Your Body Systems
advertisement

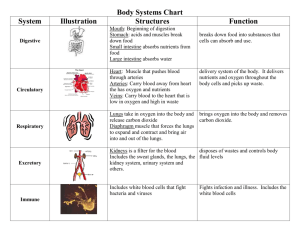
Your Body Systems Chapter 5 BELLRINGER: How many body systems can you name? Body Organization • Human Body – Complex Machine • City ( Buildings, transportation systems, Electrical energy) • Working together – Each part has role to play – Contributes to the function of the other parts of the body – ** What happens to the body when a part is not functioning properly? Cells • Simplest and most basic units of life • Human Body vs. Bacteria • Nucleus – “brain” of cell – Largest organelle of the cell – Contains the DNA Tissues • A group of cells that are similar & work together to perform a specific function • 4 Types of Main Body Tissue : – Epithelial ( Boundary) • Protects body from moisture loss, bacteria, internal injury – Muscle ( movement) – Connective Tissue ( Support & Structure) – Nervous Tissue ( Messaging System) Body Tissue Organ • Two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function Organs • How many organs are in the human body? – 78 • Which organ is the largest? – Skin • What is the major organ of the body? – Brain • Other organs of the body – http://www.organsofthebody.com/ Body System • A group of organs that work together for one purpose • Your Body Systems: – – – – – – – – Nervous System Endocrine System Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Urinary System Circulatory System Respiratory System Body System Function Nervous System Controls & coordinates activities of the body systems Endocrine System Helps nervous system control and coordinate activities of the body; helps regulate growth Skeletal System Provides a framework to support and protect the body Muscular System Works with the skeletal system to cause movement Digestive System Breaks down foods into simpler substances; transfers nutrients into the blood; eliminates solid waste products so they can be eliminated from the body; protects the body from disease Circulatory System Transports and distributes gases, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body; collects and transports waste products so they can be eliminated from the body; protects body from disease Respiratory System Exchanges oxygen from the environment and carbon dioxide from the body Urinary System Filters liquid waste products from the blood and eliminates them from the body Body Systems Work Together • Each system has a different function – Work together and help on another • Body systems depend on one another – Perform their functions properly • When working properly – The body stays alive and is healthy CELL ORGANIZATION POSTER HANDOUT BELLRINGER : ARE PEOPLE WITH BIGGER BRAINS SMARTER THAN PEOPLE WITH SMALLER BRAINS? Nervous System • Body system that gathers and interprets information about the body’s internal & external environments and responds to that information Nervous System Components • • • • Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Sensory Organs ( eyes, ears, taste buds) Nervous System • Controls voluntary & involuntary activities – Walking – Talking – Heart beat • Also allows … – – – – – Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Detect pain & pressure Nervous System controls • Conducts electrical messages to & from various parts of your body – NERVE IMPULSES • Carry information that help the organs and body systems carry out their functions correctly The Brain • Major organ • Mass of nervous tissue that is located inside your skull Brain Impulses • Sends impulses to different parts of the body • Impulses contain information about your body and about the world around you – Constantly receiving impulses • Your brain uses this information to – Tell your body how to react to the environment – Sending impulses to different body parts Structure of Brain • Cerebrum • Cerebellum • Brainstem Cerebrum • • • • Largest part of the brain Most complex Coordinates many activities of the brain Controls – Senses, emotions, voluntary muscle movements, consciousness, learning, & memory Cerebellum • Second largest part of the brain • Controls – Muscle coordination, balance, and posture Brainstem • Connects to the spinal cord • Controls – Heart rate – Blood pressure – Breathing PIN THE FUNCITON ON THE BRAIN Central Nervous System (CNS) • Includes brain & spinal cord • Spinal Cord – Bundle of nervous tissue that is about a foot and a half long and is surrounded by your back bone • Spinal cord Function – Relay impulses between the brain and different parts of the body • Interpreting impulse – Brain – spinal cord – body part – Body part – spinal cord – brain Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Composed of nerves that connect