Chemistry of Caffeine - East Stroudsburg University

By: Nevina Keskineva
Chemistry Department, East
Stroudsburg University
History
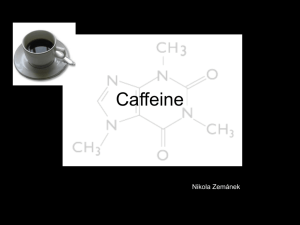
Structure
Mechanism of action
Metabolism
Average Doses – 85-250mg or 1-3 cups of coffee 1
High doses – 250-500mg 1
Restlessness 1
Insomnia 1
Seizures 1
Cardiovascular instability 1
10g of caffeine is fatal. 1
Since Stone Age
Ethiopian Legend
Friedrich Ferdinand Runge
Hermann Emil Fischer
Nitrogen
• The name derives from the word alkaline, which is used to describe any nitrogen containing base(an amine) .
• Therefore alkaloids are described as basic, nitrogen containing compounds of plant or animal origin.
• “True alkaloids” are compounds that:
• The nitrogen atom is part of a heterocyclic system
• Compound has a complex molecular structure
• Manifests pharmacological activity
• Compound is restricted to the plant kingdom.
Heterocyclic
System
Caffeine
π 𝑒
-
π 𝑒
-
π 𝑒
-
π 𝑒 -
π 𝑒 -
Caffeine Zwitterion Resonance Caffeine
• Aromatic molecules are planar, cyclic, species that have 4n +2π electrons. ( Huckel’s rule)
• Molecules with 2,6,10,14,18….π electrons are aromatic.
• Caffeine has 10π electrons, therefore is aromatic.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u0oi3V_
EqhI
Heart
Anxiety and sleep disorders
Caffeine is the most popular drug
Binds to the adenosine receptors
It is almost completely metabolized
It has positive and negative effects on the body