Principles of editing

Principles of editing
History
• Georges Méliès
• invented the Jump cut, Fade in and out, Overlapping dissolves, Stop motion Photography
• Edwin S.Porter
• Invented Temporal overlaps: shots with overlapping action
• D.W. Griffith
• (Lawrence Griffith)
• invented the cut in, Continuity editing, the 180-degree rule, Intercutting or cross cutting,
Establishing shot, Reverse, Matching eye line, Cutting on action and created the Montage theory
• Lev Kuleshov
• was a Newsreel cameraman and started the The Kuleshov workshop and created The
Kuleshov effect – the order changes the meaning (shots)
Shot styles
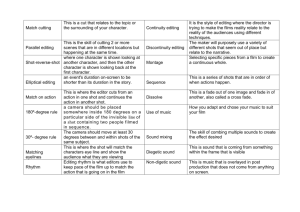
Jump Cut
• A jump cut is a cut in which two shots of the same subject are taken from a camera in different positions. The effect this has is the feeling of jumping forward in time.
Fade in and out
• A fade in and out is a gradual transition from one image to another
• The effect this has on consumers is that it softens the transitions between shots.
Shot styles
Cut in
• i.e. cutting from a wide shot of a scene into a mid shot of a subject
• This has an effect of exchanging emotions between shots
Stop motion photography
• Is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object or persona appear to move on its own.
• Georges Méliès used stop motion animation once to produce moving titlecard letters in one of his short films.
Shot styles
Temporal overlapping
• An action is duplicated from one shot to another. The effect was to show the point of view from as many times shown in the movie of
Cutting on Action
• This is were editors cut from one shot to another view that match's the first shot’s action
• The effect this has is to give the impression of continuous time when watching the edited film.
Shot styles
Continuity editing
Is were editing is used to smooth over the inherent discontinuity of the editing process and to establish a logical coherence between shots
The effect this has is to achieve continuity which helps with smooth transitions of time and space
180-degree rule
• Is the basic guideline regarding on screen spatial relationships between one chater and others, the idea is to keep the same actors on the same side as when the 1 st scene was shot.
• The effect this has is that it enables the audience to visually connect with unseen movements happening around and behind the main subject
Shot styles
Inter/cross cutting
• Is an editing technique used to establish multiple actions that are happening at the same time in different locations
• This Is most commonly used to build suspense in the audience
Establishing shot
• The establishing shot sets up the context for a scene by showing the relationship between its important subjects and objects
• The effect this is has is to help the audience have an indication of the location or time period
Shot styles
Reverse
• This is were we seen one character is shown looking at one character (which is often off screen) and then the other character is shown looking back at the 1 st character
• The effect this has it to help keep the film linearly and somewhat logical
Matching eye line
• Is were we see a character looking off into the distance (generally off screen) and then cuts to the subject that they were looking at
• The effect this has is to show the audience what the character is looking at
Montage theory
Metric
• Where the editing follows a specific number of frames, cutting to the next shot no matter what is happening within the image
• This montage is used to elict the most basal and emotional of reactions in the audience
Rhythmic
• This is were the editor cuts based on continuity from edit to edit.
Montage theory
Tonal
• Tonal uses the emotional meaning of the shots
• This is used to elicit a reaction from the audience.
Overtonal/Associational
• This is a combination of the above three methods for synergy in its effects
Montage theory
Intellectual
• This uses shots which is used to elicit an intellectual meaning
Future of editing
• Editing has come a long way since having to use scissors to cut reels of film, now we’re being able to cut and edit films on a computer. Nowadays we use every type of cut apart from jump that it has become a base line of film, it might even be considered cliché.
• One of the 1 st films ever made was of a train going by a station, compared to todays block busters you can see who far editing has come.