The Peripheral Nervous System
advertisement
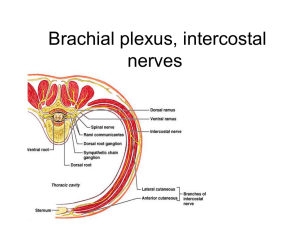
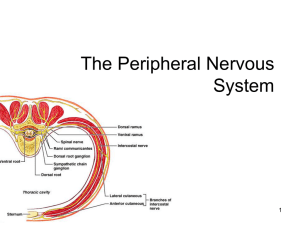
The Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 pairs of cranial nerves All of the smaller nerves that branch from larger nerves Afferent and Efferent Pathways Afferent Pathways Efferent Pathways Spinal Nerves 31 Pairs Numbered according to the level of the vertebral column at which they emerge from the spinal cavity Lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal nerves descend from their point of origin at the lower end of the spinal cord Lower end of the cord is called the cauda equina, which means “horses tail” in Latin Structure of Spinal Nerves Mixed Nerves (contain motor and sensory fibers) Attach by means of two short roots Dorsal root Has ganglion (cell bodies) Carries sensory neruons Ventral root Carries motor neurons Dorsal and Ventral Rami Soon after each spinal nerve emerges from the spinal cavity, it forms several large branches, each of which is called a ramus. Dorsal Ramus Supplies somatic motor and sensory fibers to serveral smaller nerves Ventral Ramus More complex Rami of Spinal Nerves Nerve Plexuses Ventral rami of most spinal nerves subdivide to form complex networks called plexuses. Cervical plexus Brachial plexus Lumbar plexus Sacral plexus Damage to one spinal nerve does not mean complete loss of function in any one region. Dermatomes and Myotomes Each skin surface area supplied by sensory fibers of a given spinal nerve is called a dermatome. A myotome is skeletal muscle or group of muscles that receives motor axons from a given spinal nerve. Dermatome Distribution of Spinal Nerves Myotomes and Body Movement Cranial Nerves 12 pairs Connect to the undersurface of the brain Pass through small foramina (holes) in the cranial cavity and skull Identified by names and numbers 3 Types Mixed Sensory Motor Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Motor Nervous System All the voluntary motor pathways outside the CNS (pathways to skeletal muscles) Single motor neuron whose axon stretches from the cell body in the CNS all the way to the effector Stimulates effectors by means of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine Somatic Reflexes The action that results from a nerve impulse passing over a reflex arc is called a reflex. Predictable response to a stimulus May or may not be conscious Somatic reflexes are contraction of skeletal muscle Autonomic reflexes consist of contractions of smooth or cardiac muscle, or secretion by glands Used in the diagnosis of disease Knee Jerk Reflex Autonomic Nervous System Regulates involuntary effectors Major function of the ANS is to regulate heartbeat, smooth muscle contraction, and glandular secretion in ways to maintain homeostasis. Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions Sympathetic and Parasympathetic have separate pathways Effectors may have dual innervation, that is they have input from both types of pathways Parasympathetic – “rest-and-repair” Sympathetic – “fight-or-flight” Autonomic Conduction Paths