Special Inheritance
advertisement

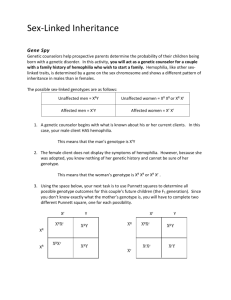
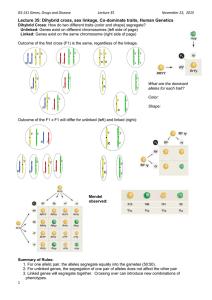
12.2 Notes Special Inheritance Autosomes--22 pairs of chromosomes in a human Sex chromosomes--23rd (last) pair of chromosomes Ex. XX-female XY-male The male always determines sex of offspring 22 Autosomes Sex chromosomes Sex-linked traits--traits located on sex chromosomes R Ex. In drosophila (fruit flies), X = red eyes, Xr = white eyes (located on X chromosome) Cross white eye male (XrY) with red eye female (XRXR) Xr Y XR XRXr XRY XR XRXr XRY Phenotypic ratio--50% male 50% female 100% red eyes White-eyed male (XrY) Red-eyed female (XRXR) Offspring: All red eyed Cross red eye male (XRY) with red eye female (XRXr) XR Y XR XRXR XRY Xr XRXr XrY Phenotypic ratio--Female: 100% red-eye Male: 50% red-eye 50% white-eye Whiteeyed male (XRY) Red-eyed female (XRXr) Simple Mendelian Inheritance-Inheritance controlled by either dominant or recessive alleles Not all traits are either dominant or recessive, some are in between Incomplete dominance—the phenotype of the heterozygous individual is an intermediate (blend) of the 2 homozygous individuals (neither allele is dominant) RR= red flower WW= white flower RW(heterozygous) = pink flower R R W RW RW W RW RW Cross red with white--The offspring are all pink because that color is in between 2 homozygous phenotypes Red (RR) White (WW) W RW RW RW RW W Offspring: All pink flowers Co-dominance--The phenotype of both homozygous individuals to be present in the heterozygous individual BB = black chicken WW= white chicken BW (heterozygous) = black and white chicken B B W BW BW W BW BW Cross black with white chicken--The offspring are all black and white because that is a combination of both homozygous phenotypes Blood type An example of co-dominance in humans Example of multiple alleles, there are more than 2 alleles for this trait It is determined by the presence or absence of proteins (chains of amino acids) on the surface of blood cell Mixing incompatible blood types can cause the cells to clump together, which can cause a person to die Human Blood Types Phenotype Genotype Blood cell surface molecules Type A IAIA or IAi A molecule Type B IBIB or IBi B molecule Type AB IAIB A and B molecules Type O ii No molecules Alleles IA and IB –are co-dominant to each other Allele i –is recessive to both IA and IB Type O blood—universal donor Has no proteins on the blood cells so any blood type can receive it Type AB blood—universal acceptor Has both A and B proteins on blood cells so this blood type can receive type A, B, AB, or O blood Cross parent with A ( IAi) blood with a parent with B blood (IBi) IA i IB IAIB IBi i IAi ii Genotypic ratio 1 IA IB : 1 IA i : 1 IB i : 1 ii Phenotypic ratio (blood type)— 1 type AB : 1 type A : 1 type B : 1 type O Multiple alleles— traits controlled by more than 2 alleles Ex. Mouse hair color is controlled by different alleles, black, brown, gray, albino, etc… Polygenic inheritance--Trait that is controlled by 2 or more different genes Ex. Blood pressure is controlled by genes for weight, cholesterol, kidney function, etc…