Commercial revolution
advertisement

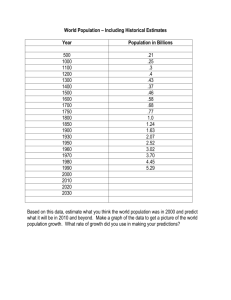
COMMERCIAL REVOLUTION Between 1000 and 1300 Agriculture Trade Finance Towns and cities grew Population growth Territorial expansion Growing food supply Need better ways of farming Switch to horsepower Oxen were easy to keep Horses could provide better production Three-Field System Organize lands Two were planted, one lay fallow (2/3 vs 1/2) Villagers had more to eat Population grew, life expectancy increased The guilds Organization of individuals in the same business or occupation working to improve the economic and social conditions of its members Merchants Craft Guilds Control the number of goods being traded Provided security Skilled artisans Quality of work Wages Working conditions Established wealth and position in society Craft Guilds - Wheelwrights - Glassmakers - Winemakers - Tailors - Druggists Apprentice Parents paid for training Lived with a master and his family Required to obey the master Trained 2-7 years Was not allowed to marry during training When trained progressed to journeyman journeymen Day worker Worked for a master to earn a salary Worked 6 days a week Needed to produce a masterpiece (his finest work) to become a master Had to be accepted by the guild to become a master master Owned his own shop Worked with other masters to protect their trade Sometimes served in civic governments Guild services To Members: To the Community Set working conditions Built almshouses for victims of misfortune Covered members with a type of health insurance Guaranteed quality work Provided funeral expenses Took turns policing the streets Provided dowries for poor girls Donated windows to the Church Fairs and trade Most trade took place in the towns Fairs held during religious festivals Cloth was the most common trade item Self-sufficient manor system no longer needed Goods from foreign lands Trade routes from England to Italy Merchants willing to take risks Buying merchandise that they could sell at a profit Reinvested the profits in more good Business and banking Needed cash and credit to exchange different types of currencies Established exchange rates Letters of credit Eliminated the need to carry large amounts of cash Made trade easier Trading firms started to form Had to borrow money Increased Trade More Workers Needed Serfs move to town; workers paid for labor More cash, banking, and lending services available More money available for building businesses Merchants’ wealth and power expand Merchants’ taxes increase the king’s power and wealth Urban life Population grew from 30 million to 42 million within 150 years As trade grew – cities and towns grew Streets narrow and dirty No sewers Little bathing and no clean or fresh water Many people wanted better opportunities Revival of learning New interest in learning Europeans able to acquire new knowledge New European institution – The University Vernacular Brought literature to many people Medieval Fashion Integral to status Wool clothing Linen undergarments Signs of wealth Brighter colors, better materials, longer jacket length Peasants Stockings or tunics Wimples for hair Outer clothing rarely washed Fur was used often Homework!!!! Read pg. 244-247 in the textbook Create a flow chart or graphic organization about the new government systems Read p. 260 in the textbook take notes Due: Tomorrow!