Your Name ______ Date ______ Chapter 16 Earth Science Word
advertisement

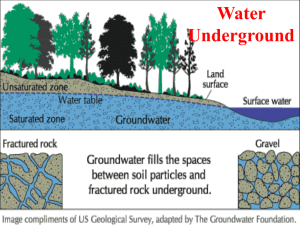
Your Name ___________________________Period ______ Date __________ Chapter 16 Earth Science Word Study Groundwater Directions: Study the following words by reading and rereading them each evening so you will be prepared for the word study test each week. You may use one index card to write as many words and definitions on as possible to use for the test. The card must written in ink, be in your handwriting, and have your name, period, and chapter recorded in the top, right corner with no obvious erasures or mark outs. If all the criteria are met, you may use your index card during the test. It will then be stapled to your test. 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) groundwater – the fresh water that is beneath the Earth’s surface held in aquifers aquifer – a body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater porosity – a measure of the empty spaces in a material or the percentage of the total volume of a rock or sediment that consists of open space permeability – the rate of flow of a liquid or gas through a porous material or the ease with which a material flows through another material (porous – the ability of permitting the movement of fluids or gases through a material by way of pores or other passages) zone of saturation – the layer of an aquifer in which the pore space is completely filled with water; it is the lower of the two zones of groundwater 6.) zone of aeration – the zone between the water table and Earth’s surface and has three regions; the uppermost region holds soil moisture, the middle region is dry except when it rains, and the bottom region, called capillary action, is also moist which attracts water molecules and pulls them up 7.) recharge zone – anywhere that water from the surface can travel through permeable rock to reach an aquifer; these regions are very sensitive because pollution in the recharge zone can enter the aquifer where our groundwater is 8.) artesian formation – a sloping layer of permeable rock that is sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rock with the permeable rock being the aquifer causing intense water pressure through which water will flow out of without being pumped when a hole is drilled 9.) hot springs – groundwater heated by magma that rises to the surface before it cools; the water must be 37o Celsius or about 98o Fahrenheit 10.) geysers – hot springs that periodically erupt from surface pools or through small vents caused from boiling water producing steam that pushes the water above it to the surface 11.) water table – the upper surface of underground water and the upper boundary of the zone of saturation 12.) soft water – water with relatively low amounts of dissolved minerals 13.) hard water – water with relatively high amounts of dissolved minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and iron 14.) cavern – a large cave that may consist of many smaller connecting chambers 15.) stalactites – a calcite buildup that forms a suspended, cone-shaped deposit on the ceiling of a cavern 16.) stalagmites – an upward pointing cone of calcite formed from calcite droplets in a cavern 17.) sinkhole – a circular depression that forms at the surface when rock dissolves in the ground, when sediment is removed, or when caves, mines, or old pipes collapse 18.) karst topography – a type of irregular topography that is characterized by caverns, sinkholes, and underground drainage and that forms on limestone or other soluble rock