Calorimetry
advertisement

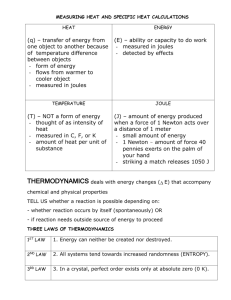
Unit 7 Honors Chemistry Temperature Change Problems Phase Change Problems Calorimetry How to use math to describe the movement of heat energy Energy Conversions Heat is a specific type of energy that can be measured in different ways. The SI unit for heat is Joules – 4.184 Joules = 1 calorie (this will be given) – 1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie – 1000 Joules = 1 kiloJoule Heat Conversions How many joules are in 130 calories? 130 calories 4.184 Joules 1 calorie = 543.92 Joules (= 540 J (Sig figs!) How many calories are in 50 Joules? 50 Joules 1 calorie 4.184 Joules = 11.95 calories Heat Conversions How many kilojoules are in 130 Calories? 130 Calories 1 kJ 4.184 Joules 1 Calorie 1000J = 0.54 KiloJoules Calorimetry Allows us to calculate the amount of energy required to heat up a substance or to make a substance change states. Molar Heat of Fusion (Hf)— The heat absorbed by one mole of a substance when changing from a solid to a liquid. For water, it = 6.0 kiloJoules/mole – or 334 Joules/gram (specific heat of fusion) Heat of solidification is opposite of heat of fusion (heat is released). Molar Heat of Vaporization (Hv)— The heat absorbed by one mole of a substance when changing from a liquid to a gas. For water, it = 40.7 kiloJoules/mole. or 2260 Joules/gram (specific heat of vaporization Heat of condensation is the opposite of heat of vaporization (heat is released) Every pure substance will have a unique Molar heat of fusion (Hf) or vaporization (Hv) Heat Required For a Phase Change Heat Absorbed or Released = q For Melting or Freezing use the following: q = (moles) x Molar Heat Fusion For Vaporization or Condensation use the following: q = (moles) x Molar Heat vaporization Calculating Heat Required To Change State Example #1: How much heat is needed to melt 56.0 grams of ice into liquid (the molar heat of fusion for ice is 6.0 kJ/mol)? q = (moles) x (Hf) 56.0 g 1 mole H2O 6.0 kJ = 18.0 g 1 mole = 18.7 kJ will be absorbed Example #2 How much heat energy in kJ will be released when 200grams steam condenses back to a liquid water? Hv = 40.7kJ/mol q = (moles) x (Hv) 200gram 1 mole 18gram 40.7 kJ 1 mole = 452 kJ released Or -452kJ Heating a Substance with No Phase Change Specific Heat Capacity--The amount of energy required to raise one gram of a substance one degree Celcius. Water’s Specific Heat (as a liquid) Cp= 4.184 Joules/gram oC *Every pure substance will have its own unique specific heat for every phase! Heating a Substance with No Phase Change When you see an increase in the temperature of a sample, the heat is being added to raise the temperature How much the temperature increases is based upon the heat capacity (Cp) and the mass of your sample The higher the heat capacity number, the longer it takes to heat a substance up and the longer the substance holds on to the heat. Energy to Change Temperature Heat Measured in Joules Change in Temperature Tfinal – Tinitial In OCelcius q = (mass) ( Cp) ( T ) Mass In grams Specific Heat Capacity Example #3 m How much energy is needed to heat 80 g of water from 10 oC to 55 oC? Tfinal Tinitial q = mCpΔT = m Cp (Tfinal – Tinitial ) = (80g) ( 4.184 J/g C) (55oC – 10oC) q = 15062 joules Is the energy absorbed or released? Absorbed, because temperature in increasing Final Answer: 15,062 J = 15.06 kJ absorbed/ endothermic Example #4 m How much energy is needed to cool 150 g of ice from -2 oC to -55 oC? Tinitial q = mCpΔT Tfinal = m Cp (Tfinal – Tinitial ) = (150g) ( 2.06 J/g C) (-55oC – -2oC) q = - 16377 joules Is the energy absorbed or released? Released, because temperature in decreasing Final Answer: - 16377 J = -16.3 kJ released/exothermic Heat Problem Road Map q = (moles)Hv q = (moles)Hf Solid Heats Melting or Freezing Vaporization or Condensation Gas Heats Liquid Heats q = mCpΔT * Add each individual energies (in kJ) together for total heat energy required for multistep problems (up to 5 steps max!) Example #5 -How much energy in kJ is needed to change 150grams of ice from 0oC to 50oC? This problem requires two steps. Since water is solid ice at 0oC, we need to melt the ice and then heat it up to 50oC. Step 1 – Calculate heat required to melt 150grams ice 150g 1 mole 18grams 6.0 kJ 1 mole = 50 kJ Step 2 - Calculate heat required to heat liquid water from 0oC to 50oC q = mC T = (150g)(4.184 J/goC)(50oC) = 31380 J convert to kJ = 31.38kJ *Add both heat values together for your final answer 50 kJ + 31.38kJ = 81.38 kJ heat absorbed. Calorimetry Formula Summary Phase Change Use Molar Heat constants Melting use q = (moles) x (Hfusion) Vaporize use q = (moles) x (HVaporization) No Phase Change Use specific heat capacity q = (mass) ( Cp ) ( ΔT )