Molecule Fact Sheet
advertisement

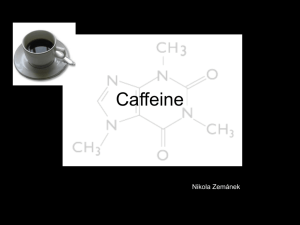
Ryan Jeffrey and Shane Degnan Molecule Fact Sheet- Caffeine Organic Molecule: Alkaloid Chemical Formula: C8H10N4O2 Structural Formula: Purpose in living world: When consumed, caffeine speeds up the blood flow causing energy to rise in a living organism. Increases adrenaline. Relaxes smooth muscles, stimulates cardiac muscles and diuresis, and can cure headaches. Its biggest effect is on an organisms central nervous system. It increases alertness and causes agitation. Caffeine may be a source of healthful antioxidant activity against some free radicals inside the body. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. Free radicals cause damage to the body. Caffeine is addictive. Naturally Found: Found in seeds and leaves of plant, mainly taken from coffee and tea plant. The molecule is formed when a xanthine and a methyl group come together. Caffeine is a solid, looks like white, prism-like crystals. Positive Effects: Its effects come on quickly. It is used in pain relievers to increase drugs speed in the body. Also, it can be useful for workouts and causes body to burn fat rather than carbs. Caffeine is taken for energy, and studies show that it makes people alert, improves short term memory, and enhance concentration. Negative Effects: Caffeine causes insomnia. It is also a drug which means that people can become reliant/dependent upon it. It has no nutritional value and is used as a stimulant in many drugs and drinks. Caffeine also dehydrates your body. High caffeine consumption accelerates bone loss. Other drugs in same class: Theophylline, Methylphenidate, Methamphetamine. They cause similar effects on the body and have very similar chemical structures and structural formulas. Theophylline: C7H8N4O2 Interesting Facts: 90% of Americans consume caffeine every day. High doses of caffeine (300 mg or higher) can cause anxiety. High caffeine consumption has been linked to an increase in the likelihood of experiencing auditory hallucinations. Biochem of Caffeine: Caffeine’s effects on the body are caused by its structural similarity of adenosine and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) -binds to receptors that normally bind to adenosine -Adenosine causes drowsiness when it binds to receptors -caffeine bonds and blocks adenosine from attaching to the receptor -cAMP provides oxygen to the body -Caffeine blocks cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from breaking down cAMP Question: What are the positive effects of caffeine? Answer: It increases energy and makes people more alert and awake for a few hours at a time. http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Caffeine http://www.aarp.org/health/healthy-living/info-10-2013/coffee-for-health.html http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/88304/caffeine