South East Asia, China and the Pacific Islands
advertisement

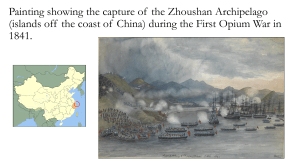
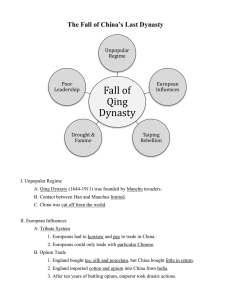
South East Asia, China and the Pacific Islands By: Esther, Jamie, and Gina Cause • Westerners saw Pacific Colonies had tropical agriculture minerals and oils • South East Asia lands were perfect for agriculture • Discovery of oil and tin on islands and desire for more rubber plantations for Dutch • America felt that they should fulfill its destiny as a world power, colonizing like Europeans • Wanted more trade possibilities and new markets • China was a very sufficient country and Europeans wanted to trade with them, so Europeans got Chinese people to smoke opium, which was very addictive Course • • • • • Dutch East Island Company controlled Indonesia France took over Indochina using force Germans had New Guinea and Solomon British got Singapore and colonies in Malaysia Siam maintained its independence while other fell under control of imperialists • U.S. got Philippine Islands, Puerto Rico, Guam, and Hawaii (port on way to China and East India) • Due to hunger China was suffering and therefore discouraged, so opium addictive rose steadily • China began to grow weaker Consequence • Dutch thought Indonesia was home, a rigid social class system formed • In Southeast Asia, transportation and communication improved • Education, health, and sanitation improved • Opium War broke out, China lost • People rebelled against Qing Dynasty and Taiping Rebellion (put a lot of pressure on Chinese government) • Boxer Rebellion • Chinese Government became responsive to their needs • Qing court realized that China needed to make big changed to survive, Dowager Empress sent some Chinese officials on world tour to study different governments Important People • • • • • • King Mongkut (1851 – 1868) Emilio Aguinaldo (near 1902) Queen Liliuokalani (1838-1917) Qing emperor (near 1793) Hong Xiuquan (1814 – 1864) Cixi (1861 – 1908) Important Dates • • • • • • • • • • 1602 – Durch East India Company chartered 1790 – US interest in Hawaii began 1820 – sugar trade changed Hawaiian economy 1840s - During the rule of anti-Christian Vietnamese emperor, seven French missionaries were killed 1842 – Treaty of Nanjing (gave Britain Hong Kong) 1890- The Mckinley Tariff Act passed 1893- Queen Lilieokalani called for new consitution that would increase her power 1894 - Sanford B, Dole, names president of new Republic Hawaii 1898- The US began to acquire territory and to establish trading posts in the Pacific 1902- US immediately plunged into a fierce struggle with the Filipino nationalists and defeated them Important Dates (2) • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1793- Qing emperor agreed to receive ambassador from England 1839- one of emperor’s highest advisors wrote letter to England’s Queen Victoria about opium 1839- Opium War 1842- signed Treaty of Nanjing 1844- U.S. and other foreign citizens gained extraterritorial rights 1850- Chinese population grown to 430 million 1853- 1 million joined Hong’s rebel forces 1864- British and French forces crushed the 14 year rebellion 1861- Cixi gains rule 1899- U.S. declare Open Door Policy 1900- Boxer rebellion 1905- Dowager Empress sent group of Chinese officials on world tour to study operation of different governments 1908- Qing court announced that it would establish a full constitutional government by 1917