Crude Oil and Cracking Hydrocarbons Self Guided Lesson As you
advertisement

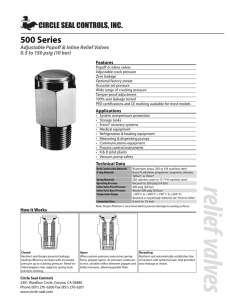
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram. 2. Soak the mineral wool in the liquid paraffin using the pipette (do not add so much that there are drops of liquid in the tub e). 3. Strongly heat the broken pot in the middle of the tub e. The heat from the flame will be transferred towards the mineral wool and will vapourise the liquid paraffin. Do not heat the mineral wool and liquid paraffin directly. 4. Position the first collecting tube over the end of the delivery tube and collect the gas being given Crude Oil and Cracking Hydrocarbons Self Guided Lesson 1. As you workoff.through the lesson, add the following information to your science journal. a. 5.Do aDiscard google search on Cracking Hydrocarbons. Define “cracking” and draw a diagram this first tube of gas and collect a second tube of gas while continuing to heat the broken pot. that demonstrates what this term means. heating the boiling tubewill until the delivery tubeto hasa been removed. 2. Click on6. theContinue following link that lead you video clip, which demonstrates the cracking of alkanes7. in the laboratory: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZYyKUePdC2Y&feature=related Stopper the test tube containing the gas and t est this sample and the original mixture by shaking with a few drops of the bromine water. Note any changes you see in of the appearance of the water insetup the trough recordnotes. them in a. 8.Draw adown labeled diagram the laboratory inandyour your results. b. Copy the data table below into your notes and record your observations as you watch the video that shows the lab being carried out. Data Table Test Result with original liquid para n Result with the gaseous product of the cracking experiment Shaking with a few drops of bromine water 3. Follow the following link: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/alkanes/cracking.html#top a. Why is cracking used in the hydrocarbons industry? b. Write down the chemical equation for the cracking of C15H32 in your notes (it is given in diagram form on the page. c. There are two types of cracking detailed on this page, thermal and catalytic cracking. Write down a description of both types of cracking in your notes. d. Do a Google search to see if you can discover any additional websites with information about cracking hydrocarbons in industry. e. Watch the following youtube video clip about hydrocarbons in the petroleum industry: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mNW_ms35JKE 4. Follow this link: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/orgpropsmenu.html#top a. Read the information to review the similarities and differences between alkanes and alkenes. Feel free to add to your notes! 5. Do a search on alkenes with 2, 3, and 4 carbons. a. Record the name, formula, and a diagram of the structural formula for these three alkenes in your notes. 6. Do a google image search for saturated vs. unsaturated. In your notes, state the what it means for a chemical compound to be saturated. 7. Go to the following video clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2C_6ax2TsV8 a. Record how the test for saturated vs. unsaturated hydrocarbons is performed and what a positive result for an unsaturated hydrocarbon looks like in your notes. Title this Bromine Test. b. Follow this link to see how an addition reaction between an alkene and bromine occurs: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/alkenes/halogenation.html#top c. Draw a 3 step diagram that shows how an addition reaction takes place when ethene (C2H4) reacts with bromine (Br2). d. Read page 254 in your textbook about addition reactions with hydrogen and steam. Draw a diagram for each addition reaction that includes the chemical equation for each reaction. 8. Do a Google search for how Ethanol is made. a. Describe the two ways in which ethanol is produced in your notes. Be sure to include the chemical reactions that happen! 9. Is ethanol is the fuel of the future? Do a search to see if you can find different viewpoints and record at least two different arguments for OR against the use of ethanol as a fuel in your notebook.