the execution of special
instructions
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
25
Interrupts
Program
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
26
Interrupts
Interrupt
Program
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
27
Interrupts
Interrupt
Program
Program
Interrupt Service Routine
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
28
Interrupt Handling
Address space in
code space
Code that deals with interrupts:
Interrupt Handler or Interrupt
Service Routines (ISRs)
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
29
Interrupt Handling
Code that deals with interrupts:
Interrupt Handler or Interrupt
Service Routines (ISRs)
Possible code:
Interrupt number
void ISR(void) interrupt 1 {
++interruptcnt;
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
30
Interrupts
fahr= (cent *
9
) +32
5
Interrupt
Program
mov R1, cent mul R1, 9 div R1, 5 add R1, 32
mov fahr, R1
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
31
Interrupts
Interrupt
Program
Program
mov R1, cent
mul R1, 9
Interrupt Service Routine
mov R1, 0x90
mov sensor, R1 ret
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
32
Interrupts
Interrupt
Program
mov R1, cent
Program
Save
Context
Interrupt
Service
Routine
Restore
Context
mul R1, 9
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
33
Interrupts
Interrupt
Program
mov R1, cent
Program
Save
Context
eg push R1
Interrupt
Service
Routine
Restore
Context
mul R1, 9
eg pop R1
time t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
34
Interrupt Overheads
Interrupt arrives
Complete current instruction
Save essential register information
Vector to ISR
Save additional register information
Interrupt
Latency
Execute body of ISR
Restore other register information
Return from interrupt and restore essential
registers
Resume task
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
Interrupt
Termination
35
Interrupt Response Time
Interrupt Latency
Interrupt Response Time= Interrupt Latency + Time in Interrupt Routine
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
36
Interrupts
Internal or External
Handling can be enabled/disabled
Prioritized
General 8051:
3x timer interrupts,
2x external interrupts
1x serial port interrupt
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
37
Interrupt Priorities
Each interrupt source has an
inherent priority associated
with it
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
38
Interrupt Priorities
Priorities can be adapted
by programs
Original 8051 provides 1bit per interrupt to set the
priority
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
39
2-bit Interrupt Priorities
The 89C52RD2 provides 2bit-interrupt priorities
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
40
2-bit Interrupt Priorities (continued)
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
41
2-bit Interrupt Priorities (continued)
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
42
External Interrupts
Pins for
external interrupts
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
43
External Interrupts
External Interrupts:
Level- or edge-triggered
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
44
External Interrupts
External Interrupts:
Level- or edge-triggered
Level-triggered
threshold
trigger point
t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
45
External Interrupts
External Interrupts:
Level- or edge-triggered
Level-triggered
threshold
t
trigger point
Edge-triggered
trigger point
t
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
46
Timer
A timer is a counter that is
increased with every time an
instruction is executed e.g.
8051 with 12MHz increases
a counter every 1.000 µs
General 8051 has 3 timer:
2 16-bit timer
1 16-bit timer with extrafunctionality (introduced
with the 8052)
Timer/Counter Mode Control Register TMOD
Timer/Counter Control Register TCON
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
47
Timer High- & Low-Registers
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
48
SFR Map – Timer Registers
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
49
Timer Control
Timer/Counter Mode Control Register TMOD
Timer/Counter Control Register TCON
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
50
SFR Map – Timer Control
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
51
SFR Map – Timer 2
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
52
Timer Code
void TimerInit(void) {
// Timer 2 is configured as a 16-bit timer,
// which is automatically reloaded when it overflows
// This code (generic 8051/52) assumes a 12 MHz system osc.
