Grade 8 Mechanical Systems Mechanical Advantage
advertisement

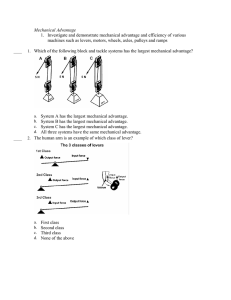
Grade 8 Mechanical Systems Topic 1: Mechanical Advantage What is Mechanical Advantage? Mechanical advantage is the comparison of the force produced by a machine to the force applied to the machine. In other words, mechanical advantage is the comparison of the size of the load to the size of the effort force. What is Mechanical Advantage? The smaller the effort force compared to the load, the greater the mechanical advantage. What is Mechanical Advantage? The formula for Mechanical Advantage is MA = Load Force(LF) Effort Force (EF) = LF EF No units are used to express mechanical advantage because it is a ratio. (The units cancel out). What is Mechanical Advantage? If a branch lever has exerted a force 5 times greater than the force you exerted on it, what does that mean? The lever makes the job 5 times easier. (It takes only 1/5 of the unaided effort to lift the car.) What is Mechanical Advantage? Machines can have a mechanical advantage that is greater than 1 or less than 1 or equal to 1. MA > 1 MA < 1 What is Mechanical Advantage? Some machines do not have any effect on the effort force that you exert. They simply change the direction of the effort force. 100 N MA = 1 MA = 1 Another Way to Calculate MA The concepts of mechanical advantage and work can be linked. The closer you are to the fulcrum, the harder it is to lift an object. The longer the effort arm, the less effort it will take to lift an object. MA = 1 MA = 5 MA = 1/5 Another Way to Calculate MA Another formula that can be used to calculate the mechanical advantage of lever is: MA = Effort Arm (EA) Load Arm (LA) = Load Force (FL) Effort Force (FE) Another Way to Calculate MA An application of levers is “keyhole surgery” wherein a long tube is pushed through the incision to the part of the patient’s body requiring surgery. Electronically controlled levers cut and sew as needed while the surgeon watches on a TV screen. Laparoscopic surgery Another Way to Calculate MA An example where you might want to increase the force that you yourself exert would be using tweezers for delicate precision work. Tweezers can be used to pick up small, delicate items that can be broken or damaged if too much force is applied. Speedy Levers The advantage of a class 3 lever is that the force will move the load a greater distance and at a faster speed. Speed is the rate of motion (how fast something moves) or the rate at which something changes position. It is defined as distance over time. Speed = distance time Speedy Levers Most of the levers inside your body have a mechanical advantage smaller than one. Because of these levers, humans are capable of precision work as well as speed and quick reflexes. Machines Made to Measure Some of the factors taken into account when designing products for people are fit, comfort, function, design (shape), ease, cost. Ergonomics is science of designing machines. Machines Made to Measure Ergonomics is especially important in the design of work environments where occupational safety is an issue. Machines Made to Measure Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common problem for people who type a lot. It causes numbness and pain in the joints. Machines Made to Measure A person can prevent or treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome by using other machines that put less stress on fingers. Review The two formulas for mechanical advantage are MA = Effort Arm (EA) or Load Force (LF) Load Arm (LA) Effort Force (EF) Review A person may choose to use a machine with a mechanical advantage of 1 because it can change the direction of the effort (e.g. a class 1 lever).