Sex-Linked Inheritance: Hemophilia Genetics Activity
advertisement
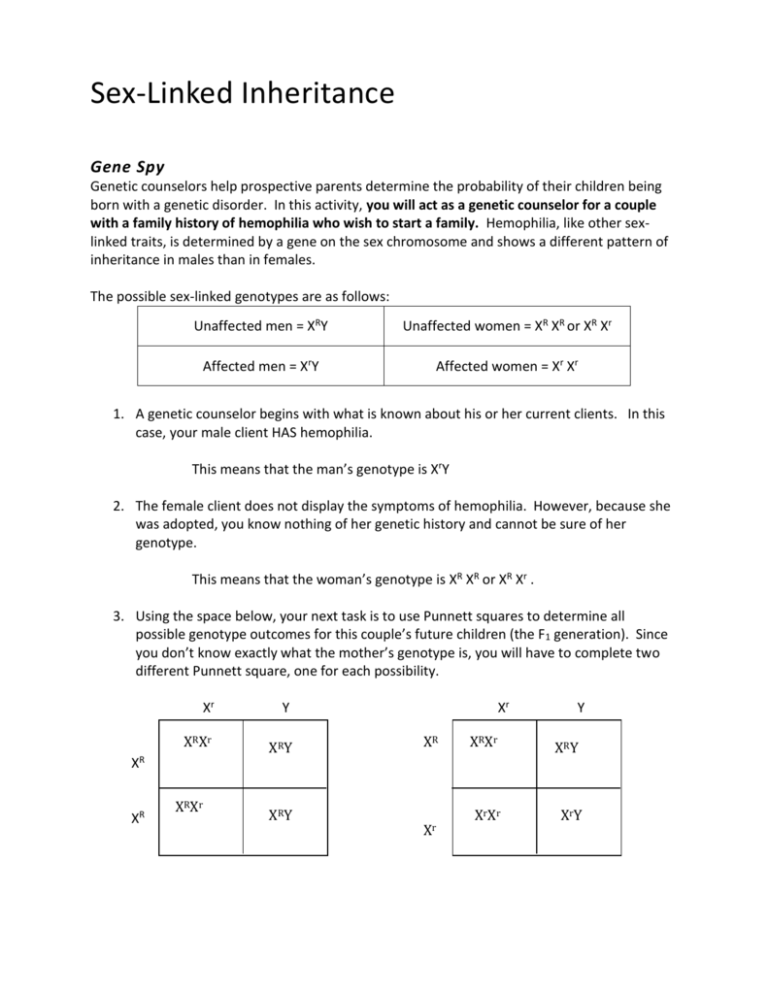
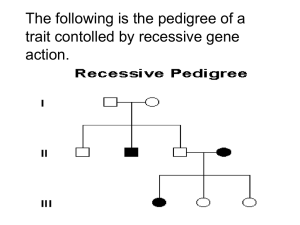
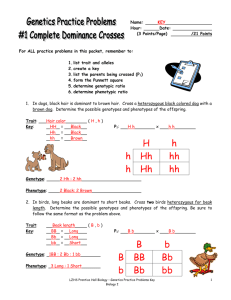
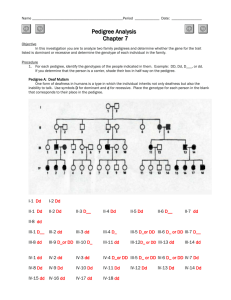
Sex-Linked Inheritance Gene Spy Genetic counselors help prospective parents determine the probability of their children being born with a genetic disorder. In this activity, you will act as a genetic counselor for a couple with a family history of hemophilia who wish to start a family. Hemophilia, like other sexlinked traits, is determined by a gene on the sex chromosome and shows a different pattern of inheritance in males than in females. The possible sex-linked genotypes are as follows: Unaffected men = XRY Unaffected women = XR XR or XR Xr Affected men = XrY Affected women = Xr Xr 1. A genetic counselor begins with what is known about his or her current clients. In this case, your male client HAS hemophilia. This means that the man’s genotype is XrY 2. The female client does not display the symptoms of hemophilia. However, because she was adopted, you know nothing of her genetic history and cannot be sure of her genotype. This means that the woman’s genotype is XR XR or XR Xr . 3. Using the space below, your next task is to use Punnett squares to determine all possible genotype outcomes for this couple’s future children (the F1 generation). Since you don’t know exactly what the mother’s genotype is, you will have to complete two different Punnett square, one for each possibility. Xr Y XRXr XRY XR XR XRXr XRY Xr XR Xr Y XRXr XRY XrXr Xr Y 4. Use the results from question #3 to complete this table. Mother’s Genotype What percentage are female AND affected? What percentage are male AND affected? Homozygous Dominant 0% 0% Heterozygous 25% 25% Analyze and Conclude 5. After talking with the couple, they decide that the risk of their children having hemophilia is not great enough to cause them to reconsider starting a family. Four years later you find out that their first child – a girl – does not display any signs of hemophilia. However, their second child – a boy – is born with the disorder. What does this information now tell you about the mother’s genotype? Explain your answer. The mother’s a carrier, so her genotype is heterozygous for the trait. This is because she couldn’t have a child that had the disorder if she was homozygous dominant 6. What are the chances that the couple’s daughter is a carrier for the disease? How do you know? The chances that the couple’s daughter is a carrier for the disease are 25%. If the mother is heterozygous as well as a carrier, the daughter has a 25% chance of carrying it. 7. If the daughter is a carrier for hemophilia and marries a non-hemophiliac man, could any of her daughters have hemophilia? Her sons? Construct a Punnett square and make a prediction on what you find out. XR XR Y Xr XRXR XRXr XRY XrY 8. In a population, 1 in 10,000 males will have hemophilia compared to only 1 in 1,000,000 females. Explain why this is so. Males have the greater chance of getting hemophilia because they have one x chromosome, and females have two which means males have a much greater chance.