UNIT 7
advertisement

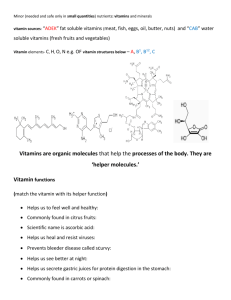
SECTION 1 HOW MUCH AND HOW MANY Ex.3 Complete the sentences: How many electrons does an atom of sodium possess? How much oxygen does the atmosphere contain? Our bodies contain a very large amount of water. A large number of whales are found in the Pacific Ocean. There is an enormous number of stars in the universe. For a rich man, one dollar is a negligible quantity of money, but for a poor man it a considerable amount. The air consists of a large amount of nitrogen (78%), a considerable oxygen (20/) a small amount of a argon (less than 1/) and negligible amount of helium, neon, krypton and xenon. An orange contains a few seeds. The number of bacteria in the air is very large. A few people can speak more than 5 languages. no , hardly any, a little, quite a lot, a lot of inverted flask no liquid spherical flask hardly any liquid Beaker a little liquid gas jar quite a lot liquid conical flask a lot of liquid Make questions and answers like the following: Example: How much liquid does the beaker contain? It contains a little liquid. How much liquid does the spherical contain? It contains hardly any liquid. How much liquid does the gas-jar contain? It contains a little liquid. How much liquid does conical flask contain? It contains a lot of liquid. How much liquid does the inverted flask contain? It contains no liquid. Some more expressions a large a fairly large (amount) a considerable (quantity) a small a minute / negligible no Look at this: a few crystals = a small number of crystals quite a few crystals = a considerable number of crystals many crystals = a large number of crystals Diagram of an atom of oxygen Oxygen has 8 electrons. This is a fairly small number. Number of electrons in one atom of some metals 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Lithium (Li) 3 Sodium (Na) 11 Magnesium (Mg) 12 Potassium (K) 19 Manganese (Mn) 25 Iron (Fe) 26 Copper (Cu) 29 Zinc (Zn) 30 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Strontium (Sr) 38 Tin (Sn) 50 Gold (Au) 79 Mercury (Hg) 80 Lead (Pb) 82 Radium (Ra) 88 Uranium (U) 92 Give the names of elements which have, in one atom: a few electrons (Na , Mg , ) a large number of electrons (K, Mn, Fe,) a very large number of electrons (Au, Hg, Pb, Ra, U) a fairly large number of electrons (Cu, Zn, Sr, Sn) a very small number of electrons (Li) Look again at the diagram of containers (exercises 1 and 2) and read this: The conical flask contains much more liquid than the beaker. The beaker contains considerably less liquid than the gas-jar. The beaker contains slightly more liquid than the spherical flask. The dish on the right contains many more crystals than the dish on the left. The dish on the left contains considerably fewer crystals than the dish in the middle. Complete these: The conical flask contains much more liquid than the gas-jar. The spherical flask contains considerably less liquid than the beaker. The beaker contains much less liquid than the conical flask. The dish in the middle contains considerably fewer crystals than the dish on the right. The dish on the right contains considerably more than the dish in the middle. Elements in the Earth’s crust Oxygen Silicon Aluminum Iron Calcium Sodium Potassium Magnesium Titanium Hydrogen Phosphorus Manganese Sulphur Carbon (O) (Si) (Al) (Fe) (Ca) (Na) (K) (Mg) (Ti) (H) (P) (Mn) (S) (C) 49% 26% 8% 5% 3% 3% 2% 2% 0.63% 0.13% 0.13% 0.10% 0.052 0.032% Make comparisons like the following examples: The Earth’s crust contains much more oxygen than magnesium. The Earth’s crust contains much more Silicon than Carbon. The Earth’s crust contains much less Potassium than Oxygen. The Earth’s crust contains slightly more Iron than Calcium. Section 2 Enough and too much These are average quantities ( )الكميات المتوسطةof food consumed by( )إستهلكَ ِمن1 person at the Asia Restaurant: Meat Rice Bread Onion Tomatoes 125 g 150 g 100 g 1 2 If the restaurant has the following quantities, calculate how much of each kind of food is available:()متوفر Meat 6 kilos (6000 g) Rice 9 kilos (9000 g) Bread 5 kilos (5000 g) Onion 60 Tomatoes 80 How many people can eat 6000 g (6 kilo) meat? 6000 ÷ 125 = 48 How many people can eat 9000 g (9 kilo) rice? 9000 ÷ 150 = 60 How many people can eat 5000 g (5 kilo) bread? 5000 ÷ 100 = 50 How many people can eat 60 onions? 60 ÷ 1 = 60 How many people can eat 80 tomatoes? 80 ÷ 2 = 40 Make sentences like this: Example: There is enough meat for 48 people. (rice, bread, onions, tomatoes) Ex.7 Say whether the supply of each kind of food is adequate or not when exactly 50 people eat at the restaurant. Example: There is exactly enough bread. too much / too many ( i.e. more than enough ) too little / too few (not enough ) a) There is too much rice. b) There are too many onions. c) There is too little meat. d) There are too few tomatoes. One day 55 people come to the restaurant, which has these quantities of food: Meat 7 kilos (7000 g) [ 56 people can eat ] Rice 8.25 kilos (8250 g) [ 55 people can eat ] Bread 5 kilos (5000 g) [ 50 people can eat ] Onion 50 [ 50 people can eat ] Tomatoes 120 [ 60 people can eat ] Write down how much (or how many) of each kind of food there is (or are) using these words: a) too little [ There is too little bread. ] b) too few [ There are too few onions. ] c) exactly enough [ There is exactly enough rice. ] d) too much [ There is too much meat. ] e) too many [ There are too many tomatoes. ] Look at these examples: right quantity of enough To be healthy, you must eat a sufficient amount of an adequate amount of but and too much an excess of excess of food, of food makes you fat, too little a lack of an insufficient quantity of an inadequate amount of food makes you thin, and hungry. From your own knowledge can you say which is the right phrase in each of these sentences? a) (Too much /a lack of/ an excess of) iron causes anemia. b) (A lack of/ a sufficient quantity of / an excess of) c) d) e) f) g) h) carbohydrate