Small Engine Terminology
advertisement

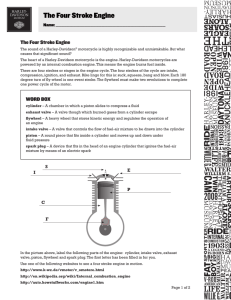
Small Engine Terminology Performance Objectives: Students will be able to define, recognize, and utilize terms concerning small engines effectively. Enabling Objectives Students will define small gas engine terms. Students will use correct terminology in discussion of small engines. Students will recognize small gas engine terminology and be able to effectively apply terms to usage and maintenance of the engine. “How does this whachamacallit fit into the whozamathingy?” “I need a flappy white thing that goes on the top of the engine.” “ Effectively communicating your intentions is a key point to success. Terminology is the key!” Small Engine Maintenance Internal Combustion Engine- Device that burns fuel inside a cylinder to create a force that drives a piston. Piston- A sliding cylinder fitting within a cylindrical vessel that receives the force of combusting fuel. Crankshaft- A shaft with an offset projection that converts circular motion to reciprocal motion, or vice versa. Reciprocating- return; move back and forth Horizontal shaft engine- An engine with a crankshaft that lies crossways for normal operation Vertical shaft engine- an engine whose crankshaft is vertical for normal operation Stroke- the movement of a piston from top to bottom or from bottom to top Cycle- All the event that take place as an engine takes in air and fuel, compresses the air fuel mixture, burns the fuel, and expels the burned gasses. Also the current produced by one turn of a generator armature. Four- stroke cycle- four strokes per cycle Two-stroke cycle- two strokes per cycle Poppet valve- a valve that controls the flow of air and gasses by moving up and down. Port- a special hole in the cylinder wall of a two cycle engine to permit gasses to flow in or out of the cylinder. Reed valve- a flat, flexible plat that permits air or liquid to pass on one direction but seals when the flow reverses. Intake stroke- engine process of taking fuel and air into the combustion chamber Compression stroke- Movement of an engine piston to squeeze or compress the air-fuel mixture Compression ratio- the relationship between the volume of an engine cylinder at the beginning and end of the compression stroke. Top Dead Center (TDC)- position of a piston when at its highest point (furthest from the crankshaft) Bottom Dead Center (BDC)- piston at its lowest point ( point nearest the crankshaft) Fire- flame; to make a spark jump across an air gap Ignition- a spark igniting an air-fuel mixture Power stroke- the engine process in which burning fuel expands rapidly but evenly to drive the piston down Exhaust- burned gasses removed by the motion of a piston Exhaust Stroke- Movement of a piston which expels burned gases from a cylinder Revolution- one complete turn of 360 degrees Momentum- turning force of the flywheel and other moving parts that carries an engine through nonpower strokes. Maintenance- doing the tasks that keep a machine in good condition Troubleshooting- determining what causes a malfunction in a machine or process. Repair- to replace a faulty part or make it work correctly. Adjust- to set a part or parts to function as designed. Contaminant- any material that does not belong in a substance Saturate- to add a substance until the excess starts to run out. Dual-two Precleaner- a device that removes large particles from air entering an air cleaner Shroud- to cover; a cover Score- to scratch Torqued- A twisting force; to twist Speed indicator- a device used to measure revolutions per minute (RPM) of a turning shaft or part. RPM-revolution per minute Leaner- a greater proportion of air and lesser proportion of fuel in an air-fuel mixture. Richer- a mixture with an increased proportion of fuel to air Labor- to struggle or work hard to keep running Small Engine Adjustment and Repair Overhaul- complete disassembly with cleaning and reconditioning or replacement of most moving parts. Governor- Speed control device Air Vane- type of governor used on small engines Carburator- Provides fuel and air to the engine in appropriate portions and volume. Needle- A long tapered shaft A hole shaped to receive the needle and control the flow of fuel. Jet or Seat- a hole shaped to receive the needle and control the flow of fuel. Battery- produces electricity by chemical action. Magneto- produces electricity by magnetism Condensor- stores and releases current to boost current in the Primary circuit Primary circuit- low-voltage circuit of an ignition system