Brain Anatomy Part Deux
advertisement

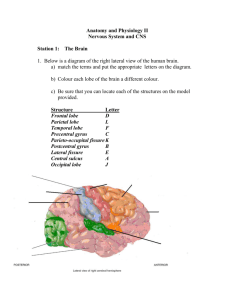
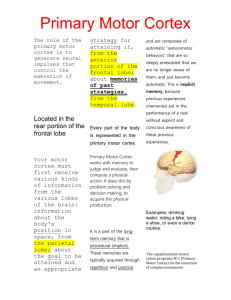
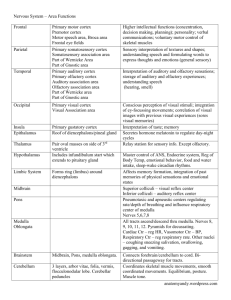
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pu bmed/9367261 link on T and CorpusCallosum Brain Anatomy Regions and their functions By By Anthony Mr. Verdi has a new favorite student… Hippocampus and Amygdala 4 major regions • • • • Cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon Brain stem Cerebellum Cerebral Hemispheres • • • • Right and Left Superior part of brain Most of mass of the brain Shallow groove = sulcus Elevated area by groove = gyrus Cerebral Cortex • • • • • .125 inch thick… 40% of brain mass Motor areas Sensory areas Association areas Contralateral control • Central sulcus • Precentral gyrus = primary motor Primary Motor Cortex • Precentral gyrus • Controls voluntary movement Premotor Cortex • Learned motor skills Broca’s area • Speech! Left hemisphere Broca's area and Wernicke's area are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the arcuate fasciculus. Damage to the arcuate fasciculus causes a disorder called conduction aphasia. People with conduction aphasia can understand language, but their speech does not make sense and they cannot repeat words. Primary Somatosensory Cortex • Postcentral gyrus • Right hemisphere gets information from left, and upside down • Somatosensory Association cortex • Posterior to postcentral gyrus Visual area • Extreme posterior tip of occipital lobe Visual Association Area • Surrounds the visual area… determines what you are seeing – i.e. 2 pretty eyes, long hair, ears… its Zooey ! Auditory Areas • Top of temporal lobe = primary auditory area • Posterior of temporal lobe = auditory association area Olfactory cortex • primitive brain new functions • Rhinencephalon = Memory! • Why we remember smell of Grandma’s old smoky apartment, with dentures and those weird mints now only seen at midlevel restaraunts Diencephalon • • • • 3 paired structures Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus Thalamus • Large number of nuclei • “Afferent impulses from all senses and all parts of the body converge on the thalamus • Includes sensory, visceral, emotional, etc. Hypothalamus 7 functions 1.) Autonomic control center 2.) Center for emotional response 3.) Body Temperature Regulation Hypothalamus 4.) Regulation of Food Intake 5.) Regulation of Water balance and thirst 6.) Regulation of sleep-wake cycles SCN 7.) control of endocrine system functioning Epithalamus • Pineal gland – melatonin hormone • Makes you sleeeepppppyyyy Brain Stem • Midbrain – Some grey matter involved in pain suppression and fight and flight • Superior colliculi – Visual reflex • Inferior colliculi – Auditory reflex Brain Stem • Pons • Helps communication between motor cortex and cerebellum Medulla Oblongata • Cardiovascular center • Respiratory center • Various other centers Cerebellum • Think Coordination! • Coordinates inputs from tons of sensory and motor regions of the brain