all parts of your body to the CNS • Uses nerves to control the actions of different parts of the body Nerves • A bundle of cells that conducts electrical signals through the body • Like an electrical cable – Many small wires • ** ONLY IN THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM *** Nerves • Means of communication in the CNS • CNS & skeletal system – When & how to move • CNS & Skin – Heat – Pressure – Pain – Other sensations from the environment Common Problems of the Nervous System • • • • • • • Meningitis Rabies Concussions Stroke Paralysis Epilepsy Cerebral Palsy Meningitis • Infection, inflammation of the protective covering of the brain & spinal cord – Bacterial & viral • Bacterial ( antibiotics ) • Vaccine • No vaccine to treat / prevent viral form Rabies • A viral infection of the brain that causes irritation of the brain and spinal cord • Passed by saliva of an infected animal • Avoid wild / unfamiliar animals • Medical treatment needed Concussion • Blow to the head • May cause brief memory loss; unconsciousness • Preventative measure – Wear protective headgear Stroke • Death of brain tissue – Lack of blood going to brain • Medical attention & hospitalization Paralysis • Partial / total loss of the ability to use muscles – Caused by damage to brain or spinal cord • May be permanent Epilepsy • Disorder of the nerves and brain that are characterized by uncontrollable muscle activity • Form of seizure • Treated with medication Cerebral Palsy • Very poor muscle control – Caused by damage of the brain • No cure or prevention – Physical therapy Endocrine System • Network of tissues and organs that release chemicals that control certain body functions Hormones • Chemicals that travel in the blood and cause changes in different body parts • Tells body how to grow or develop • Stressful Situations – Fight or Flight – Epinephrine Rush Hormone Facts • Makes & releases between 50-100 different hormones • Every hormone has an important function for the body • Most glands make & release different hormones • Each function of the body is controlled by more than one hormone • Hormones work together to cause changes in the body Gland A tissue or group of tissues that makes and releases chemicals • Endocrine Glands make hormones* • Specific Endocrine Glands • Hormones released into blood • Control certain body functions Types of Glands • • • • • • • • Thyroid Gland Adrenal Gland Pancreas Ovaries Testes Thymus Gland Parathyroid Glands Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland • Controls the rate at which your body uses energy • Located in the neck area Adrenal Glands • Helps the body respond to stress or danger • Located above kidneys Pancreas • Regulates blood sugar levels • Located on the bend of stomach Ovaries • Females Only • Produce hormones involved in reproductions – Estrogen & progesterone Testes • Males Only • Produce hormones in reproduction – Testosterone Thymus Gland • Regulates the immune system, which helps body fight disease • Located between Lungs Parathyroid Gland • Regulates the calcium level in the blood • Located behind thyroid Pituitary Gland • Secretes hormones that affect other glands & organs • Located in the Brain Types of Hormones • • • • • • • Thyroxine Testosterone Estrogen Progesterone Insulin Human Growth Hormone Epinephrine & Norephinephrine Thyroxine • Thyroid • Stimulates body metabolism • Regulates body growth & development Testosterone • Testes • Stimulates secondary sex characteristics in males • Stimulates sperm production Estrogen • Ovary • Stimulates secondary sex characteristics in females Progesterone • Ovary • Allows the uterus to prepare for pregnancy • Regulates menstrual cycle Insulin • Pancreas • Regulates the amount of sugar in blood Human Growth Hormone • Pituitary Gland • Stimulates body growth Epinephrine & Norepinephrine • Adrenal • Stimulate the body systems and metabolism in emergencies & during stress HORMONE & BONE GROWTH ACTIVITY Common Problems of the Endocrine System • Too much / Too little of a hormone • Interfere with – Normal Structure – Function of the Body • Endocrine System Problems – Type II Diabetes – Gigantism – Hyperthyroidism – Hypothyroidism Type II Diabetes • • • • High level of sugar in the blood Body does not produce enough insulin Body’s cells do not Treatment – Diet & Exercise – Insulin Injection – Pills Gigantism • Individual has a very large body size • Excess production of human growth hormone by pituitary gland • Treatment – Medication Hyperthyroidism • Produces too much of the thyroid hormone • Body Systems become too active • Lead to rapid & unhealthy weight loss and other problems • Treatment – Medications – Radiation – Surgery Hypothyroidism • • • • Produces too little of the thyroid hormone Body system slow down Can lead to rapid and unhealthy weight gain Treatment: – Medication that replace missing hormones BELLRINGER: HOW MANY BONES & MUSCLES ARE IN THE HUMAN BODY? Skeletal System • Bone – Is a living organ made of bone cells, connective tissues, and minerals • Bone, Cartilage, & special structures make up the system Skeleton • • • • • Body’s framework Support the Body Protect organs Store Minerals Work with your muscles to move HEALTHY VS UNHEALTHY BONES 2 Types of Bone Tissue • Compact Bone – Is dense bone tissue found outside of all bones • Spongy Bone – Many air spaces – Lighter & less dense than compact bone and found inside most bones Compact & Spongy Bone Cartilage & Marrow • Cartilage – Ends of many bones which are covered by a soft, flexible tissue • Marrow – Soft tissue inside bones • 2 Types – Red Marrow – makes red & white blood cells – Yellow Marrow – stores fat Joints • Place in the body where 2 or more bones connect • Allow movement – When muscles attached to the bone contract • Classified by how bones move • Fixed Joints – Joints allow little or no movement • Ligaments – Flexible bands of connective tissue JOINT ACTIVITY Skeletal / Joint Problems • • • • Break Dislocate Stretch or torn Aging / poor diet – – – – – – – – Osteoporosis Fracture Osteomyelitis Arthritis Osteoarthritis Rickets Scoliosis Sprain Osteoporosis • • • • Density of bone decreases Bones are weak More likely to break Treatment – Exercise – Calcium / Vitamin D – Medications Fracture • Break in a bone • Caused by accident or injury • Treatment – Cast – Surgery Osteomyelitis • Bacterial infection of the bone and marrow • Treatment: – Antibiotics – Surgery • Prevention: – Clean deep wounds / cuts Arthritis • Joint inflammations • Treatment : – Physical Therapy – Medications Osteoarthritis • Caused by aging • Joints are stiff & painful • Treatment: – Anti-inflammatory Drugs – Physical Therapy – Surgery Rickets • Children • Causes the body to have difficulty absorbing calcium • Bones soften • Caused by lack of vitamin D • Treatment: – Medication with vitamin D Scoliosis • Curvature of the spine • Uneven growth of the body • Treatment: – Exercise – Brace – Surgery Sprain • Injury to ligaments at a joint • Treatment: – Rest – Ice – Cast Types of Muscle • Muscle – Any tissue that is made up of cells or fibers that contract & expand to cause movement • Types of Muscle – Smooth Muscle – Cardiac Muscle – Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle • Move materials such as food through internal organs • Makes up internal organs – Stomach – Intestines Cardiac Muscle • Found in the heart • Blood is pushed through the body Skeletal Muscle • Muscle attached to bones • Attached to bones by connective tissue – Tendons • Pull onto the bones they are attached to – causes body to move • Release energy – Maintains body temperature Muscular System • The muscles that move your body How muscles Move • Skeletal muscles work together – Make your Body move • Movement – Result of muscles pulling on bones Muscle Contraction- Flex • Gets shorter • ONLY pull bones closer together • Flex – Bend • Example : Bicep – Pulls the bones of the forearm toward shoulder Muscle Contraction – Extend • Extend • Example : Triceps – Pulls the bones of the forearms away from the biceps Muscular System Problems • • • • Tired & Sore Strained & Torn Warm up, cool down, stretch Problems: – – – – – – Muscular Dystrophy Inguinal Hernia Muscle Cramp Strain Tendinitis Shin Splints Muscular Dystrophy • Genetic Diseases – Causes muscle weakness • Destruction of skeletal muscle tissue • Treatment: – No Cure – Physical Therapy – Surgery Inguinal Hernia • Intestine bulges through abdominal muscles • Causes • Caused: – Lifting heavy objects – Improper lifting • Treatment: – Surgery Muscle Cramp • • • • Sudden & painful contraction of a muscle Night After Exercise No Treatment Strain • Overstretching • Tearing of a muscle due to overuse / misuse • Treatment : – Rest – Ice – Wrapping Injury Tendinitis • Inflammation of a tendon – Aging – Excessive Exercise • Treatment – Rest – Hot or Cold compresses – Ant – inflammatory medications Shin Splints • Pain in the shin caused by damage • Irritation to the muscles in the front of the leg • Treatment: – Rest – Ice – Pain Medication Exercise Circuit Activity BELLRINGER: NAME DIFFERENT SYMPTOMS THAT OCCUR WHEN YOU HAVE PROBLEMS DIGESTING YOUR FOOD. Digestion • Digestion – Process by which your body breaks down food you eat Digestive System • Group of organs and glands that work together to physically & chemically break down, or digest food • Mouth • Stomach • Small Intestine • After Digestion – Food is absorbed in the blood Nutrients • Substances in foods that your body needs to function properly • Produce Energy – Growth – Maintenance – Repair Journey of Food- Mouth • Mouth • Chewing – Food particles are smaller – Makes digestion easier • Saliva – Moistens food – Makes it easier to follow Journey of Food – Throat • • • • Pushed by your tongue Throat Pharynx Esophagus to Stomach Journey of Food – Stomach • Food Particles – Mixed with acidic juices • Stomach churns – Mixes food & juices • Stays in stomach for a few hours – Travels to large intestine Journey of Food – Small Intestine • Most chemical digestion happens • Food moves by contractions – Smooth muscle of small intestine • Contractions – Push food through the organ • Liver, gall bladder, pancreas – Release chemicals into the small intestine • Leaves small intestine to large intestine Journey of Food – Large Intestine • • • • No digestion happens Mostly waste products Pushed out Takes about 24 hours Body Absorbs Nutrients • Absorbed in bloodstream • Alcohol, simple sugars, & simple salts – Absorbed in stomach • Small Intestine • Carbohydrates, proteins, fats – Absorbed in small intestine Villi • Inner wall of the small intestine covered in fingerlike projections • Increase the surface of the intestinal wall • Nutrients – Pass easily from the small intestine to the blood • Large intestine – Water – Simple Salts Common Digestive Problems • Improper Chewing • Too much Acid • Problems: – – – – – – – – Indigestion Heartburn Diarrhea Constipation Ulcers Appendicitis Hemorrhoids Stomach & Colon Cancer Indigestion • Pain / discomfort in stomach • Treatment: – Antacids – Medication Heartburn • Burning feeling in the esophagus – Backflow of acidic stomach contents • Treatment: – Antacids – Medication Diaherrea • Increase amount & number of times a person passes waste • Treatment: – Medication Constipation • Passing solid waste is difficult & infrequent • Treatment: – Medication – Fluids Ulcers • Round, open sore in the lining of stomach or small intestine caused by bacteria • Treatment: – Avoiding certain foods – Antacids – Antibiotics Appendicitis • Inflammation of the appendix – Releases harmful bacteria into the abdomen • Treatment: – Surgical removal of the appendix Hemorrhoids • Swollen tissues of the rectum and anus – Contain blood vessels that may bleed • Treatment: – Usually does not require treatment – May require surgery Stomach & Colon Cancer • Tumor in the stomach, colon, rectum of large intestine – Age – Diet • Treatment: – Surgical removal of the affected organ – Chemotherapy – Radiation TRAVEL BROCHURE Excretion • Removal of liquid wastes from the body • 3 Body Systems Involved: – Skin & Water • Releases products • Sweating – Lungs • Get rid of Carbon Dioxide – Urinary System • Removes waste products from blood Urinary System • Group of organs that work together to remove liquid wastes from the blood • Carries waste from cells to kidneys • Kidneys – Clean the blood of liquid waste • Ureters – Waste passed from kidneys to tube like structures Urinary System • Bladder – Muscular, baglike organ that stores this liquid waste until it can be released from the body • Urethra – When bladder is full, waste leaves the body through a single tube like structure • Urination – Release of the waste Filtering Blood • Kidneys – clean you blood – Regulate amount of water in body • Blood Contains – Nutrients, gases, water, & waste • Kidney Removes – Waste & excess water from the blood Kidneys • Nephrons – Remove harmful products from your blood • Filtration – A process where nephrons remove the wastes from the blood • Urine – Liquid waste Common Problems of the Urinary System • Waste products can build up in the blood – Lifetime threatening conditions • Uncomfortable or painful • Problems: – Urinary Tract Infection – Stones – Urinary Incontinence – Overactive or Neurogenic Bladder Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) • Infection of one or more of the organs of the urinary system – – – – Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites • More common in women • Treatment: – Antibiotics – Antiviral drugs Stones • Crystallized mineral chunks that frequently from in the kidneys and bladder • Small stones leave body with urine • Larger stones may be trapped • Treatment: – Medications – Ultrasound waves – Surgery Urinary Incontinence • Uncontrollable loss of urine from the bladder • Inability to control urination – Aging • Treatment: – Medication – Surgery Overactive / Neurogenic Bladder • Inability to control urination – Damage to