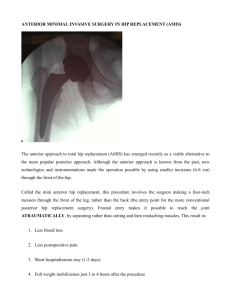
Supplementary Materials This appendix has been provided by the
advertisement

1 Supplementary Materials This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about his work. Supplement to: Cookson RA, Gutacker N, Garcia-Armesto S, Angulo-Pueyo E, Christiansen E, Bloor K, Bernal-Delgado E. Socioeconomic inequality in hip replacement in four European countries from 2002 to 2009 – area level analysis of hospital data. Eur J Public Health. 2015; CONTENT Appendix Table A. Descriptive statistics about the quintile groups of administrative areas. Appendix Table B. ECHO Coding of Hip Replacement. Appendix C. Larger-scale version of Figure 2 split into three separate graphs. Figure C1. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – age-sex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group. Figure C2. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – absolute differences in agesex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group. Figure C3. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – relative differences in agesex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group. Appendix D. National level association between hip replacement rate and GDP. Figure D1. Hip replacement rate versus GPD per capita in 2009 for OECD countries, with bubble size proportional to population and regression line weighted by population. Table D1. OECD data for the year 2009 on hip replacement rate, GPD per capita and population in OECD countries. Countries are ranked by hip replacement rate. 2 Appendix Table A: Descriptive statistics about the quintile groups of administrative areas 2002 Total % Median population population income* † N N Denmark Q1 12 592,466 19.8% 34,051 € 12 Q2 16 604,341 20.2% 36,966 € 16 Q3 21 567,917 19.0% 38,408 € 22 Q4 23 629,416 21.0% 40,466 € 22 Q5 26 602,357 20.1% 47,769 € 26 England Q1 48 5,439,039 19.9% 21.5% 49 Q2 46 5,278,998 19.4% 16.0% 54 Q3 68 5,546,538 20.3% 12.5% 67 Q4 81 5,522,852 20.2% 9.0% 76 Q5 83 5,486,995 20.1% 6.0% 80 Portugal Q1 100 1,104,406 20.0% 5,183 € 99 Q2 99 1,094,770 19.8% 6,143 € 98 Q3 44 1,112,234 20.1% 7,076 € 44 Q4 22 1,071,450 19.4% 7,907 € 23 Q5 13 1,142,230 20.7% 8,992 € 14 Slovenia Q1 3 Q2 2 Q3 3 Q4 2 Q5 2 Spain Q1 51 4,529,079 19.7% 8,800 € 51 Q2 37 4,273,693 18.6% 9,750 € 37 Q3 44 4,927,217 21.5% 11,700 € 44 Q4 44 4,539,788 19.8% 12,400 € 44 Q5 23 4,680,936 20.4% 14,000 € 23 * England: percentage of people receiving benefits; Spain: midpoint of income group † Based on exchange rate on 01/07/2002 and 01/07/2009 2009 Total % Median population population income* † 613,170 632,740 651,972 620,052 649,607 19.4% 20.0% 20.6% 19.6% 20.5% 33,970 € 36,878 € 38,318 € 40,447 € 47,655 € 5,762,757 5,819,699 5,808,909 5,842,997 5,858,907 19.8% 20.0% 20.0% 20.1% 20.1% 24.0% 17.0% 14.0% 10.0% 8.0% 1,185,949 1,186,673 1,228,696 1,164,530 1,242,934 19.7% 19.7% 20.4% 19.4% 20.7% 6,351 € 7,406 € 8,273 € 9,332 € 10,418 € 415,904 346,782 150,043 183,049 103,362 34.7% 28.9% 12.5% 15.3% 8.6% 9,701 € 10,003 € 10,293 € 10,609 € 11,387 € 5,290,654 5,017,326 5,879,871 5,345,286 5,457,656 19.6% 18.6% 21.8% 19.8% 20.2% 8,800 € 9,750 € 11,700 € 12,400 € 14,000 € The average income of the quintile group is based on area level data on mean income for Denmark, Portugal, Slovenia and Spain and mean deprivation score for England. In each case we compute the quintile group average as the median value among all the areas within the group. We cannot compute the quintile group level mean because for Spain we only have data on interval bands for area level mean income and the first and last intervals have no lower and upper bound, respectively. 