X-LINKED ALLELES
advertisement

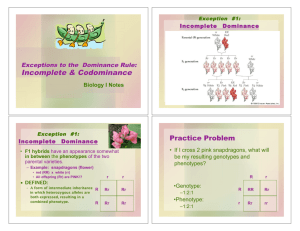
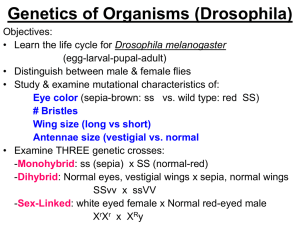
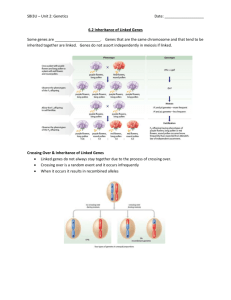
th 13 Friday March Day 1 What are the male and female sex chromosomes? Human Genetics Codominance Two alleles are expressed (multiple alleles) in heterozygous individuals. Example: 1. 2. 3. 4. blood type type type type type A = B = AB= O = IAIA or IAi IBIB or IBi IAIB ii Codominance Problem Example: homozygous male Type B (IBIB) x heterozygous female Type A (IAi) IA i IB IAIB IBi IB IAIB IBi 1/2 = IAIB 1/2 = IBi Another Codominance Problem • Example: male Type O (ii) x female type AB (IAIB) IA IB i IAi IBi i IAi IBi 1/2 = IAi 1/2 = IBi Codominance Question: If a boy has a blood type O and his sister has blood type AB, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of their parents? boy - type O (ii) girl - type AB (IAIB) Codominance Answer: IA IB i i IAIB ii Parents: genotypes = IAi and IBi phenotypes = A and B Sex-linked Traits Traits (genes) located on the sex chromosomes Sex chromosomes are X and Y XX genotype for females XY genotype for males Many sex-linked traits carried on X chromosome Sex-linked traits Morgan performed experiments that proved some genes are on the X chromosome 2. Used fruit flies – Drosophila a. Easily and inexpensively raised in lab glassware b. Females mate only once and then lay hundreds of eggs c. Generation time is short d. They have same sex chromosomes as humans 1. MORGAN’S EXPERIMENT 1. Crossed red eye female with white eye male – got all red eyed offspring a. Red must be dominant 2. Crossed the red eye offspring – expected 3 red eye to 1 white eye a. He got that, but only males were white eyed 3. Eye color must be on the X sex chromosome SEX-LINKED PROBLEMS XR = red eyes Xr = white eyes XRXR = red-eyed female XRXr = red-eyed female (carrier) XrXr = white-eyed female XRY = red-eyed male XrY = white-eyed male SEX-LINKED PROBLEMS Example: Cross a red-eyed heterozygous female with a white-eyed male XRXr x XrY XR Xr 25% red-eyed female Xr XRXr XrXr 25% white-eyed female 25% red-eyed male 25% white-eyed male Y XRY XrY CARRIERS 1. 2. 3. Females that are heterozygous for the trait Carriers do not show the recessive abnormality; they pass it on to male offspring Males cannot be carriers – their either dominant or recessive SEX-LINKED TRAITS IN HUMANS 1. Color blindness a. Caused by a recessive Xlinked allele b. Females are carriers 2. Hemophilia a. Results in excessive bleeding b. Chemical missing for normal clotting c. Recessive allele 3. Sex-limited traits a. Only expressed in the presence of sex hormones and observed in one sex or the other b. Both sexes carry the alleles, but one sex will show the trait c. Color in animals d. Beard growth in males 4. Sex-influenced traits a. Are expressed in both sexes, but they are expressed differently b. Allele for baldness – in males it is dominant, in females it is recessive Polygenic Inheritance - When 2 or more genes affect a single trait - Examples are height and skin color Environmental influence Environment can affect trait just as much as genotype - In a Siamese cat, the enzyme for black fur is only affective in cold temperatures – that’s why black is only on extremities - Nutrition affects growth in humans