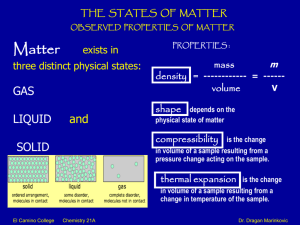
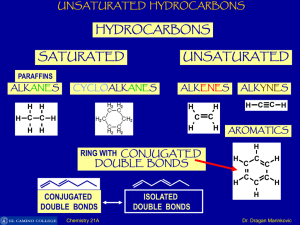
Chemistry 21 A
advertisement

CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 (this Assignment is for two weeks of homework) _________________________________________ Student Name / registration number ________________ Date 1. a) Brønsted base is: b) Brønsted acid is: c) Arrhenius acid is: d) Arrhenius base is: e) Conjugate base is: 2. Name the following acids and the corresponding anions: HNO3 NO3- HNO2 NO2- HClO ClO- HClO2 ClO2- HClO3 ClO3- HClO4 ClO4- H2SO4 SO42- H2SO3 SO32- H3PO4 PO43- H3PO3 PO33- H2CO3 CO32- HC2H3O2 (CH3COOH) CH3COO- CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic H2C2O4 (HOOCCOOH) C2O42- (-OOCCOO-) H3BO3 BO33- H2SiO3 SiO32- HF F- HCl Cl- HBr Br- HI I- H2S S2- Assignment #10 3. Write the formulas of the following bases: Sodium Hydroxide Potassium Hydroxide Ammonium Hydroxide Calcium Hydroxide Magnesium Hydroxide Barium Hydroxide Aluminum Hydroxide Ferrous Hydroxide [Iron (II) Hydroxide] Ferric Hydroxide [Iron (III) Hydroxide] Zinc Hydroxide Lithium Hydroxide 4. Write the reaction of self-ionization of water and the corresponding equilibrium constant equation. 5. What is ion product of water?. 2 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 6. What is pH? What is pOH? 7. What is a) a cation? b) an anion? c) a neutralization reaction?. d) water of hydration? e) an equivalent of salt? f) a diprotic acid? g) an equivalent point of titration? h) an end point of titration? i) a hydrolysis reaction? j) a buffer? k) buffer capacity? l) pKa? m) Henderson-Hasselbalch equation? n) an electrolyte? 3 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 8. For the following acids and bases write disociation reactions – with water (every step for polyprotic a cids and polybasic bases): a) Nitric Acid - HNO3 b) Perchloric Acid - HClO4 c) Sulfuric Acid - H2SO4 d) Phosphoric Acid - H3PO4 e) Carbonic Acid - H2CO3 f) Boric Acid - H3BO3 g) Potassium Hydroxide - KOH h) Ammonium Hydroxide - NH4OH i) Barium Hydroxide - Ba(OH)2 j) Aluminum Hydroxide - Al(OH)3 9. Write a formula for the conlugate base formed when each of the following behaves as Brønsted acid: a) HSO4b) HPO42c) HClO4 d) NH4+ 4 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 10. Write a formula for the conlugate acid formed when each of the following behaves as Brønsted base: a) NH2b) CO32c) OHd) (CH3)2NH e) NO2- 11. Write equations to illustrate the acid-base reactions of each of the following pairs of Brønsted acids and bases: a) HOCl and H2O b) HClO4 and NH3 b) H2O and NH3 c) H2O and OCld) HNO2 and NH3 12. Calculate the molar concentration of OH- in water solutions with the following H3O+ molar concentrations: a) 0.044 b) 1.3x10-4 c) 7.9x10-10 13. Calculate the molar concentration of H3O+ in water solutions with the following OH- molar concentrations: a) 6.9x10-5 5 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 b) 0.074 c) 4.9 d) 9.2x10-9 14. Determine the pH of water solutions with the following characteristics. Clasify each solution as acidic, basic or neutral: a) [H+] = 4.1x10-9 b) [OH-] = 9.4x10-4 c) [OH-] = 10[H+] d) [H+] = 2.3x10-2 15. Convert the following pH values into both [H+] and [OH-] values: a) pH = 3.95 b) pH == 4.00 c) pH = 11.86 16. Write balanced molecular equations to illustrate the following characteristic reactions of acids, using nitric acid (HNO 3): a) with water to form hydronium ions b) with the solid CaO 6 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 c) with Mg(OH)2 d) with CaCO3 e) with KHCO3 f) with Mg metal g) CH3COONa (sodium acetate) 17. Write balanced molecular, total ionic and net ionic equations to illustrate each of the following reactions. All the metals form 2+ ions: a) tin with H2SO4 b) Magnesium with H3PO4 c) calcium with HBr 18. Some polyprotic acids can form more than one salt depending