outcomes-based learning objectives
advertisement

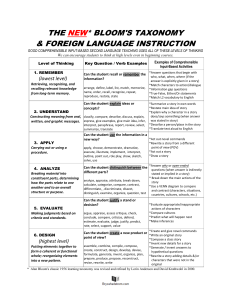
LEARNING ASSESSMENT AND OUTCOMES-BASED TEACHING (Learning) OBJECTIVES Certification 130 (UPR-BT 1999-00) Marta Colón de Toro, SPHR Assessment Coordinator CBA-UPRM October 28, 2004 Our Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will be able to: Identify major provisions of Certification 130 Rewrite your course syllabus according to Certification 130 Rewrite course objectives to reflect learning outcomes. ELEMENTS OF A SYLLABUS According to Certification 130 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Heading Course Code and Title Crds/Hrs Pre/Co requisites and other requirements Course Description 7. According to Official Bulletin 11. 6. 8. 9. 10. 12. Course objectives Course Content with Time Distribution Teaching strategies and methodology Learning Resources Evaluation Strategies Grading System Bibliography Outcomes based 13. (List specific topics and sub-topics) