File

Name: _____________________________________________________ Per: ________
By the end of this unit, you will be able to:
Describe what makes up matter
Give examples of important interactions between substances in living things
Define the properties of water
Describe the four chemicals of life, how they are formed and what they do.
Date Activities
Lecture: Matter and substances
Draw a model of an atom
Worksheet/Reading (51-54)
Bill Nye: Atoms
Lecture: Water and solutions
Foldable: Properties of water
Worksheet: Matter and Water
Worksheet/Reading (55-57)
Lecture: Acids and Bases
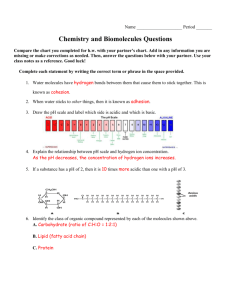
LAB: pH of household substances
Work time and review
BIG QUIZ: matter, substances, water and solutions Lecture: Carbon Compounds
Round Robin: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
Foldable: Carbon Compounds
Worksheet/Reading (59-63)
Worksheet: Comparing Macromolecules
Biomolecule Jeopardy!
Work Time
BIG QUIZ: Carbon Compounds
Lecture: Energy and Metabolism
Worksheet/Reading (64-67)
Unit Review (70-72)
20 Questions
Unit Packets DUE!!
Video
Next class: CELLS!!
**Assignments in italics go in your FOLDER ***Assignments in bold/underline turn in the box**
Vocabulary for this unit:
Atom
Element
Valence electrons
Compound
Molecule
Ion
Cohesion
Matter and Substances
Adhesion
Solution
Acid
Base
pH
Buffer
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
Amino acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleotide
DNA
RNA
ATP
Energy
Reactant
Product
Enzyme
Substrate
Active site
• Every living and nonliving thing is made up of ___________________
• Matter us anything that has a ___________________________________________
• To understand how living things work and interact, you must understand the
__________________________________ of matter
Atoms
• All matter is made of _________________________
• An atom is the __________________________________ of matter that cannot be broken down by physical means
• An atom has a ______________________charged core surrounded by a
__________________charged region
Atomic Structure
• Atoms are made of three types of particles
Elements
– _______________: have a positive charge
– __________________: have a negative charge
– __________________: Have no charge
• An __________________ is a substance made up of atoms that all have the same number of protons…
– For example, each atom of carbon has 6 protons.
********************************************************************************************
Chemical Bonds
• ____________________________________- electrons in the outermost level/shell of the atom
• ____________________________________form between groups of atoms because most atoms become stable when they have eight electrons in the valence shell… therefore they like to give, take electrons or share electrons
Compound
• A __________________ forms when atoms of different elements bond, it is a substance made of the bonded atoms of two or more different __________________
• __________________ (Na) has an extra electron. __________________ (Cl) is missing one electron. When Sodium gives its electron to Chlorine they become a compound and have a chemical bond between them…
Na + Cl = NaCl
Polarity
• In some covalent bonds, the ____________________________________are attracted more strongly to one atom than another. As a result, one end, or pole, of the molecule has a partial negative charge while the other end has a ____________________________________
• When a molecule, like water, has a partial negative and partial positive side, it is said to be
__________________
• When a molecule, like CH4, is totally balanced and does NOT have any partial positive or negative sides (oil, grease, fat, wax)… it is said to be__________________
Solubility
• Because of the charges involved, ____________________________________POLAR molecules
• __________________ substances do NOT dissolve in water.
Hydrogen Bonds
• When bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atoms, a hydrogen atom has a partial charge nearly as great as a proton’s charge. It attracts the negative pole of other nearby molecules
• This attraction is called a ____________________________________
• Hydrogen bonding plays an important role in many of the __________________
__________________things.
Water and Solutions
• A human can survive for a few weeks without food, but only a few days without
__________________. In fact, all of the Earth depends on this simple substance
• Most of the unique properties of water result because water molecules form
__________________ with each other
Properties of water
• ___________________________________- when water freezes, hydrogen bonds lock water molecules into ____________________________________with empty spaces. This makes frozen water less dense than liquid water… allowing it to float
• ______________________________________________________: Hydrogen bonds are constantly forming and breaking between water molecules, because of this, water can absorb a large amount of heat without changing temperature… it is also why water takes a longtime to cool.
• ______________________________________________________hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together much the same way hold hands keeps a crown of people together. This is why small drops of water make a ball.
• __________________- attraction of particles of the same substance. Water is cohesive
• __________________________________________________________: attraction between particles of different substances is called adhesion.
• __________________ is the attractive force between two bodies of different substances that are in contact with each other.
********************************************************************************************
Solutions
• A __________________ is a mixture in which two or more substances are uniformly dispersed
• Dissolving salt into water creates the solution: salt water
• ____________________________________can move more easily within and between cells
Acids and Bases
• Some water molecules break apart to form ions.
• In pure water __________________ions (H+) & __________________ ions (OH-) are present in equal numbers
• In solution, some substances change the __________________ of these ions.
ACIDS
• __________________: any compound that increases the number of hydronium (H+) ions when dissolved in water o __________________ o HCl (Hydrochloric acid) o __________________
BASES pH
• __________________: any compound that increases the number of hydroxide (OH-) ions when dissolved in water o __________________ o Antacid (tums) o Hand soap
• pH is a measure of how ____________________________________a solution is.
– The pH scale goes from 0 to 14.
• 0 is the most acidic possible
• 14 is the most basic possible
• __________________ (neither acidic or basic)
Buffers
• The pH of the solutions in living things must be stable. The pH of human blood is about 7.4. If the pH goes down to 7.0 or up to 7.8, the person will die within minutes!
• A __________________ is a substance that reacts to __________________ pH changes in solutions. It helps to __________________the pH of a solution.
********************************************************************************************
Carbon Compounds
• The parts of a cell are made up of large, carbon based, complex molecules, often called
__________________
– __________________
– Proteins
– __________________
– Nucleic acids
Biomolecules
• A biomolecule is a ____________________________________from a few smaller, simpler substances, repeating units arranged in an extremely precise way.
• They are the molecules of __________________!
Carbohydrates
• A __________________________ is a biomolecule that includes sugars, starches and fiber
• It is made of __________________, hydrogen and oxygen in predictable rations (CH
2
O)
• __________________ are the building blocks of carbohydrates
• A single sugar molecule is called a __________________
– Glucose
• __________________can be linked to make a disaccharide
– Sucrose and lactose
• __________________ sugars can be lined to make polysacchrides
– Starch, cellulose and glycogen
• They are a major source for __________________
• __________________ (a type of carbohydrate) is important in providing structural support in shells and cell walls
• The basic unit of a carbohydrate is a SUGAR!
Lipids
__________________ are biomolecules that are made of fat (waxes and steroids)
The main function of lipids are to __________________, control water movement and insulation/protective coatings.
Lipids also include steroid hormones, used in signaling molecules.
Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and hydrogen atoms, they also have
__________________
There are much __________________ oxygen atoms in lipids than in carbohydrates
– Beef Fat (C
57
H
110
O
6
)
• Lipids are i__________________ (do not dissolve) in water
• They are made of a __________________and a __________________
Proteins
A __________________is made of one or more chains of amino acids that
____________________________________ into certain shapes that determine what the proteins do.
It is an important part of every single cell
Proteins: ____________________________________, enable movement, aid in communication and help carry out chemical reactions
A protein molecule is made of __________________
Every amino acid has an amino group (NH2), a __________________ (-COOH) and a variable side group (can be many different things)
The carboxyl group of an amino acid can link with the amino group of another amino acid and form a __________________
Nucleic Acids
• All of your cells contain __________________
• Nucleic acid is a long chain of nucleotide units
• A nucleotide is a molecule made up of three parts:
– A __________________
– A base
– __________________
• Nucleotides of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA contain the sugar __________________
• Nucleotides of ribonucleic acid or RNA, contain the sugar __________________
• DNA molecules act as “__________________” for the processes of an organism’s life. These instructions called the genetic code, depend on the order of the bases in the nucleotides that spiral around each other.
• Nucleic acids store and transmit ____________________________________
• Some single nucleotides have important roles. Cells need a steady supply of adenosine triphosphate (_______) to function.
• ATP is a nucleotide that has three phosphate groups
• ATP __________________when it breaks apart
********************************************************************************************
Biological Reactions
• Living things carry out many chemical reactions that help maintain a stable internal
__________________Many of these reactions require large amounts of
__________________ to get started. Many of these reactions would not occur without the help of __________________
Enzymes
• An enzyme is a molecule that ____________________________________of a biochemical reaction
• Enzymes hold molecules close together and in the correct orientation
• By assisting in necessary biochemical reactions, enzymes help organism maintain
__________________, without enzymes, chemical reactions would not occur quickly enough for life to exist!
Metabolism
• Your cells get most of the energy needed for__________________from the food you eat.
When food is digested, it is broken down into small molecules that enter the blood, which delivers them to the cells.
• In the cells, ____________________________________release energy by breaking down the food molecules so that cells can use it