causes fatness. If your food has not (sufficient / excessive/ insufficient) calories, you will not have enough energy. (The right quantity/ an inadequate amount/ an excess) of vitamins is necessary for health. (An adequate amount/ an excessive amount / an inadequate amount) of calcium causes bone disease. If you have (an insufficient amount/ an excessive amount/ a sufficient amount) of clothing, you will be too hot. If you have (an adequate amount of / an excess of / too little) clothing, you will be too cold. Unless they have (a lack of / an adequate amount of / an excessive amount of) water, plants will not grow. Look at this example: Why can’t you take photograph? (light) Because the light is insufficient. Answer the following questions, using these words: insufficient, inadequate, sufficient, adequate, Why is the tyre flat? (air pressure) Because the air pressure is insufficient. b) Why has the tyre burst? (air pressure) Because the air pressure is excessive. c) Why does the light shine brightly? (current) Because the current is adequate. d) Why will the boat sink? (cargo) Because the cargo is excessive. e) Why can’t the boat go further? (water) Because the water is insufficient. f) Why can’t the boat move? (wind) Because the wind is inadequate. g) Why can the plane leave the ground? (speed) Because the speed is sufficient. a) excessive. Section -3 Too small and big enough Look at these examples: Why can’t you write your name in this rectangle? Because it’s too small to write in. Why can you write it here? It is big enough to write in. Answer these questions: a) Why can’t you put an elephant in your pocket? (small) Because it is too small to put an elephant. b) Why can’t you touch the ceiling? (tall) Because I’m not tall enough to touch the ceiling. c) Why can’t you lift a lorry? (heavy) Because it is too heavy to lift. d) Why does a cork float? (light) Because it is light enough to float. e) Why can’t the lorry go down the street? (wide) Because it is wide enough to go down the street. f) Why can’t you cut a diamond? (hard) Because it is too hard to cut. g) Why can you cut cheese? (soft) Because it is soft enough to cut . h) Why can you bend rubber? (flexible) Because it is flexible enough to bend. i) Why can’t you bend concrete? (rigid) Because it is too rigid to bend. j) Why can you see bacteria with a microscope? (powerful) Because it is powerful enough to see bacteria. k)Why can’t you see bacteria with a magnifying glass? (weak) Because it is too weak to see bacteria. l) Why can’t you see through paper? (opaque) Because it is too opaque to see through. 12. Look at these examples: Europe is too cold for tea plants. Parts of India are warm enough to grow tea in. Write ten sentences like these examples with too / enough and for (+ noun) or to (+ verb), using these words: cold the Antarctic warm the Sahara Desert hot the Atlantic Ocean dry the Red Sea damp Russia deep the River Nile big the Nile Valley wide the Amazonian jungle narrow Northern Europe salty China fertile etc. infertile temperate high for to penguin flowers camels tea plants bananas apples people fresh water fish wheat walk across live in (or on) visit in one day grow many plants in drink irrigate a large area of land Support a large population swim across 13. Look at the map again and answer the following questions: Where is there a lack of oxygen? (Mount Everest.) Where is there an excess of salt? Where is the land over-populated? (China , India) (i.e. population is excessive) Where is the land under-populated? (i.e. there is lack of population) Where is there a lack of vegetation? (Sahara Desert) Where is the cold excessive? (Antarctic) Where is the rainfall inadequate? Section – 4 Reading Read the text and find the answer to the following questions: Which vitamins do the following foods contain? Milk – Liver –Eggs – Cheese – Fruit – Vegetables- Fish – Oil Vitamins Food contains only minute quantities of the substances called vitamins, but they are vital for good health. For example, if you eat a diet of meat, bread, sugar and fat, you may become ill with a disease called scurvy. About fifty different vitamins have been identified, and a deficiency in many of these can lead to illness. Vitamin A is most important for good eyesight, but I s also important for general good health. Liver contains a considerable amount of vitamin A, but vitamin A is also found in fish, meat, milk, butter some fruits and vegetables. Vitamin B in fact consists of twelve different chemicals, which are found in eggs, cheese, butter, whole meal flour and vegetables. If a person has an adequate amount of vitamin B in his diet, this may affect his whole body, particularly the skin, the nervous system and the heart. Deficiency in vitamin B results in a disease called beri-beri. Vitamin C prevents scurvy and helps to heal injuries. Some doctors believe that large quantities of vitamin C help people to avoid colds. Fruits and uncooked vegetables are rich in vitamin C, but when they are overcooked, or left for a long time, they lose most of their vitamins. Vitamin D is essential for the growth of bones and teeth and is found in fish, ,liver, oil and milk. Vitamin D is the only vitamin which the body can make for itself, but it can only do this if there is sufficient sunlight. A lack of both sunlight and vitamin D can result in a disease called rickets, which causes bones to soften and to be deformed. Vitamins are only needed in very small quantities. A quantity sufficient for a whole life would weigh only a quarter of a kilogram. Vitamins can be manufactured and are sold as additions to our food, but a wellbalanced diet will provide and adequate amount of vitamins. Complete the following table: Name of vitamin Food the vitamin is found in Result of a deficiency of the vitamin 16. If a person is suffering from the following diseases, which foods will help him? Scurvy Rickets Beri-beri Poor eyesight Pellagra ( a disease which affects the skin and the nervous system)