// The Timer 2 resolution is then 1.000 µs
// Reload value is FC18 (hex) = 64536 (decimal)
// Timer (16-bit) overflows when it reaches 65536 (decimal)
// Thus, with these setting, timer will overflow every 1 ms
T2CON
TH2
RCAP2H
TL2
RCAP2L
=
=
=
=
=
ET2 = 1;
TR2 = 1;
0x04;
0xFC;
0xFC;
0x18;
0x18;
//
//
//
//
//
Load
Load
Load
Load
Load
Timer
Timer
Timer
Timer
Timer
2
2
2
2
2
control register
high byte
reload capt. reg. high byte
low byte
reload capt. reg. low byte
// Enable interrupt
// Start Timer 2 running
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
53
Interrupt Code for Timer 2
void handleTimer2 (void) interrupt 5 {
/* execute interrupt code */
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
54
Interrupt Flags
Bits that are set if the
interrupt occurs
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
55
Code for Interrupt Flags
/* Configure Timer 0 as a 16-bit timer */
TMOD &= 0xF0;
/* Clear all T0 bits (T1 left unchanged) */
TMOD |= 0x01;
/* Set required T0 bits (T1 left unchanged) */
ET0 = 0;
/* No interrupts */
/* Values for 50 ms delay */
TH0 = 0x3C;
/* Timer 0 initial value (High Byte) */
TL0 = 0xB0;
/* Timer 0 initial value (Low Byte) */
TF0 = 0;
/* Clear overflow flag */
TR0 = 1;
/* Start Timer 0 */
while (TF0 == 0); /* Loop until Timer 0 overflows (TF0 == 1) */
TR0 = 0;
/* Stop Timer 0 */
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
56
Summary: Interrupts
Definition of ‘Interrupt’:
Event that disrupts the normal
execution of a program and causes the
execution of special instructions
Level-triggered
threshold
Handling can be enabled/disabled
Prioritized
Internal or External
External Interrupts:
trigger point
t
Edge-triggered
Level-triggered
Edge-triggered
8051: 3 timer interrupts, 2 external
interrupts & a serial port interrupt
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
trigger point
t
57
Real-Time Systems
Definition:
A real-time system needs to be
predictable
in terms of values and time
Correctness of an RT system depends on functionality
as well as temporal behaviour
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
58
Clock Driven Scheduling
Invoke Scheduler
Pick & dispatch a job
Timer Interrupt Service Routime
Decision on what job execute
are made at specific time
instants chosen a priori before
the system starts operation
A schedule of jobs is created
off-line and used at run time
The scheduler dispatches jobs
according to the stored
schedule at each scheduling
decision time
Clock-driven scheduling has
minimal overhead during run
time
Set timer
No interrupt
Start
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
Block waiting for timer
interrupt
59
Cyclic Executive
#define TASK_MAX 4
typedef void (func_ref)(void);
int delay[TASK_MAX];
func_ref task_ref[TASK_MAX];
void cyclic_executive() {
int task= 0;
while(1) {
settimer(delay[task]);
taskref[task]();
task= (task==TASK_MAX) ? task+1 : 0;
clear(time_flag);
while (time_flag) enterIdleMode();
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
60
Cyclic Executive (continued)
void timer(void) interrupt 5 {
set(time_flag);
}
void EnterIdleMode(void) {
PCON |= 0x01;
}
Frame
Tdelay,1
T1
T2
T3
T1
T2
T3
t
IdleMode
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
61
Problems with Cyclic Executives
Timing Accuracy
Actually constructing the cyclic executive
(Typical realistic problem: 40 minor cycles and 400 entries)
Inflexibility
must reconstruct schedule even for minor changes
Incorporating Aperiodic/Sporadic Tasks, or very
long period tasks
I/O only by polling
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
62
General Embedded Programming
Endless loops
Idle mode for 8051
Generic main() function
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
63
Endless Loops
Two types of tasks:
Run-To-Completion tasks
Endless-Loop tasks
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
64
Endless Loops
Two types of tasks:
Run-To-Completion tasks
Endless-Loop tasks
Interrupt handler are run-to-completion tasks
The majority of generic tasks are endless loops
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
65
Endless Loops
Two types of tasks:
Run-To-Completion tasks
Endless-Loop tasks
Interrupt handler are run-to-completion tasks
The majority of generic tasks are endless loops
Example Code:
void ExampleTask(void) {
while(1) {
waitForActivation;
doTask;
}
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
66
Idle Mode
8051s implement an “idle” mode
which consumes less power
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
67
Idle Mode
8051s implement an “idle” mode
which consumes less power
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
68
Idle Mode
8051s implement an “idle” mode
which consumes less power
from Pont: Atmel 89S53
normal mode
idle mode
11mA
2mA
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
69
Idle Mode
8051s implement an “idle” mode
which consumes less power
from Pont: Atmel 89S53
normal mode
idle mode
11mA
2mA
Example Code:
void EnterIdleMode(void) {
PCON |= 0x01;
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
70
Generic main() Function
void main(void) {
/* initialize system */
/* initialize tasks */
while (1) {
EnterIdleMode();
}
/* loop forever */
/* PCON |= 0x01*/
}
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
71
Summary
Cyclic executives
Endless loops
Idle mode
UBC 104 Embedded Systems
72


![July 31 Connect eupdate DRAFT [1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008100166_1-21bd0e395dcbfd67aaad5f18dd4ec08e-300x300.png)