Mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions
advertisement

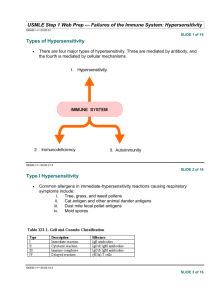
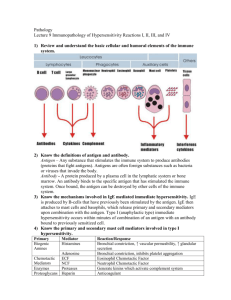
Hypersensitivity immunology What is hypersensitivity? the violent reaction of the immune system leading to severe symptoms and even death in sensitised animal when it is reexposed to the same antigen for the second time. It is nothing but allergy. Extreme sensitivity to antigens. Immune response is always directed towards the protection of the host. But in hypersensitivity the immune response becomes injurious to the host. Hence, the immune response becomes a destructive process in hypersensitivity. In protective immune response, the antigen or bacteria or virus is killed or neutralized. But in hypersensitivity, the cells of the host are killed of the host itself is damaged or killed. Hypersensitivity is the changed reactivity of the immune system. It is a beneficial protective system gone out of order. Situation in which host immune response contribute to tissue injury are collectively referred to as hypersensitivity states. The factors causing hypersensitivity are called allergens. In clinical terms, hypersensitivity is called allergy. Factors causing hypersensitivity 1. 2. 3. 4. Drugs Air borne particles Infectious organisms Food Types of hypersensitivity Type I: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions. Type II: Antibody Dependent Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity Reactions Type III: Immune-Complex mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions. Type IV: Cell- Mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions Type I: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions is mediated by IgE antibodies which have bound to the Fc receptors of circulating basophils and tissue mast cells, thereby sensitizing them. When antigen contacts the sensitized cells, an immediate skin reaction occur leading to intense local inflammation typified by diffuse infiltrations by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, which results in a soft, swollen red skin reaction. The chemical basis of reaction is the release of histamine, serotonin, and heparin by the sensitized basophils and mast cells. Besides skin reaction it also affects smooth muscles, vessel walls characterized by the symptoms of irritation, rashes, swelling, wheezing shock and occasionally death anaphylactic reactions Eg.Allergic reactions to mosquitoes and wasps bites Type II: Antibody Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity Reactions is mediated by IgM and IgG antibody reacting with cellular or particulate antigens. This antibody-dependent cytotoxic hypersensitivity results in complement-mediated cytolysis, antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), or the opsonization and increased phagocytosis of particles sensitized by antibody or fixed complement. Type II hypersensitivity can also damage the host because of circulating antibodies. Type II hypersensitivity reactions differ from type I in three different ways: 1. Antibody combine with antigenic determinants on the cell surface through its Fab portion before any Fc interaction occurs. 2. Interaction of antibody with the target cell directly result in cell death. 3. IgE is not involved Type III: Immune-Complex mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies which react with soluble antigens. This causes the formation of circulating immune complexes (IC) which can cause widespread inflammatory responses called serum sickness Bacterial toxins and free viral proteins are presumably the intended targets, can cause severe organ dysfunction such as kidney failure, rheumatoid arthritis, and types of toxic shock syndrome. Type IV: Cell- Mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions mediated by sensitized T-lymphocytes which can cause direct target cell-mediated lysis and the release of soluble lymphokines. T cell arrive at a skin containing antigen after infection producing a typical hard swelling -called delayed reaction. cytotoxic T-lymphocytes are important in killing cells infected with intracellular parasites such as viruses, bacteria, and trypanosomes as well as fungi and perhaps cancer cells. T cell mediated hypersensitivity is responsible for accelerated graft reaction and allergic reactions caused by contact with chemical or metal allergens called- contact sensitivity. END