on number of H+s that react with base. Write balanced molecular, total ionic and net ionic equations to represent the following neutralization reactions between KOH and: a) H3PO4 (react two H’s) b) H3PO4 (react three H’s) 7 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 c) H2C2O4 (oxalic acid, HOOCCOOH, react one H) 19. Identify with ionic formulas the castions and anions of the following salts: a) CuCl2 b) (NH4)2SO4 c) Li3PO4 d) MgCO3 e) Ca(C2O4)2 f) KNO3 20. Calculate the mass of water that would be released if the water of hydration were completely driven off 1.0 mol of: a) borax, Na2B4O7x10H2O b) TSP (trisodium phosphate) Na3PO4x12H2O 21. Write formulas for the acid and indicated solid that could be used to prepare each of the following salts: a) CuCl2 (solid is an oxide) b) MgSO4 (solid is a carbonate) 8 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 22. Determine the number of equivalents and miliequivalents for the each of the following: a) 0.22 mol of ZnCl2 b) 0.45 mol of CsCl c) 3.12x10-2 mol of Fe(NO3)2 23. The Ka values have been determined for four acids and are listed below. Arrange the acids in the order of increasing strength (weakest first, strongest last) and arrange the corresponding conjugate bases too (weakest first, strongest last): Acid A (Ka = 2.6x10-3) Acid B (Ka = 1.8x10-3) Acid C (Ka = 1.3x10-4) Acid D (Ka = 1.1x10-3) 24. Write dissociation reactions and Ka expressions for the following weak acids: a) nitrous acid HNO2 b) hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3- c) dihydrogen phosphate ion, H2PO4- (first H only) 25. Describe the difference between the information obtained by measuring pH of an acid solution and by titrating the solution with base. 9 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 26. Write a balanced molecular equation to represent the neutralization reaction between HCl and the following: a) Sr(OH)2 b) Ni(OH)3 c) Fe(OH)2 27. A 20.00 mL sample of each of the following solutions is to be titrated to the equivalence point with 0.120 M NaOH solution. Determine the number of milliliters of NaOH solution that will be needed for each acid sample: a) 0.200 M HClO4 b) 0.125 M H2SO4 c) 0.500 mol HClO3 in 250 mL of solution 28. The following acid solutions were titrated to the equivalence point with the base listed. Use the titration data to calculate the molarity of each acid solution: a) 5.00 mL of dilute H2SO4 required 29.88 mL of 1.17 M NaOH solution b) 10.00 mL of vinegar (acetic acid) required 35,62 mL of 0.250 M KOH solution c) 10.00 mL of HCl required 20.63 mL of 6.00 M NaOH 10 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 29. A solution of solid Na2CO3 dissolved in pure water has a pH significantly higher than pH of pure water. Explain why. 30. Predict the relative pH (7, greater than 7, lower than 7) for water solutions of the following salts. Write ionic equations to justify your response. a) sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl b) sodium formate, NaCHO2 (HCOONa) c) potassium nitrate, KNO3 d) sodium phosphate, Na3PO4 31. Calculate the pH of a buffer that is: a) 0.1 M in lactic acid (C2H4OHCOOH, Ka = 1.4x10-4) and 0.1 M in sodium lactate (C2H4OHCOONa) b) 1 M in lactic acid (C2H4OHCOOH, Ka = 1.4x10-4) and 1 M in sodium lactate (C2H4OHCOONa) c) What is the difference between buffers described in parts a) and b)? 11 CHEMISTRY 21A Instructor: Dr. Dragan Marinkovic Assignment #10 32. Calculate the pH of buffers that contain the acid and conjugate base concentrations listed below (HPO42- Ka = 2.2x10-13; HNO2 Ka = 4.6x10-4; HCO3- Ka = 5.6x10-11): a) [HPO42-] = 0.33 M, [PO43-] = 0.52 M b) [HNO2] = 0.029 M, [NO2-] = 0.065 M c) [HCO3-] = 0.50, [CO32-] = 0.15 M 33. What ratio of concentrations of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4 in solution would give a buffer with pH = 7.65? (H2PO4- Ka = 6.2x10-8) 12