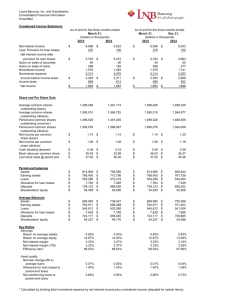
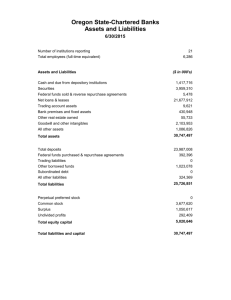
CHAPTER 3 ANSWERS 1. Report of Condition Total assets
advertisement

CHAPTER 3 ANSWERS 1. Report of Condition Total assets Cash and due from depository institutions Securities Federal funds sold and reverse repurchase agreements Gross loans and leases Loan loss allowance Net loans and leases Trading account assets Bank premises and fixed assets Other real estate owned Goodwill and other intangibles All other assets Total liabilities and capital Total liabilities Total deposits Federal funds purchased and repurchase agreements. Trading liabilities Other borrowed funds Subordinated debt All other liabilities Total equity capital Perpetual preferred stock Common stock Surplus Undivided profits a. b. c. d. e. f. $4,000.00 90.00 535.00 45.00 $2,900.00a 200.00 2,700.00 20.00 220.00b 15.00 200.00 175.00 4,000.00c 3,580.00d 2,920.00e 80.00 10.00 50.00 480.00 40.00 420.00f 5.00 25.00 320.00 70.00 Gross loans and leases = Net loans and leases + Loan loss allowance ($200.00 + $2,700.00) This is the only asset missing and so it is total assets less all of the rest of the assets listed above. ($4,000.00 − $90.00 − $535.00 − $45.00 − $2,700.00 − $20.00 − $15.00 − $200.00 − $175.00) Total liabilities and capital = Total assets ($4,000.00) Total liabilities = Total liabilities and capital − Total equity capital ($4,000.00 − $420.00) Total deposits = Total liabilities − All of the other liabilities ($3,580.00 − $80.00 − $10.00 − $50.00 − $480.00 − $40.00) Total equity capital = Perpetual preferred stock + Common stock + Surplus + Undivided profit ($5.00 + $25.00 + $320.00 + $70.00) Page 1 2. Report of Income Total interest income $200 Total interest expense 140a Net interest income 60 Provision for loan and lease losses 20b Total noninterest income 100 Fiduciary activities 20 Service charges on deposit accounts 25 Trading account gains and fees 25c Additional noninterest income 30 Total noninterest expense 125 Salaries and employee benefits 95d Premises and equipment expense 10 Additional noninterest expense 20 Pretax net operating income 15 Securities gains (losses) 5 Applicable income taxes 3 Income before extraordinary items 17e Extraordinary gains—net 2 Net income 19f a. Total interest expense = Total interest income − Net interest income ($200 − $60) b. Provision for loan and lease losses = Net interest income + Total noninterest income − Total noninterest expense − Pretax net operating income (60 + $100 – $125 – $15) c. There are four areas of Total noninterest income and only one is missing and the total is given. ($100 − $20 − $25 − $30) d. There are three areas of Total noninterest expense and only one is missing and the total is given ($125 – $10 – $20) e. Income before extraordinary items = Pretax income + Security gains – Taxes ($15 + $5 – $3) f. Net income = Income before extraordinary items + Extraordinary gains—net ($17 + $2) 3. Net interest income Net noninterest income Pretax net operating income Net income after taxes Total operating revenues Total operating expenses Dividends paid to common stockholders a. b. c. $40a −15b 20c 16d 215e 195f 10g Total interest income − Total interest expense ($140 − $100) Total noninterest income − Total noninterest expense ($75 − $90) Net interest income + Net noninterest income − PLL ($40 – $15 − $5) Page 2 d. e. f. g. Pretax net operating income − Taxes ($20 − $4) Interest income + Noninterest income ($140 + $75) Interest expenses + noninterest expenses + Provision for loan losses ($100 + $90 + $5) Net income after taxes − increases in bank’s undivided profits ($16 − $6) 4. Total assets Net loans Undivided profit Fed funds sold Depreciation Total deposits $405a $285b $7c $20d $5e $335f a. b. c. d. e. f. Total liabilities + Total equity capital ($30 + $375) Gross loans − Allowance for loan losses ($300 – $15) Total equity capital – Preferred stock – Common stock – Surplus ($30 – $15 – $5 – $3) This is the only asset missing so subtract all other assets from total assets Bank premises and equipment, gross – bank premises and equipment, net ($25 – $20) Total liabilities less nondeposit borrowings ($375 – $40) 5. a. The dollar figure for Net Loans before the charge-off is _____. Net Loans = Gross Loans –ALL = $800 − $45 = $755 million b. After the charge-off, what are the dollar figures for Gross Loans, ALL and Net Loans assuming no other transactions? Gross Loans = $800 million – ($10 million − $7 million) = $797 million ALL =$45 million – ($12 million− $2 million − $7 million) = $42 million (The amount of the loan that is bad) Net Loans = Gross Loans – ALL = $797 − $42 = $755 million c. If the Sunset Hotel sells at auction for $10 million, how will this affect the pertinent balance sheet accounts? Gross loans and ALL would not change as the bank would recover all the money invested earlier. Page 3 6. For each of the following transactions, which items on a bank’s statement of income and expenses (Report of Income) would be affected? a. Office supplies are purchased so the bank will have enough deposit slips and other necessary forms for customer and employee use next week. This would be part of Additional noninterest expense and part of Total noninterest expense. b. The bank sets aside funds to be contributed through its monthly payroll to the employee pension plan in the name of all its eligible employees. This would be part of Salaries and Benefits and part of Total noninterest expenses. c. The bank posts the