chapter
13
Designing the Marketspace
Matrix
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Designing the Marketspace Matrix —
Today’s Objectives
Objectives will be to:
Introduce the Marketspace Matrix
Examine the role of the 2Is across all categories of marketing
levers
Review how the marketing levers are used to establish and
maintain customer relationships
Examine the principles and guidelines firms can use when
designing the Marketspace Matrix
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
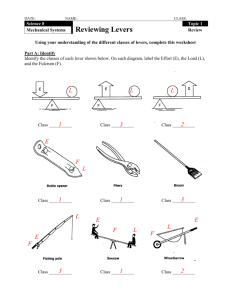
Exhibit 13.1: The Marketspace Matrix
Relationship Stages
Awareness
Exploration
Commitment
Categories of Levers
Product
Price
Communication
Community
Distribution
Branding
Dissolution
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
Exhibit 13.2: The 2Is
Interactivity
Individual
Product
Pricing
Communication
Community
Distribution
Branding
Result
1. More efficient advancing of customers through the relationship stages
2. More possibilities to sustain commitment
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
Exhibit 13.3: Moving Through the
Relationship Stages
Awareness
Exploration/
Expansion
Commitment
Dissolution
Profitable
Uncommitted
Customer
Customers can advance through the stages in several different ways
Exhibit 13.4: The Marketspace Matrix
Relationship Stages
Awareness
Product
Packaging
Exploration / Expansion
Attributes
Customer-specific
Mass
Incremental allocated
Click-through
Post-sales
customized product
Breadth
Price
Dissolution
Customer
care
support
benefits
Experience
of inventory
Upgrades
Customer
enabling community
Functionality
Customer
relationship management
Availability
Customer
care
of complementary products
Targeted
promotions
Future price promotions
Tiered
loyalty programs
Wide variety of pricing plans
Discontinue
Bricks-and-clicks
Justify
prices
Become
Decrease
profit programs
Loyalty
programs
Profit
Terminate
direct marketing
promotions
price discounts
Bundle
promotions
Future
price promotions
Fairness
as a sign of quality
Hi-lo
Subscription
pricing (as a novel approach — group
buying, C2C)
EDLP
EDLP
Dynamic
Dynamic
pricing (group buying, C2C)
Television
Television
Permission
Magazines
Radio
Loyalty
Radio
Newspapers
Customer
Yellow pages
Packaging
Loyalty
Telemarketing
Loyalty
Customer
Billboards
Customer
Online
/ outdoor advertising
billboards (banners / buttons)
Search
pricing promotions
loyalty programs
discount promotions
Targeted
pricing
Prestige
Price
evangelists (affiliate)
Reconfigure
enhancing programs
Volume
Frenzy
Categories of Levers
attributes and features
promotions
Web referral promotions
Web
Communication
Commitment
and features
Fulfillment
engines
Loyalty
programs
E-mail
Links
Viral marketing
E-mail
service
e-mail
Personalized
programs
Interactive
service
programs
Permission
service
marketing with targeted offers
programs
pages
online billboards lending to website
from search lead to website
with information and link to website
Viral marketing
leading to website and / or
download
Website
Serial marketing
Community
Distribution
Outline
community benefits clearly and early on in
the process
Anticipate and readily answer questions and
concerns, quickly establishing a sense of trust
Establish a call for action and further exploration
Makes
community exploration easy through
efficient site structure
Show everyone individual attention (e.g.,
welcoming e-mails, guides for novices, chat
conversations for new members, use of CRM
marketing to tailor site functionality)
Begin the process of equity creation (e.g., member
points and loyalty programs)
Increase
equity building (e.g., through tiered loyalty
programs, increased rewards)
Recognize individuals’ contributions and
participation
Develop members (e.g., through leadership
opportunities, community roles — guides or watchpersons)
Spot
Number
of intermediaries
Degree
of integration
Degree
Elimination
Number
of channels
Number
of channels
of interest
Intermediary
Number
type
of channels
Internal function
Branding
departing friends early and find solutions to
prevent dissolution
Make the “leaving process” fair and efficient
Seek
and listen closely to feedback
Allow the
option of returning
of types
Reduction
of intermediaries
Reduction
of integration
Exhibit 13.6: Lever Selection Process
Objective
Positioning
Current
Relationship
Phase
Lever
Segment
Targeting
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
Exhibit 13.7: Principles for
Marketspace Matrix Design
Which levers
are customers
most
responsive to?
Which levers
are least likely
to generate a
competitive
response?
• Principle 1: Base
the levers on
consumers
behavior.
• Principle 5:
Anticipate your
competitors’
likely responses.