3 Appendix Table B: ECHO Coding of Hip Replacement DEFINITION Discharges, aged 35 years and older, with any procedure code for primary hip replacement excluding diagnoses of fractures and accidents. Numerator type: Discharges, aged 35 years and older, with any procedure code for primary hip replacement excluding fractures and accidents diagnosis. Denominator type: Population aged 35 and older. CODING CROSSWALKS SPAIN/PORTUGAL ICD-9-CM Primary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions 733.10, 733.14, 820, 821, E800-E849.9 ICD-9-CM Secondary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions E800-E849.9 ICD-9-CM Procedures Inclusions Exclusions 81.51 81.52 DENMARK ICD-10 Primary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions S720 S721 S722 S729 M844 M80 V01-V99 NOMESCO Procedures Inclusions Exclusions NFB ICD-10 Secondary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions V01-V99 4 ENGLAND ICD-10 Primary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions S720 S721 S722 S729 M844 M80 V01-V99 ICD-10 Secondary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions V01-V99 OPCS Procedures Inclusions Exclusions W371 W378 W379 W381 W388 W389 W391 W398 W399 W461 W468 W469 W471 W478 W479 W481 W482 W488 W489 W931 W941 W948 W949 W951 W958 W959 SLOVENIA ICD-10 Primary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions S720 S721 S722 S729 M844 M80 V01-V99 ACHI Procedures Inclusions Exclusions 4931500 4931800 4931900 ICD-10 Secondary Diagnosis Inclusions Exclusions V01-V99 5 Appendix C: Larger scale version of Figure 2 split into three separate graphs Figures C1, C2 and C3 reproduce the three panels of Figure 2 on a larger scale, enabling readers of a printed version to discern finer points of detail. Figure C1. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – age-sex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group Q1 is the poorest and Q5 the richest administrative area. 95% confidence intervals are not shown, for ease of viewing. 6 Figure C2. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – absolute differences in age-sex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group Q1 is the poorest and Q5 the richest administrative area. 95% confidence intervals are not shown, for ease of viewing. 7 Figure C3. Trends in socioeconomic inequality 2002-9 – relative differences in age-sex standardised rate of hip replacement per 10,000 adults over 35 by quintile group Q1 is the poorest and Q5 the richest administrative area. 95% confidence intervals are not shown, for ease of viewing. 8 Appendix D: National level association between hip replacement rate and GDP 300 400 Figure D1. Hip replacement rate versus GPD per capita in 2009 for OECD countries, with bubble size proportional to population and regression line weighted by population Germany Switzerland Denmark France Norway 200 Luxembourg United Kingdom Slovenia Czech Republic Italy Greece United States Australia 100 Canada Hungary Poland Israel Korea 0 Mexico Portugal Spain 10000 30000 50000 GDP per capita in US dollars PPP 70000 Source: Hip replacement rates for 2009 from OECD Health at a Glance 2011; GDP and population data for 2009 from OECD Library Stat Extracts: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/health_glance-2011-en/04/07/index.html?itemId=/content/chapter/health_glance2011-35-en http://stats.oecd.org/index.aspx?queryid=558 http://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=POP_FIVE_HIST 9 Table D2: OECD data for the year 2009 on hip replacement rate, GPD per capita and population in OECD countries. Countries are ranked by hip replacement rate. OECD data for the year 2009 on hip replacement rate, GPD per capita and population in OECD countries. Countries are ranked by hip replacement rate Country Germany Switzerland Belgium Austria Denmark Norway France Luxembourg Sweden Netherlands Slovenia United Kingdom Finland United States Iceland Czech Republic Australia Italy New Zealand Greece Canada Ireland Hungary Spain Portugal Estonia Slovak Republic Israel Poland Chile Korea Mexico OECD Hip rate GDP per capita Population (000) in per 100,000 in (US$ PPP) in 2009 2009 2009 296 287 240 238 236 232 224 222 214 213 194 194 188 184 173 166 154 150 149 140 123 117 99 93 88 88 78 51 44 19 17 8 35.972,6 46.970,2 36.926,5 39.375,4 38.634,8 55.317,0 34.110,8 79.027,0 37.604,7 41.381,7 27.022,5 35.103,2 35.874,0 46.927,2 37.680,5 25.875,2 40.613,2 32.518,7 30.010,2 29.474,9 38.632,1 40.230,5 20.441,4 32.251,3 25.125,3 19.948,2 22.761,1 27.210,1 18.972,0 15.925,0 26.337,5 14.369,6 81.904 7.744 10.796 8.365 5.523 4.829 62.615 498 9.299 16.530 2.042 60.927 5.339 306.772 319 10.491 21.779 59.752 4.316 11.283 33.727 4.537 10.023 45.929 10.568 1.338 5.386 7.486 38.153 16.929 49.182 112.853 The OECD crude rates differ slightly from ECHO crude rates due to subtle differences in the codes used to define a “hip replacement”. Source: As for Figure D1.