amount of interest earned on the savings account of one of its customers. This would be part of Total interest expenses. d. Management expects that among a series of real estate loans recently granted the default rate will probably be close to 3 percent. This would be part of Provision for loans and losses to go into reserves for future bad debts. e. Mr. and Mrs. Harold Jones just purchased a safety deposit box to hold their stock certificates and wills. This would be part of Additional noninterest income and part of Total noninterest income. f. The bank collects $1 million in interest payments from loans it made earlier this year to Intel Composition Corp. This would be part of Total interest income. g. Hal Jones’s checking account is charged $30 for two of Hal’s checks that were returned for insufficient funds. This would be part of Service charges on Deposit accounts and then part of Total noninterest income. h. The bank earns $5 million in interest on the government securities it has held since the middle of last year. This would be part of Total interest income. Page 4 i. The bank has to pay its $5,000 monthly utility bill today to the local electric company. This would be part of Premises and equipment expenses and part of Total noninterest expenses. j. A sale of government securities has just netted the bank a $290,000 capital gain (net of taxes). This would be part of Security gains (losses). 7. For each of the transactions described here, which of at least two accounts on a bank’s balance sheet (Report of Condition) would be affected by each transaction? a. Sally Mayfield has just opened a time deposit in the amount of $6,000, and these funds are immediately loaned to Robert Jones to purchase a used car. Gross loans + $6,000 b. Arthur Blode deposits his payroll check for $1,000 in the bank, and the bank invests the funds in a government security. Government securities + $1,000 c. Total Deposits − $2,500 The bank purchases a bulldozer from Ace Manufacturing Company for $750,000 and leases it to Cespan Construction Company. Cash and Due from Bank − $750,000 f. Common stock/surplus + $100,000 Jane Gavel withdraws her checking account balance of $2,500 from the bank and moves her deposit to a credit union; the bank employs the funds received from Mr. Alan James, who has just paid off his home equity loan, to provide Ms. Gavel with the funds she withdrew. Gross Loans − $2,500 e. Total deposits + $1,000 The bank sells a new issue of common stock for $100,000 to investors living in its community, and the proceeds of that sale are spent on the installation of new ATMs. Bank premises & equipment, gross +$100,000 d. Total deposits + $6,000 Gross Loans and Leases + 750,000 Signet National Bank makes a loan of reserves in the amount of $5 million to Quesan State Bank and the funds are returned the next day. Page 5 On the day the funds are loaned the accounts are affected in the following manner: Cash and Due from Bank − $5,000,000 Federal Funds Sold +$5,000,000 When the funds are returned the next day, the process is reversed. g. The bank declares its outstanding loan of $1 million to Deprina Corp. to be uncollectible. Gross Loans −$1,000,000 ALL −$1,000,000 8. Off-balance-sheet items for John Wayne Bank (in millions of $) Total unused commitments Standby letters of credit and foreign office guarantees (Amount conveyed to others) Commercial letters of credit Securities lent Derivatives (total) Notional amount of credit derivatives Interest rate contracts Foreign exchange rate contracts Contracts on other commodities and equities All other off - balance -sheet liabilities Total off-balance-sheet items Total assets (on-balance sheet) Off-balance-sheet assets ÷ on-balance-sheet assets a. b. $8,000 1,350 −50 60 2,200 100,000 22,000 54,000 22,800a 1,200 49 111,609b 12,000 9.30% Total derivatives − All other derivatives [100,000 – (22,000 + 54,000 + 1200)] The sum of all of the off-balance sheet items The Off-balance-sheet-assets of John Wayne Bank are in proportion with other banks of the same size. Page 6 9. Bluebird State Bank Report of Income (in millions of dollars) Total interest income Interest on loans Int earned on government bonds and notes Total $90 $9 $99 Total interest expense Interest paid on federal funds purchased Interest paid to customers time and Savings deposits Total $40 $45 Net interest income Provision for loan loss $54 $5 $5 Total noninterest income Service charges paid by depositors Trust department fees Total $3 $3 $6 Total noninterest expenses Employee wages, salaries and benefits Overhead expenses Total $13 $3 $16 Net noninterest income ($10) Pretax income Taxes paid (28%) Securities gains/(losses) $39 $11 ($7) Net income Less dividends $4 Retained Earnings from Current Income $17 $21 Page 7 10. The items which would normally appear on a bank's balance sheet are: Federal funds sold Credit card loans Vault cash Allowance for loan losses Commercial and Industrial Loans Repayments of credit card loans Common stock Federal funds purchased Deposits due to bank Leases of business equipment to customers Savings deposit Undivided profits Mortgage owed on the bank’s buildings Other real estate owned Additions to undivided profits The items which would normally appear on a bank’s income statement are: Interest received on credit card loans Depreciation on premises and equipment Interest paid on money market deposits Securities gains or losses Utility expense Provision for loan losses Service charges on deposits Page 8