Economic Order Quantity
advertisement

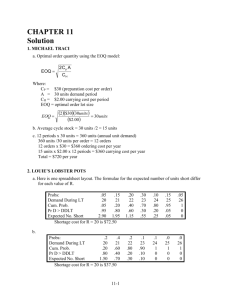
Economic Order Quantity Bus M361-2 Sabrina Wu 11/28/2005 Economic Order Quantity Definition of EOQ How to use the EOQ model in a business organization How the EOQ model works Real world example The Definition of EOQ EOQ, or Economic Order Quantity, is defined as the optimal quantity of orders that minimizes total variable costs required to order and hold inventory. How to use EOQ in your organization How much inventory should we order each month? The EOQ tool can be used to model the amount of inventory that we should order each month. How EOQ Works The Principles Behind EOQ: The Total Cost Curve & How EOQ Works The Principles Behind EOQ: The Holding Costs Keeping inventory on hand Interest Insurance Taxes Theft Obsolescence Storage Costs How EOQ Works The Principles Behind EOQ: The Holding Costs Interest Obsolescence Storage How EOQ Works The Principles Behind EOQ: The Procurement Costs Primarily the labor costs associated with processing the order: Ordering and requisition A portion of the freight if the amounts vary according to the size of the order Receiving, inspecting, stocking Invoice processing How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula Total Cost = Purchase Cost + Order Cost + Holding Cost How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula This represents the unchanging fixed costs P = Purchase cost per unit R = Forecasted monthly usage How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula This represents the variable order costs P = Purchase cost per unit R = Forecasted monthly usage C = Cost per order event (not per unit) Q = The number of units ordered How EOQ Works The Total Cost Formula This represents the variable holding costs P = Purchase cost per unit R = Forecasted monthly usage C = Cost per order event (not per unit) Q = The number of units ordered F = Holding cost factor How EOQ Works The EOQ Formula Total Cost Formula Taking the derivative of both sides of the equation and setting equal to zero to find the minimum value of the function, one obtains: How EOQ Works The EOQ Formula The result of differentiation The Economic Order Quantity How EOQ Works The EOQ Formula Review and Summary of the EOQ Formula P = Purchase cost per unit R = Forecasted monthly usage C = Cost per order event (not per unit) F = Holding cost factor How EOQ Works The EOQ Formula Review and Summary of the EOQ Formula Here is the a graphic representation of the EOQ equation Real Life Example: Real Life Example: Real Life Example: First, Recall the EOQ Equation: P = Purchase cost per unit R = Forecasted monthly usage C = Cost per order event (not per unit) F = Holding cost factor Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… Forecasted Amount Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… Ordering Costs Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… Cost per Unit Real Life Example: Next let’s identify the correct variables… Holding Cost Factor Real Life Example: R = Annual demand C = Fixed ordering cost P = Cost per case F = Holding Cost Factor Real Life Example: R = 5200 C = $10 per order P = $2 F = 20% of value of inventory per year Real Life Example: R = 5200 C = $10 per order P = $2 F = 20% of value of inventory per year EOQ = 2(10) (5200) (2 )(.20) Real Life Example: EOQ = 2(10) (5200) (2 )(.20) EOQ = 510 cases Wrapping It Up EOQ, or Economic Order Quantity, is defined as the optimal quantity of orders that minimizes total variable costs required to order and hold inventory. Closing Comments EOQ is a tool, not a simple solution. EOQ is useful in determining optimal order quantity Understand the equation and what you are trying to find Find accurate inputs for the equation Additional Resources on EOQ • http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0KAA/is_5_31/ ai_94771293 • http://www.inventoryops.com/economic_order_quantity.htm • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_order_quantity