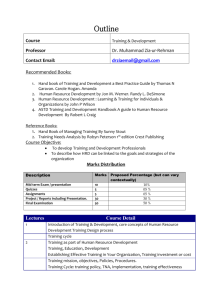
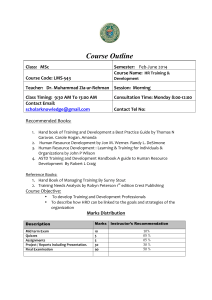
A Study of Admission Requirements, Curricula

5th Annual Hawaii International
Conference on Education,
January 06-09, 2007, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA
“A Study of Admission Requirements, Curricula, and Program
Requirements of Ph.D. Programs in Human Resource
Development/Similar Fields at U.S. Universities” by
Vichet Sum, M.M.S, M.T.D, PH.D. (in process) http://www.vichetsum.com
[ Outline ]
Abstract
Introduction
Highlight of Literature Review
Methodology
Findings
Conclusion and Recommendations
Questions & Comments
[ Abstract ]
Admission requirements, curricula and program requirements.
An important reference.
Ph.D. program development assistance.
[ Introduction ]
HRD is a “bread and butter activity”.
(Gray, 1997)
Strong demand for advanced degrees in HRD.
(Gray, 1997)
Ph.D. program development.
[ Introduction (Cont’d) ]
The Purpose of this Study
To collect crucial information regarding admission requirements, curricula, program requirements of
Ph.D. programs in HRD/similar fields.
[ Introduction (Cont’d) ]
Significance of this Study
An important reference for the creation of the
Ph.D. program in HRD/similar fields.
[ Introduction (Cont’d) ]
Research Questions
1. What are the current admission requirements for a Ph.D. program in HRD/similar fields?
2. What courses are offered in Ph.D. programs in
HRD/similar fields?
3. What are the program requirements of Ph.D. programs in HRD/similar fields?
[ Introduction (Cont’d) ]
Delimitation
Limited to Ph.D. programs in HRD/similar fields from U.S universities that are currently offering a
Ph.D. program in this field.
[ Introduction (Cont’d) ]
Limitation
The universities’ websites may not contain all the information related to admission requirements, courses and program requirements.
[ Highlight of Literature Review ]
Development of HRD programs.
(Kuchinke, 2001; Gaudet & Vincent, 1993)
Offering of certificates and degrees in HRD.
(Chalofsky & Larson-Dougherty, 1996)
Profiling professors of HRD.
(Peterson and Provo, 1996)
Recent changes in HRD programs.
(Milton, Watkins, Spears & Burch, 2000)
[ Highlight of Literature Review (Cont’d) ]
HRD curriculum development.
(Hatcher, 1998; Gay, 1997; Willis & Kahnweiler, 1995; Baylen,
Bailey, & Samardzija, 1996; Leach, 1993; Dare & Leach, 1999;
Kuchinke, 2002)
HRD Definitions.
(McLagan, 1989; Swanson, 1995; Watkins & Marsick, 1993;
Kuchinke, 1999; McLean & Mclean, 2001)
History and Institutional Characteristics of HRD programs.
(Kuchinke, 2002)
[ Methodology ]
Target Population
Ph.D. programs in human resource development/workforce development, career development, organizational development, and/or training and development.
Sample
Doctoral programs in HRD/similar fields in U.S. universities.
[ Methodology (Cont’d) ]
Sampling Procedure
Purposive sampling is a non-probability method that follows specific criteria to collect information.
(Cooper & Schindler, 1998)
Data Collection
- University Websites were accessed and scanned.
- Selection criteria were degree title and program name.
- 14 Ph.D. programs were examined and considered.
[ Methodology (Cont’d) ]
Data Source http://www.hre.uiuc.edu/ucwhre
(The University Council for
Workforce and Human Resource Education) and http://www.gradschools.com.
Data Analysis
- Conceptual content analysis.
(Krippendoft, 1980; Palmquist, Carley, & Dale, 1997)
- Summarization of important data in each of the programs examined.
(Stewart & Shamdasani, 1990)
[ Findings ]
Fourteen Universities:
Barry University (BU)
- Boston University (BOU)
Colorado State University (CSU)
Florida International University (FIU)
George Washington University (GWU)
Georgia State University (GSU)
Ohio State University (OSU)
Pennsylvania State University (PSU)
Southern Illinois University Carbondale (SIUC)
University of Georgia (UG)
University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign (UI)
University of Louisville (UL),
University of Minnesota (UM),
University of North Texas (UNT)
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Admission Requirements (Table 1)
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Curricula
Number of Core Courses
Universities
PSU
BU and UM
GSU, SIUC, and UNT
FIU and GWU
BOU, CSU, OSU, UI, and UL
UG
Number of Core Courses
7
6
5
10
9
4
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Curricula
Number of Research Courses
Universities
GWU and UG
BU, CSU, GSU, OSU, UL, UM, and UNT
BOU and UI
FIU
PSU and SIUC
Number of Research Courses
6
5
4
3
2
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Curricula
Number of Elective Courses
Universities
UI
UM
UL and UNT
GWU
SIUC
CSU and GSU
BU and FIU
UG
BOU, OSU and PSU
Number of Elective Courses
38
28
21
18
17
15
12
9
N/A
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Common Attributes of Required Courses
[ Findings (Cont’d) ]
Program Requirements (Table 4)
[ Conclusion and Recommendations ]
Similar admission requirements among the universities.
An institution can study and assess these criteria to determine admission requirements for its Ph.D. program in HRD.
[ Conclusion and Recommendations (Cont’d) ]
Development of Ph.D. program of study based on the attributes of human resource development/similar category, educational theories/philosophy organizational studies, research methods, and statistics.
Table 4 shows program requirement criteria at the universities.
An institution can adopt these criteria in developing its Ph.D. program requirements.
[ Conclusion and Recommendations (Cont’d) ]
A few directions for future study include:
1. The development of an accrediting agency for the
HRD field.
2. The impact of admission requirements on applicants’ success in the Ph.D. program in HRD.
3. The comparison, effectiveness and accountability of programs of study in a Ph.D. program in HRD.
4. The challenges of the development and creation of a
Ph.D. program in HRD.