Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
advertisement

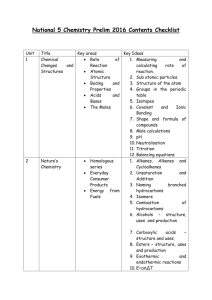
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS HYDROCARBONS SATURATED PARAFFINS ALKANES UNSATURATED CYCLOALKANES H H ALKENES H C H C C H H H H RING WITH CONJUGATED DOUBLE BONDS ALKYNES H C C H H C H AROMATICS H H H CONJUGATED DOUBLE BONDS Chemistry 21A ISOLATED DOUBLE BONDS C C C C C C H H H Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS ethene (ethylene) propene (propylene) 1-butene (1-butylene) cis-2-butene Chemistry 21A chloroethene (chloroethylene) vinyl chloride trans-2-butene Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS cyclopropene C23H46 Muscalure, or cis-9-tricosene, is the sex pheromone of the female common housefly (Musca domestica) butadiene cyclopentadiene cycloheptene cyclooctene propan-1,2-diène Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Alkane R–CH2–CH2–R CnH2n+2 This is the maximum H/C ratio for a given number of carbon atoms. Alkene R–CH=CH–R CnH2n Each double bond reduces the number of hydrogen atoms by 2. Alkyne R–C≡C–R CnH2n-2 Each triple bond reduces the number of hydrogen atoms by 4. Each ring reduces the number of hydrogen atoms by 2 Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS p-orbitals s-orbitals sp2-orbitals Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS In sp2 hybridization the 2s orbital is mixed with only two of the three available 2p orbitals: forming a total of 3 sp2 orbitals with one p-orbital remaining. In ethylene (ethene) the two carbon atoms form a σ bond by overlapping two sp2 orbitals and each carbon atom forms two covalent bonds with hydrogen by s–sp2 overlap all with 120° angles. The π bond between the carbon atoms perpendicular to the molecular plane is formed by 2p–2p overlap. Chemistry 21A π-bond Ethylene (ethene), showing the pi bond in green Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Since sp2 hybrid orbitals are always in the same plane, the entire ethylene molecule is planar. Cis-/trans- isomerism are the consequence of the planarity of all atoms bonded to double-bonded (C=C) carbon atoms. cis-2-butene Chemistry 21A trans-2-butene Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS cyclopropene H2 C H2C H2C All are cis cycloheptene H3C H CH3 H cis-2-butene Chemistry 21A H3C H CH C C H2 H2 H H3C H CH3 H3C H trans-2-butene CH methylpropene Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS C18H34O2 Elaidic acid is a trans unsaturated fatty acid often found in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. Oleic acid is a cis unsaturated fatty acid that comprises 55–80% of olive oil. C18H36O2 Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid found in animal fats and is the intended product in full hydrogenation. Stearic acid is neither cis nor trans because it has no double bonds. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Elaidic acid C18H34O2 Unsaturated fatty acids become rancid relatively quickly. To combat the instability of unsaturated fatty acids, manufacturers began to "hydrogenate" them, a process that makes them more stable. The result was a more solid and longer lasting form of vegetable oil, called "partially hydrogenated" oil, in which a new type of fatty acid is formed. This new type of fatty acid is called trans fatty acid. Trans fatty acids turn out to increase total cholesterol levels and LDL cholesterol levels, and to reduce HDL cholesterol levels. In other words, trans fatty acids are detrimental to cardiac health. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Wachenroder isolated β-carotene from carrots in 1831 giving the extracted crystals the name 'carotene'. Ripe gac fruits β-carotene Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Physical properties of alkenes (and alkynes) are very similar to the physical properties of alkanes with the same number of carbons (and skeletal structure). Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Addition of hydrogen (hydrogenation) across carbon-carbon double bond converts alkenes into alkanes. CH3 CH3 H2C CH H2C CH2 C H2 C H2C H CH2 H2C C H2 CH2 Additions of halogens (Cl2, Br2, I2, etc) also called halogenation: Bromine and chlorine add readily to ethene to form 1,2-dibromoethane and 1,2-dichloroethane respectively. The reaction occurs even in the dark at room temperature. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Markovnikov's Rule In the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as HCl, HBr and H2O to a double bond of an alkene, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon of the double bond with the greatest number of hydrogen atoms. H2C H C Br C H2 CH3 + HBr CH3 C H3C H C H2 1-butene H C H2C CH3 C C H2 H2 2-bromobutane + H2O 1-methylcyclopentene Chemistry 21A H2C acid H2 OH C CH3 C C H2 H2 1-methylcyclopentanol Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Poly(ethene) (polythene or polyethylene) an example of addition polymerisation Temperature: about 200°C Pressure: about 2000 atmospheres Initiator: a small amount of oxygen as an impurity The number of molecules joining up is very variable, but is in the region of 2000 to 20000. Low density poly(ethene) is used for familiar things like plastic carrier bags and other similar low strength and flexible sheet materials. High density poly(ethene) is used to make things like plastic milk bottles and similar containers, washing up bowls, plastic pipes and so on. Look for the letters HDPE near the recycling symbol. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Poly(propene) (polypropylene): PP It has uses in packaging - for example, in plastic film for shrink wrapping food. There are also medical uses - for example, in medical tubing and for medical bags and pouches. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Poly(chloroethene) is commonly known by the initials of its old name (polyvinyl chloride), PVC. Poly(tetrafluoroethene): PTFE You may have come across this under the brand names of Teflon or Fluon. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS “it takes alkynes to make a world” Chemist humor The chemical bonding in compounds such as alkynes with triple bonds is explained by sp hybridization. In this model the 2s orbital mixes with only one of the three p-orbitals resulting in two sp orbitals and two remaining unchanged p orbitals. The chemical bonding in acetylene (ethyne) (C2H2) consists of sp–sp overlap between the two carbon atoms forming a σ bond and two additional π-bonds formed by p–p overlap. Each carbon also bonds to hydrogen in a sigma s–sp overlap at 180° angles. