Life in the Late Middle Ages
advertisement

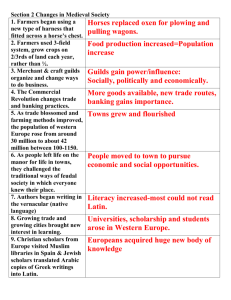
Life in the Late Middle Ages More Farming & New Methods -Warmer climate, farming in regions previously too cold to grow crops. • The Heavy Plow • The Horse Collar • The Three-Field System – 2 out of 3 fields used…why? Innovations increased food production • Heavier plow needed for the rich deep soil of the Western River Valley area • Horse collar • Twice as much land could be plowed in a day using a horse rather than oxen The horse played a vital role • Three Field System • More land is available for planting increasing the production of food • Peasants have a healthier diet and a longer life span • One field will lay fallow or not planted • Fallow field allows the ground to retain and renew its nutrients • More Food leads to population growth. • The Bourgeoisie is created. • Trade Increased • Trade Unions are created • Town Fairs and Tournaments Results of the increase in food production in Western Europe • • • • A surplus of food to trade An increase in the population The rise of towns Decline in feudalism Medieval Walled Towns The town was called a burgh. The town dwellers were know as burghers Merchant Guilds, such as the Hanseatic League also controlled towns & trade routes Guilds • An association of people who worked in the same occupation. • Merchants formed the first guilds • Merchant guilds controlled all the trade in a town Medieval Guild Halls • Guild members erected guild halls where they met to make rules and arrange the details of their businesses • Members of the merchant guild controlled all the trade in their town. • Example: Only a member of the local merchants guild could sell Flemish wool in their town Craft Guilds • Skilled artisans also banned together to create craft guilds • Both husbands and wives worked in the family business • Craft guilds also trained new workers Since most people could not read, craftsmen used signs to advertise their specialty Baker Barber Cobbler - Shoemaker Tailor How the Guild functions • Each guild had their own standards of quality dealing with the size, weight, and price of an item • Guild members who sold substandard goods could be punished by the guild • Each guild had a monopoly or exclusive control of their product Neck violin for feuding women Bakers Baptism for selling under weight bread Training new workers • Apprentice – person learning a craft, who also lives with the master craftsman. • Parents usually paid a fee to the master to train their child • An apprenticeship lasted for 3 to 12 years, without pay except for room and board • Apprentices were not rapidly promoted Journeyman • After the period of apprenticeship you became a journeyman • A journeyman is paid a daily wage • A journeyman can become a master if his “masterpiece” meets guild standards • If accepted, he can train apprentices, hire journeyman, and open a shop • As time went on, it became increasingly difficult to become a master. Medieval Walled Towns By 1200, towns were growing in population and gaining liberties. Towns were independent of the feudal system. Women’s roles change during the High Middle Ages • The idea of romantic love placed women on a pedestal to be worshipped • In the Early Middle Ages many Queens participated in ruling their kingdoms • In the Late Middle Ages Queens did not play a large role in ruling kingdoms • During the High Middle Ages the role of women was limited to the home and convent Marriage in the High Middle Ages • Girls from noble families usually married around age 16 to men in their 30’s – 50’s • Young men could not marry until had property of their own • Girls had little choice of a husband • Women had their greatest power and independence while their husbands were away fighting. 15th century clothing of the nobility Medieval Fairs - Chartres • Peasants came to sell their goods to the towns people during the local fairs. • The great fairs provided customers with goods such as cloth, fur, iron, dyes, honey, oil, butter, fruit, wine, etc. Some goods were from far away places. • No longer was everything produced on the manor • Fairs also provide entertainment. The Moral of the Story • Life becomes much safer and pleasant in the Late Middle Ages. • More food exists and with increased trade and guilds there is less poverty and starvation.