• Principle 2:
Choose levers to
effect change.
• Principle 6: Build
on your firm’s
skills and
resources.
• Principle 3:
Measure the
impact of each
lever.
• Principle 4:
Overcome
barriers to
advancement.
Which levers
work best
together?
Which levers
are consistent
with strategy?
• Principle 7: Look
for interaction
effects.
• Principle 9:
Levers create
the position.
• Principle 8:
Integrate across
levers.
• Principle 10:
Focus on
superior
customer value.
Exhibit 13.8: Amazon’s 1-Click
Ordering Process
Barrier
User in
Exploration/
Expansion
Stage
Places Book
in Shopping
Cart
Has to Enter
Name,
Address,
Credit Card
Commitment
1-click ordering bypasses barrier
Exhibit 13.10: Integration of Levers
Targeted
Segment
Online
Levers
Integrated
Levers
Positioning
and
Message
Offline
Levers
Exhibit 13.11: Functional, Symbolic,
and Hedonic Explained
Functional
Product’s Ability to
Provide Utility
Symbolic
Benefits That Relate to the
Anticipated Reaction of
Other Individuals
Hedonic
Sensual (Taste, Sound,
Sight, Touch) Benefits
Derived From the Product
Exhibit 13.12: Marketspace Matrix for
EBay, 1995
Relationship Stages
Categories of Levers
Awareness
Exploration
Features:
Product
Search,
security, ease
of use
Price
Dynamic
pricing
Communication
Trade
shows
Website
Viral
marketing
Community
Communicate
benefits
Establish call
to action
Easy
to
explore
Build user
equity
Distribution
Branding
Commitment
Facilitate
P2P
community
Dissolution
Exhibit 13.13: Marketspace Matrix for
EBay, 1998–1999
Relationship Stages
Awareness
Categories of Levers
Product
Exploration
Features:
search,
security, ease of use
Complementary
Products: Escrow,
Insurance
Price
Dynamic
Communication
Trade
Shows
Website
Trade
Publication Ads
User
Radio
Advertisements
Banners
Viral
Marketing
Enable
Community
Dissolution
Customer
Care
Customer Care
Customer-Specified
Attributes
Upgrades
Tiered
Loyalty
Programs
Pricing
AOL
Commitment
Personalized
Pages
Notifications
Publicity / Promotion
Community
Communicate
benefits
early
Establish
Action
Call to
Make
Community
Exploration Easy
Equity
Building
Show
Recognize
Begin
Develop
Everyone
Individual Attention
the Process of
Equity Creation
Distribution
Increase
Number
of Channels
Branding
Individual’s
Contributions
Members
Make
Leaving Process
Fair and Efficient
Exhibit 13.14: Marketspace Matrix for
EBay, 2000–Present
Relationship Stages
Awareness
search,
security, ease of use
Product
Categories of Levers
Exploration
Features:
Facilitate
New
Customer
Auction
categories
Complementary
Products: Escrow,
Insurance, Billpoint
Price
Dynamic
Pricing
to
Encourage New
Product Adoption
Communication
Buy
It Now!
Promotions
Promotions
Trade
Shows
Website
Trade
Publication Ads
User
Radio
Advertisements
Television
AOL
Commitment
Dissolution
P2P
Community
Care
Customer-specified
Attributes
Upgrades
Tiered
Loyalty Programs
to
encourage trial
Personalized
Pages
Notifications
Ads
Banners
Viral Marketing
Publicity
/ Promotion
Television
Community
Outline
Ads
Benefits Early
Establish
Call to Action
Make
Community
Exploration Easy
Show
Everyone
Individual Attention
Begin
the Process of
Equity Creation
Distribution
Number
of Channels
Branding
Increase
Equity Building
Recognize
Individual’s
Contributions
Develop
Members
Make
Leaving Process
Fair and Efficient
Chapter 13: Designing the
Marketspace Matrix
The Marketspace Matrix
Role of the 2Is Across All Categories of Marketing Levers
How Marketing Levers Are Used to Establish and Maintain
Customer Relationships
Principles and Guidelines for Matrix Design
Conclusion
Designing the Marketspace Matrix —
Conclusion
The Marketspace matrix is intended to help firms build a marketing plan within
the context of moving customers through the relationship stages.
The 2Is allow firms to choose levers that can move customers through the
relationship stages faster and more effectively than ever. Also, the 2Is offer
firms new and improved possibilities to maintain commitment.
The 10 principles of matrix design can help marketing managers select and
implement appropriate levers. The principles span four categories:
Which levers are customers most responsive to?
Which levers are least likely to generate a competitive response?
Which levers work best together?
Which levers are consistent with strategy?