ServSafe Food Safety Study Guide
advertisement

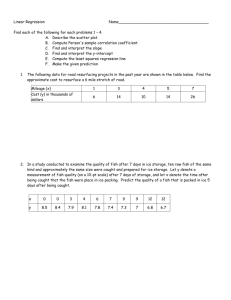
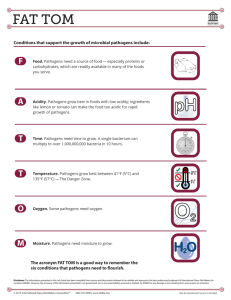
SERVSAFE, FOODS II- Enterprise Foodborne illness A disease transmitted to people by food Foodborne-illness outbreak When two or more people have the same symptoms after consuming the same food Contamination The presence of harmful substances in food. Time-temperature abuse When food has stayed too long at temperatures that are good for the growth of pathogens Cross-contamination Pathogens can be transferred from one surface to another TCS food Food requiring time and temperature control for safety Ready-to-eat food Food that can be eaten without any further prep High-risk populations Some groups of people that have a higher risk of getting a foodborne illness than others. Immune system ` The body's defense system against illness. Challenges to food safety time and money language and culture unapproved suppliers literacy and education pathogens staff overturned high risk customers When is it considered an outbreak? when two or more people have the foodborne illness investigation conducted by state and local authorities Cost of foodborne illness loss of customers and sales loss of reputation negative media exposure staff retraining lowered staff moral lawsuits and legal fees staff missing work High risks of foodborne illness elderly, infants, and people with other illnesses Potential Hazards Biological, physical, and chemical Example of biological pathogens Example of chemical sanitizers, polishes, machine lubricants Example of physical foreign objects: hair, bandages, metal staples How food becomes unsafe purchasing food from unsafe sources failing to cook food adequately holding food in incorrect temps using contaminated equipment practicing poor hygiene Three main factors for unsafe food time and temp. abuse cross-contamination poor personal hygiene Types of Pathogens viruses bacteria parasites fungi What do Pathogens need to grow? (FAT TOM) food acidity temperature time oxygen moisture I. Food to grow pathogens need an energy source TCS foods support the growth of bacteria better than other types of food II. Acidity pathogens grow best in food that contains little or no acid 0= high acidic 14= highly alkaline III. Temperature pathogens grow well in food held between 41- 135 F known as danger zone bacteria grow rapidly in 70-125 IV. Time when food is in Danger Zone they will grow to a high level in the matter of 4 hours V. Oxygen pathogens need oxygen to grow VI. Moisture grow with high levels of moisture scale 0.0-1.0 1.0= water TCS foods dairy products eggs meat fish bake potatoes Ready to eat foods bakery items deli meats washed veggies or fruits Characteristics of bacteria live in and on our bodies cannot be seen, smelled or tasted grow rapidly controlling time and temp can prevent them from causing illness contaminants come from animals we use for food, air, contaminated water, and dirt people: deliberately, accidentally Common symptoms: diarrhea fever nausea cramps vomiting jaundice On set times: depends on foodborne illness ranges from 30mins to 6 days Seafood toxins produced by pathogens found on certain fish in certain fish that eat smaller fish that have consumed the toxin When to wash your hands before work after touching hair, face or body after sneezing or coughing clearing tables handling money Times to change gloves when they are torn changing task every 4 hours What do managers have to do to create safe policies? train food handlers model correct behavior at all times Restricting (when sick) still come to work but can’t be around food Excluding they can’t come to work (depends on population) Flow of food purchasing cooking serving receiving holding storing cooling preparation reheating Preventing cross contamination separate equipment clean and sanitize prepare food at different times buy prepared food Time and temp control 41-135 when held in wrong temperature, lukewarm. avoid time temp abuse monitor time and temp make sure your thermometer is calibrated minimize the time food spends in the temperature danger zone Monitoring time and temp thermocouples and thermistors infrared thermometer time temp indicator strip General hand washing guidelines wash, rise, sanitize and air dry How long do you submerge the thermometer into ice water to calibrate? 30 seconds Freezing point 32 degrees F Boiling point 212 degrees F FIFO first in first out cook or use the food that was bought first use new food last to limit waste Purchasing and receiving purchase food from approved supplier been inspected meets all applicable local, state and federal laws Key drop deliveries supplier is given after hour delivery times Recalls identify recalled food items remove items from inventory and place in a secure location inform staff not to use the product Milk can be delivered at what temperature? 45 or lower within four hours Eggs can be delivered at what temp? 45 or lower For fish, shell fish documentation must be required tags with dates and times labeling food for on site common name Labeling for retail sale quantity, common name, ingredients, list of artificial colors and flavors Date marking ready to eat TCS foods stored for 7 days in 41 or lower Food and color additives use additive approved by local regulatory authority never use more additives never use to alter appearance never add sulfites to produce that will be eaten raw Do not use the following to misrepresent the appearance food additives or color additives lights color overwrap When food must be thrown out employee is sick (cold, flu, virus, hepatitis, etc.) contaminated by hands or body fluids cross-contamination, dripping when it exceeded time and temp requirements when in doubt, throw it out expired Prepping produce it can be washed in water containing ozone when soaking or storing produce in standing water or an ice water slurry do not mix Prepping ice use ice scoops to transfer ice, no glass scoops stored outside of ice chest, upside down in a container Thawing refrigerate at 41 or lower running underwater at potable water 70 thaw in microwave thaw during cooking When serving eggs to a high risk population use pasteurized eggs use pasteurized shell eggs if pooling eggs can use pasteurized shell eggs if dish will NOT be cooked (exp. Frosting) Pooling eggs break out of the shell then put in a container Poultry 165F internal temperature Stuffed meats, fish, poultry and pasta 165F Ground meat, injected meat, eggs help for service 155F Steaks and chops, roasts, fish, eggs serviced right away 145F Pasta, fruits and veggies 135F Cooling food properly ice bath ice paddle blast chiller Reheating 165 for 15 seconds within 2 hours cold food below 41F hot food at 135F Sneeze guard (buffets) 14 inches above food Workflow prep tables near refrigerator and freezer, cooled drawers What is the temp of the water at the hand washing stations? 100F Food contact surfaces qualities Pitting Chopping Decomposition Scratching Scoring Distortion crazing Machine equipment should be how much off the floor? 6 inches Station areas should be how far off the ground? 6 inches Table top equipment should be how far off the table? 4 inches HACCP 7 principles conduct hazard analysis determine critical control points establish critical limits establish monitoring procedures identify corrective actions verify systems that work establish procedures for record keeping and documentation HACCP approach based identifying on biological, chemical or physical hazards has to be specific to menu When is HACCP plan required? smoking food cureing food sprouting beans or seeds offering live, shellfish from display tank Salmonella typhi carriers can spread infection without showing any signs treatment: antibiotic treatment or vaccine for typhoid fever Norovirus incubation period between 24-48 hours symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and stomach cramping prevention: good hand washing procedures Shigella spp. transmission is through fecal oral route drinking and swimming in contaminated water can come from flies E. coli associated with the consumption of undercooked beef, raw milk, unpasteurized apple juice, contaminated water, red leaf lettuce and alfalfa sprouts Hepatitis A flu like symptoms, jaundice through the fecal oral route