Secondary circuit- high-voltage circuit of an ignition system. High-tension wire- high voltage wire in a secondary circuit Electromagnetic induction- conversion of low-voltage current to high-voltage current with a coil. Ignition spark- hot electrical arc across an air gap Ignition points- interrupt the flow in the primary circuit at the correct time to induce the high voltage flow to the spark plug. Discharge- loss of power from a battery Electrolyte- acid solution in a battery Distilled water- free of iron or other parts Armature- the rotating part of a motor. Also the iron core portion of a magneto. Head gasket- seal between the head and the cylinder block Valve Spring Compressor- compresses the valve spring to remove keepers. Valve keeper- transfers spring force to valve stem Stem- long, round section of a valve Margin- outer edge of a valve head Face- surface that is intended for use. Also tapered section of a valve head. Lapped in- grinding valves to fit the seat for a perfect seal Lapping compound- gritty material used for lapping in valves Valve grinding- the process of grinding valves Valve guide- holds valve stem in alignment Valve stem clearance- air gap between valve and push rod. Cylinder- engine cavity containing a piston Head- flat part of a valve; cylinder cover containing the spark plug and combustion chamber. Piston- a sliding cylinder fitting within a cylindrical vessel that receives the force of combusting fuel. Rings- complete the seal between the piston and cylinder wall. Inside micrometer- telescoping gauge used to measure inside surfaces of hollow objects. Telescoping gauge- inside micrometer Cylinder hone- Tool for restoring cylinders Ring expander- tool used to remove and install piston rings Blow-by- compression leakage past pistons Piston ring compressor- used to force piston rings into their grooves Wrist pin (Crank pin)- pin between a connecting rod and piston Micrometer- Used to measure outside surfaces of round objects Plastigage- carefully designed material that flattens out uniformly when pressed. Rope starter- rope wrapped around a pulley for turning power to start an engine Wind up starter- uses a lever to coil a spring for cranking an engine. Valve pin- Transfers spring force to valve stem Head- flat part of a valve; cylinder cover containing the spark plug and combustion chamber. Vocabulary Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Burned gases removed by the motion of the a piston. The movement of a piston from top to bottom or from bottom to top. A sliding cylinder fitting within a cylindrical vessel that receives the force of combusting fuel. The engine process in which burning fuels expands rapidly but evenly to drive the piston down. Movement of a piston which expels burned gases from a cylinder. A. B. C. D. E. Exhaust stroke Power Stroke Piston Stroke Exhaust 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Doing the tasks that keep a machine in good condition. Engine process of taking fuel and air into the combustion chamber Movement of an engine piston to squeeze or compress the air-fuel mixture. A spark igniting an air-fuel mixture Turning force of the flywheel and other moving parts that carries an engine through nonpower strokes. To replace a faulty part or make it work correctly A. B. C. D. E. F. Repair Momentum Intake stroke Ignition Compression Stroke Maintenance Determining what causes a malfunction in a machine or process. 13. All the events that take place as an engine takes in air and fuel, compresses the air-fuel mixture, burns the fuel, and expels the burned gases. 14. Device that burns fuel inside a cylinder to create a force that drives a piston. 15. A shaft with an offset projection that converts circular motion to reciprocal motion, or vice versa. 12. Crankshaft B. Troubleshooting C. Cycle D. Internal Combustion Engine A. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Provides fuel and air to the engine in appropriate portions and volume. Produces electricity by magnetism The rotating part of a motor. Seal between the head and the cylinder block Complete the seal between the piston and the cylinder wall. Stores and releases current to boost current in the Primary circuit. A. B. C. D. E. F. Head gasket Armature Condensor Magneto Carburetor Rings 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Used to measure outside surfaces of round objects. Inside Micrometer Flat part of the valve A twisting force Compression leakage past pistons A. B. C. D. E. Telescoping gauge Blow-by Torque Head Micrometer