nerves that go to the urinary bladder • Treatment: – Medications – Surgery – Catheter BELLIRINGER: WHY DO YOU THINK PEOPLE ASSOCIATE LOVE WITH THE HEART? Circulatory System • Made up of three parts – Clean blood – Help regulate the amount of waster in your body • Functions – Transport nutrients and gases to a different parts of the body where they can be used by the cells – Take waste materials from the cells to kidneys, lungs, and skin, where wastes can be removed Heart • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mH0QTW zU-xI Blood • 5 liters • Tissue that is made of liquid, cell parts, and 2 types of cells • Liquids & solids • Components: – Plasma – Platelets – Red Blood Cells – White Blood Cells BLOOD VISUAL Plasma • • • • 55% of blood 90% of plasma is water Fluid Carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products from one part of the body to another Platelets Solids 45% of blood Carried by plasma Cell fragments that help repair blood vessels and form blood clots • Made in bone marrow • Clump together in the damaged area of body • • • • – Forms blood clots & stops you from bleeding Red Blood Cells ( RBCs) • Most numerous blood cells • Transport oxygen & carbon dioxide through the body • Hemoglobin – Protein – Oxygen & carbon dioxide attach – Carries gases through the body White Blood Cells ( WBCs) • Large cells that help you stay healthy by fighting infection and protecting the body from foreign particles Supply Lines • Arteries – Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart • Veins – Blood vessels that carry blood to the heart • Capillaries – Microscopic blood vessels of the body that link the arteries and veins – Nutrients, carbon dioxide, and waste products enter and leave the blood stream Common Circulatory Problems • Cells do not get oxygen & nutrients – They will die • Wastes are removed from cells – They will die • Problems: – – – – – – Hypertension Heart Attack Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia Leukemia Hemophilia Hypertension • Abnormally high blood pressure • Increase the chance of stroke/ heart attack • Treatment: – Losing Weight – Eating healthy – Not Smoking – Medication Heart Attack • Blood supply to the heart is reduced or stopped – Injures heart • Treatment – Medical emergency – Medical professional Anemia • Number of blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin is below normal • Treatment: – Treated with vitamin B 12 – Iron supplements – Medications Sickle Cell Anemia • • • • Blood cells are sickle cell shaped Contain an abnormal type of hemoglobin Genetic Treatment: – Cannot be cured – Hospitalization at times Leukemia • Cancer of the tissues of the body that produce white blood cells • Treatment: – Chemotherapy Hemophilia • • • • Genetic disorder Blood does not clot Clots very slowly Treatment: – Blood transfusions – Avoiding situations that may cause bleeding Respiratory System • Body system that brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide from the body • Gases forced in & out of the lungs through breathing Respiratory system 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nose & Mouth Pharynx ( throat) Voice Box ( Larynx) Windpipe ( trachea ) Bronchi 1. Allows air to enter lungs Lungs • Large sponge like organs in which oxygen and carbon dioxide are passed between the blood and environment How you Breathe • Diaphragm – Movement of air in & out of the lungs – Dome shaped muscle beneath the lungs • Contract – Air enters lungs • Relax – Air leaves lungs LUNG MODEL Alveoli • Gases move between the blood and tiny air sacs Common Respiratory problems Air may contain harmful materials Avoid smoking tobacco & using drugs Problems: Tuberculosis Pneumonia Asthma Emphysema Lung Cancer Tuberculosis • Contagious infection that infects the lungs – Chest pain – Difficulty breathing – Bacteria in the air • Treated with antibiotics Pneumonia • Inflammation of the lungs – Alveoli become filled with thick fluid • Treatment: – Rest – Fluids – Antibiotics Bronchitis • Inflammation of the bronchi – Includes cough • Treatment: – Rest – Aspirin – Cough medicine – Antibiotics Asthma • Allergic response in which airways fill with mucus • Triggers – – – – – – Pollen Dust Smoke Cold air Stress Strenuous exercise • Treatment – Drugs Emphysema • Condition in which the alveoli in the lungs break – Difficulty breathing • Treatment – Can’t be cured – Medication Lung Cancer • Cancer destroys lung tissue • Most common type of cancer – Men & Women • Treatment – Surgery – Chemotherapy – Radiation Therapy BELLRINGER: MAKE A LIST OF HABITS THAT ARE ASSOCIATED WITH GOOD HEALTH AND BAD HEALTH WANTED: BODY ORGANS ADVERTISEMENT