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS H C C H HC CH Acetylene is a colorless, unpleasant-smelling gas (bp 28.1°C), which burns in air to produce a very sooty flame. In the presence of pure oxygen, however, it burns at very high temperatures (up to 2800°C), and is used in welding and cutting torches. Chemistry 21A Two pairs of p-orbitals forming a π-bond sp-sp s bond In acetylene, the H-C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes tend to be rod-like. C 2 H2 acetylene (ethyne) Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS two depictions of propyne the naturally-occurring 1-phenylhepta-1,3,5-heptatriyne Capillin is an antifungal agent. the strained cycloheptyne Pargyline is an antihypertensive agent, sold under the trade names Eudatin® and Supirdyl® IUPAC Nomenclature 1. alkane name - “ane” + “yne” ethyne (acetylene) Chemistry 21A butynes Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS R-C≡C-R + H2 & Lindlar catalyst ——> cis R-CH=CH-R Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Discovery in 1825 by Michael Faraday In 1858, August Kekule proposed a rapid oscillation (I & II) between the 3 C=C and the 3 alternating C-C of hexagonal benzene (C6H6). Linus Pauling proposed resonance theory in 1931 C6H 6 BENZENE Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS All the C-atoms in benzene are sp2-hybridized. Two sp2-hybrid orbitals of each C-atom overlap with two sp2-hybrid orbital of two other C-atoms to form sigma bonds. In this way there are six sigma bonds are formed between six C-atoms which are 120o apart. Remaining six sp2-orbital of six C-atoms overlap with 1s orbital of six H-atoms individually to form six sigma bonds. Since sigma bond results from the overlap of above said planar orbital, all H and C atoms are in the same plane and their generate a hexagonal ring of C-atoms. Each C-atom in benzene also has an unhybrid 2pz-orbital containing one electron. These 2pz-orbital are perpendicular to the plane of sigma bonds Actually these 2pz-orbital produce a pi-molecular orbital containing six electrons. One half of this pi-molecular orbital lies above the plane of hexagonal ring and remaining half below the ring like a sandwich. The overlap of these 2pz-orbital result in the formation of a fully delocalized pi-bond, which extends all over the six C-atoms of benzene nucleus. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS chemical formulas of benzene π-electrons in benzene Kekule Pauling Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS heterocyclic aromatic compound heterocyclic aromatic compound naphthalene Why is Trinitrotoluene (TNT) Explosive? Because nitrogen in the nitro group (NO2) has a charge of +1, the nitro group has a very strong tendency to withdraw (pull) electrons from the aromatic ring. Therefore, attaching three nitro groups to a benzene ring leads to an extremely unstable or explosive compound. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS C6H5- C6H5CH2- phenylcyclohexane OH benzyl alcohol Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Benzene boils at 80°C - rather higher than other hydrocarbons of similar molecular size (pentane and hexane, for example). This is presumably due to the ease with which temporary dipoles can be set up involving the delocalized electrons. Methylbenzene (toluene) boils at 111°C. It is a bigger molecule and so the van der Waals dispersion forces will be bigger. You might have expected that methylbenzene's melting point would be higher than benzene's as well, but it isn't - it is much lower! Benzene melts at 5.5°C; methylbenzene at -95°C. Molecules must pack efficiently in the solid if they are to make best use of their intermolecular forces. Benzene is a tidy, symmetrical molecule and packs very efficiently. The methyl group sticking out in methylbenzene tends to disrupt the closeness of the packing. If the molecules aren't as closely packed, the intermolecular forces don't work as well and so the melting point falls. The arenes (aromatic compounds) are insoluble in water. Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Benzene is resistant to addition reactions. Adding something new to the ring would need you to use some of the delocalized electrons to form bonds with whatever you are adding. That results in a major loss of stability as the delocalization is broken. Instead, benzene mainly undergoes substitution reactions – replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by something new. That leaves the delocalized electrons as they were. Br + Chemistry 21A Br2 + HBr Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are chemical compounds that consist of fused aromatic rings and do not contain heteroatom or carry substituents. PAHs occur in oil, coal, and tar deposits, and are produced as byproducts of fuel burning (whether fossil fuel or biomass). As a pollutant, they are of concern because some compounds have been identified as carcinogenic, mutagenic, and teratogenic. PAHs are also found in foods. Studies have shown that most food intake of PAHs comes from cereals, oils and fats. Smaller intakes come from vegetables and cooked meats. The term carcinogen refers to any substance, radionuclide or radiation that is an agent directly involved in the promotion of cancer or in the increase of its propagation Chemistry 21A mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material teratology generally refers to disfiguring birth defects or malformations Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS However, please, keep in mind that most aromatic compounds are beneficial (many medical drugs are aromatic) and some even essential in our diet and nutrition (some amino acids, vitamins…) phenylalanine tryptophan tyrosine tyroxine Alpha-tocopherol (Vitamin E) Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) Riboflavin (vitamin B2) Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS DNA A, C, G, T RNA A, C, G, U Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS Chemistry 21A Dr. Dragan Marinkovic