Instrumental Chemistry
advertisement

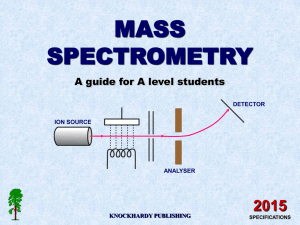
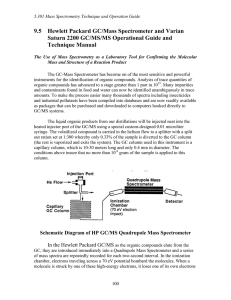
Instrumental Chemistry Chapter 11 Atomic Mass Spectrometry Atomic mass The mass of a single atom, usually expressed in atomic mass units (amu) Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the protons and neutrons contained in the nucleus Each proton or neutron weighs about 1 amu, and thus the atomic mass is always very close to the mass number (total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus) Mass Spectrometers • Mass spectrometers use the difference in mass-to-charge ratio (m/e) of ionized atoms or molecules to separate them from each other • In general a mass spectrometer consists of an ion source, a massselective analyzer, and an ion detector Diagram of a Mass Spectrometer Stage 1: Ionization • • The atom is ionized by knocking one or more electrons off to give a positive ion These positive ions are persuaded out into the rest of the machine by the ion repeller which is another metal plate carrying a slight positive charge Ionization (cont.) Stage 2: Acceleration The ions are accelerated so that they all have the same kinetic energy All the ions are accelerated into a finely focused beam Acceleration (cont.) Stage 3: Deflection • The ions are then deflected by a magnetic field according to their masses The lighter they are, the more they are deflected • The more the ion is charged, the more it gets deflected Deflection (cont.) Stage 4: Detection The beam of ions passing through the machine is detected electrically When an ion hits the metal box, its charge is neutralized by an electron jumping from the metal on to the ion That leaves a space amongst the electrons in the metal, and the electrons in the wire shuffle along to fill it Detection (cont.) Fourier-Transform MS Magnetic-sector MS Quadrupole MS Time-of-flight MS ICP-MS Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry In ICP-MS, the plasma is formed from Argon gas Plasma is defined as a gas consisting of ions, electrons, and neutral particles SSMS Spark Source Mass Spectrometry Semi-quantitative trace element technique for the analysis of solids and liquid materials Advantages include total simultaneous elemental coverage, low detection limits, semi-quantitative accuracy (+2-3x), and high resolution capabilities to eliminate many spectral interferences GDMS Glow-Discharge Mass Spectrometry Analytical technique for the bulk elemental analysis of inorganic solid samples The most comprehensive and sensitive technique available for the analysis of solids Glow Discharge Ion Source Useful Websites Dealing With Mass Spectrometry • • • • • • • • • http://www.anachem.umu.se/jumpstation.htm http://userwww.service.emory.edu/~kmurray/mslist.html http://www.chemcenter/org http://www.sciencemag.org http://reference.allrefer.com/encyclopedia/A/atomMas.html http://www.webref.org/geology/a/atomic_mass.htm http://www.chemguide.co.uk/analysis/masspec/howitworks.html http://www.northernanalyticallab.com/tech2.htm http://www.shivatec.com/new/gdmsdesc.php4