BIOLOGY

BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Date_________________Hr________
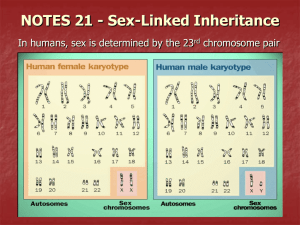
Sex-linked traits are controlled by genes that are found on the X chromosome, but not on the Y chromosome in humans. The X chromosome is larger and has more genes than the Y chromosome. This complicates the inheritance of traits on the X chromosome since we expect that a normal diploid cell will have two alleles for any gene. Such is not the case for males since they are XY and will only have one copy of the genes that are located on the X chromosome.
Females (XX) will have two alleles for a gene located on the X chromosome. Males (XY) will only have one allele for that trait. Thus, females with one dominant and one recessive allele for a gene on the X chromosome would display the dominant phenotype. However , a male will always display the phenotype of the one allele that they have for the trait that is carried on the X chromosome.
A new way of writing alleles:
X
R —normal eyesight
X r —colorblind
Genotypes: X
R
X
R
X
R
X r
X
R
Y X r
X r
X r
Y
Phenotypes: Normal Eyesight and Colorblind
Remember to follow the same steps in order to solve problems:
1.
Assign letters to represent the genes
2.
Determine the parental phenotypes and genotypes.
3.
Predict the outcome of a cross between the possible gametes from the two parents.
4.
State phenotypic and genotypic ratios present in the offspring.
5.
Don’t forget to answer the question within the problem.
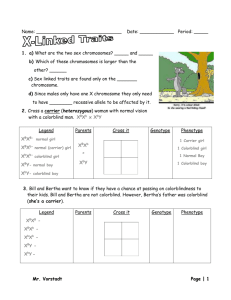
Example 1: In fruit flies, the gene for red eyes is dominant over the gene for white eyes. The trait is sex-linked on the X chromosome. Cross a homozygous, red-eyed female with a white-eyed male. What is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the offspring?
Step 1: X
R —
Red Eyes X r —
White Eyes
Step 2: Parents’ phenotype: Red-eyed fem ale x White Eyed Male
Parents’ genotype: X
R
X
R x X r
Y
Step 3: Step 4
X R X R
X
Y r
X
X
R
R
X r
X
R
Y X
R
X r
Y
Genotypic
Ratio
½ X R
X r
½ X R
Y
Phenotypic Ratio
½ red eyed female
1/2 red eyed male
Step 5: See the ratios in the table in step 4.
Step 5:
Example 2: Using the information above, cross a heterozygous female with a white-eyed male. What is the probability of getting red-eyed males? (You must include the probability of getting males AND red eyes).
Step 1: X
R —
Red Eyes X r —
White Eyes
Step 2: Red-eyed female x White-eyed male
X
R
X r
x X r
Y
Step 3:
X
R
X r
Step 4:
Genotypic
Ratio
X r
X
R
X r
X r
X r
Y X
R
Y X r
Y
¼ X R X r
1/4
X r
X r
¼ X R
Y
¼ X r Y
Phenotypic Ratio
¼ red-eyed female
¼ white-eyed female
¼ red-eyed male
¼ white-eyed male
Step 5: One out of four (25% of) offspring will be both male, and have red eyes.
Example 3: Steps 1 and 4 are given to you- check to see if you get the right ratio.
“Bent” is a dominant X-linked gene in mice. It results in a short, crooked tail. It’s a recessive allele that produces normal tails. If a normal-tailed female is mated to a bent-tailed male, what are the phenotypic and genotypic ratios for the next generation of baby mice?
Step 1: X B = Bent X b = Normal
Step 2: Parents: _________ x ____________
_________ x_____________
Step 3: Step 4:
Genotypic
Ratio
½ X B X b
½ X b Y
Phenotypic
Ratio
½ Bent tail female
½ normal tail male
BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Practice 1 Date_________________Hr________
1. In humans the gene for normal blood clotting is dominant to the gene for hemophilia. This gene is on the X chromosome. A woman heterozygous for the trait (a carrier) marries a man with hemophilia. What is the probability of the couple having: a. a normal (non carrier) daughter? b. a normal son? c. a hemophilic son?
2. Suppose that a normal woman marries a man with hemophilia. What is the probability of the couple having a hemophilic son, and a hemophilic daughter?
3. A certain form of muscular dystrophy is inherited as a sex-linked, recessive gene. Jack has muscular dystrophy. (Neither of his parents has this disease.) Jane, Jack’s wife, does not have muscular dystrophy, but her father does. What fraction of their daughters would you expect to have muscular dystrophy? What fraction of their sons would you expect to have muscular dystrophy?
BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Practice 2 Date_________________Hr________
1. In humans, the gene for normal blood clotting is dominant to the gene for hemophilia. Persons with hemophilia do not have the correct blood proteins for the normal clotting of blood. This gene is on the X chromosome. Suppose that a woman heterozygous for the trait (but with normal blood clotting) marries a man with normal blood clotting. Determine the following probabilities: a) The probability of getting a hemophilic child_________ b) The probability of getting a “carrier” (heterozygous) child___________ c) The probability of getting a normal (neither hemophilic nor carrier) child_____ d) The probability of having a son that is normal________ e) The probability of having a son that is hemophilic________ f) The probability of having a son that is a carrier__________
2. Clouded leopards are a medium sized, endangered species of cat, living in the very wet cloud forests of Central America. Assume that the normal spots, pictured here, are a dominant, sex-linked trait and that dark spots are recessive. What would be the genotypic ratio if a Normal male leopard was crossed with a dark spotted female leopard?
3. Using the information in the question above, suppose a male and female leopard have four cubs and, conveniently, two are male and two female. One each of the male and female cubs has normal spots and one each has dark spots. What is the genotype and phenotypes of the leopard parents?
BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Practice 3 Date_________________Hr________
1. The bison herd on Konza Prairie has begun to show a genetic defect. Some of the males have a condition known as "rabbit hock" in which the knee of the back leg is malformed slightly. Assume the genes controlling this trait are sex-linked and that the “rabbit hock” is recessive. Now, suppose that the herd bull is normal and mates with a cow that is a carrier for rabbit hock. What are the chances of producing a normal son?
2. If this bull mates with this cow every year, what percentage of their daughters will have normal knees?
3. What percentage of their daughters will be carriers of rabbit hock?
4. A rancher owns a bull with many desirable characteristics. Unfortunately, he also has a sex-linked trait that in the recessive form leads to no pigment formation in the iris of the eye. This makes the bull very sensitive to sunlight and could lead to blindness. The rancher wishes to breed him to a cow that will minimize the chances of any offspring showing this trait. She would especially like to produce another bull with most of his sire's desirable qualities but without the nonpigmented eye. a) Two cows with the dominant normal colored eyes (X
N
) are available that have been genetically typed for this particular trait. Cow 1 has a genotype of X N X N and cow 2 is X N X n . Which of these two cows should the rancher choose as a mate to her bull if she wishes to minimize the occurrence of the nonpigmented eye in his offspring? b) What percentage of the male offspring from the preferred cross will have nonpigmented eyes?
BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Practice 4 Date_________________Hr________
1. Muscular dystrophy is a group of disorders that involve muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue that get worse over time. Muscular dystrophy is expressed in the recessive with the dominant gene being “normal” or without muscular dystrophy. A normal man who has a brother with M.D. marries a homozygous normal woman. What is the probability that any of their children will have M.D.?
2. A heterozygous female has children with a male who has M.D. What are the odds that they will have a child who is both male AND has M.D.?
3. A homozygous female with MD and her husband, also with MD, want to know if their children will be affected. Write a detailed explanation to them of how sex-linked traits work and what phenotypic ratios they can expect.
BIOLOGY: Genetics Name :__________________________
Sex-linked Inheritance Practice 5 Date_________________Hr________
On this sheet you’ll find a higher density of problems for you to practice with. You’ll likely need to use your own paper to work them out. Write step five below the questions. Don’t forget to use all five steps and to show your work so you can practice getting all the points on your quiz!
1. In a cross between a white-eyed female fruit fly and red-eyed male, what percent of the female offspring will have white eyes? (White eyes are X-linked, recessive)
2. In a cross between a pure bred, red-eyed female fruit fly and a white-eyed male, what percent of the male offspring will have white eyes?
3. A white-eyed female fruit fly is crossed with a red-eyed male. What are the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring?
4. A human female “carrier” who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait causing red-green color blindness marries a normal male. What proportion of their male children will have red-green color blindness?
5. A human female “carrier” who is heterozygous for the recessive, sex-linked trait red color blindness, marries a normal male. What are the odds that they would have female offspring that will show the trait?
Try these for some more challenging problems! These are more difficult questions that will test your overall understanding. You may need to refer to information within problems 1-5 in order to answer these questions.
6. A female Drosophila of unknown genotype was crossed with a white-eyed male fly. Half of the male and half of the female offspring were red-eyed, and half of the male and half of the female offspring were whiteeyed. What was the genotype of the female fly?
7. Women have sex chromosomes of XX, and men have sex chromosomes of XY. Which of a man’s grandparents could not be the source of any of the genes on his Y-chromosome?
8. Which of a woman’s grandparents could not be the source of any of the genes on either of her Xchromosomes?
9. A boy, whose parents and grandparents had normal vision, is color-blind. What are the genotypes for his mother and his maternal grandparents?