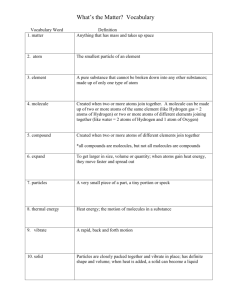
Chemistry - Lyons USD 405

Chemistry
Counting Particles too small to see
John Dalton (1776-1844)
Proposed Atomic Theory
• Each element is made up of tiny, indivisible atoms. Different elements have different atoms.
• Compounded substances
(compounds) are composed of fixed groupings of atoms called molecules
(“little lumps of matter”)
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
(1778-1850)
• Discovered that gases at constant pressure and temperature always combine in definite volume ratios.
• 1 Liter of hydrogen gas + 1 Liter of chlorine gas always produced 2
Liters of hydrogen (mono)chloride.
• 2 Liters of hydrogen gas + 1 Liter of oxygen gas always produced 2 Liters of water vapor
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
(1778-1850)
• Concluded equal volumes of gas must have the same number of particles.
• 1 Liter of hydrogen gas has the same number of hydrogen particles as 1 Liter of oxygen gas.
• 2 Liters of water vapor has 2X the number of particles as 1 Liter of oxygen gas.
Consequences of Gay-
Lussac’s Findings
5 atoms of gas A
• How is it possible to get two volumes
(liters) of product when you only started with one volume (liter) of reactants?
5 atoms of gas B
5 molecules of gas C
Should Equal
But the results continued to yield two volumes of gas C
Instead of one
Amedeo Avogadro
(1776-1856)
Explained Lussac’s findings by:
• Realizing that some gas particles are actually diatomic molecules instead of atoms.
• Diatomic means they are made up of two of the same atoms bonded together.
5 molecules of gas A
5 molecules of gas B
10 molecules of gas C
Equal
Empirical Formula
• Based on the ratio of volumes of reactants and products, a chemical formula for the product can be deduced
• 2 volumes of hydrogen combine with
1 volume of oxygen to produce 2 volumes of water
• Thus, the formula for water must be
H
2
O.
Relative Mass of Atoms
• Scientists also noticed that gases combined in specific mass proportions.
• Two volumes of hydrogen gas (each with a mass of 0.5g) always combined with one volume of oxygen gas (with a mass of 8g)
• Thus, oxygen’s mass relative to hydrogen is
8 g
16
0 .
5 g
Relative Mass of Atoms
This means:
• 1 volume of oxygen has the same number of particles as 1 volume of hydrogen, but the mass of the volume oxygen is 16 times greater than the mass of the volume of hydrogen.
• If the relative mass of hydrogen is 1, then the relative mass of oxygen would be 16.
The Mole
• Weighable amount of an element or compound.
• If the relative mass of hydrogen is 1 and the relative mass of oxygen is
16, then H
2
O molecule would have a relative mass of 18.
Relative mass of 16
Relative mass of 1
Relative mass of 1
Molecular Mass
• The mass of the smallest unit of an element or compound.
• Determined by the mass of the elements in the formula and the number of atoms.
• Measured in Atomic Mass Units
(amu) because it is more convenient than grams
• The molecular mass of H
2 amu
O is 18
Molar Mass
• The number of grams equivalent to the molecular mass of an element or compound.
• 1amu is equivalent to 1gram
• If the molecular mass of H
2
O is
18amu, then the molar mass of H
2 is 18 grams.
O
• 1 Molar mass of a substance = 1 mole of substance.
Number of Particles in a Mole
• Thus, one molar mass (mole) of any substance (element or compound) has the same number of particles.
• 1 gram of substance = 6.022 x 10 23 amu.
• This means there are 6.022 x 10 23 particles of a substance in one mole of that substance.
How Much?
• 1 mol of a substance = 1 molar mass
• 1molar mass = 6.022 x 10 23 particles
• The molar mass of the substance is equal to the molecular mass of the substance determined by the chemical formula for the substance.