Chapter Three (The External Environment Part Two)
advertisement

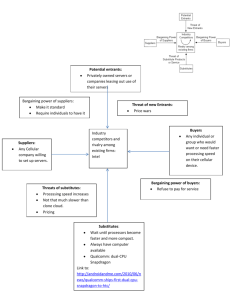
The External Environment (Part Two) Porter’s Five Forces Industry Life Cycle Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of the Suppliers Inter-Firm Rivalry Threat of Substitutes Bargaining Power of the Buyers Porters Five Forces Areas of Microeconomics Bargaining Power of Suppliers Supply and demand theory, cost and production theory, price elasticity Bargaining Power of Buyers Supply and demand theory, customer behavior, price elasticity Inter-Firm Rivalry Market structures, number of players, market size and growth rates Threat of Substitutes Substitution effects Threat of New Entrants Industry attractiveness Market entry barriers Profitability, supernormal profits What is it? What is it trying to communicate? How can it be used by strategic managers? Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Who are the Buyers? Factors impacting the bargaining power of the buyers: Standardized industry product Purchases are made in large volume Number of buyers is small Significant threat of backward integration Switching costs are low Buyers are well-informed about the seller’s costs Bargaining Power of the Buyers Strong? Medium? Weak? Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Factors impacting the bargaining power of the suppliers: Bargaining Power of the Suppliers Strong? Medium? Weak? Product represents a significant % of purchaser’s final product Few suppliers Unique product or input Significant threat of forward integration Supplied product is less expensive for the purchaser to buy than make Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Threat of New Entrants Strong? Medium? Weak? Why are New Entrants a threat? Factors impacting the threat of New Entrants: Economies of scale Capital Requirements Access to Distribution Channels Other entry barriers (regulation) Competitive retaliation High industry profitability and growth Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) What is a substitute? Why are substitute products a threat? Factors impacting the threat of substitute products: Price of available substitutes Switching costs Industry growth and demand Comparability of substitute in terms of quality, performance, other features Threat of Substitutes Strong? Medium? Weak? Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Factors impacting Inter-Firm Rivalry: Concentration Product Differentiation Excess Capacity Exit Barriers Cost Conditions Industry Life Cycle # of equally balanced competitors Inter-Firm Rivalry Strong? Medium? Weak? Be Careful with the Categories in the Five Forces Model Specialty Chemicals Pharmaceuticals Hospitals Bargaining Power of the Buyers Pharmaceuticals Firms Hospitals, Pharmacies Consumers, Managed Care Bargaining Power of the Suppliers Basic Chemical Firms Specialty Chemical Firms Pharmaceuticals Interfirm Rivalry Specialty Chemical Firms Pharmaceutical Firms Hospitals Porter’s Five Forces Model (Competitive Forces) Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of the Suppliers Inter-Firm Rivalry Threat of Substitutes Bargaining Power of the Buyers Industry Life Cycle Mature Decline Emerging and Growth Characteristics of an Emerging and Growth Industry Markets are new and unproven Most buyers are first-time users Companies are in build and grow mode (supplier implications) Technological know-how is just emerging Information about customers, market conditions and how buyers use the product is underdeveloped and hard to get Uncertainty First generation products tend to be improved rapidly Example: Elder day care, genetic engineering, w ireless telecommunications Characteristics of a Mature Industry Slowing growth in buyer demand (head to head competition for market share) Buyers are more sophisticated Greater emphasis on cost and service Overcapacity Process Innovation Internationalization Industry profitability shrinks Consolidation Examples: Automotive, Personal and Household care, Ready to Eat Breakfast Characteristics of a Declining Industry In general, demand grows slower than the economy as a whole based on: technological substitution (calculators/slide rules; computers/typewriters), demographic shifts (increase/decrease in older or younger people) or a shift in needs/tastes (decreased need for red meat). Greater consolidation Competitive pressures intensify To grow and prosper companies must take market share away from rivals Example: Railroad transport industry Fragmented Industries Absence of highly visible, well-known market leaders Low entry barriers Absence of scale economies Market for industry’s product is local Market is so diverse that it takes a large number of firms to accommodate buyer requirements Examples: Funeral industry, hair care/beauty salons, restaurants How would you describe the hotel industry?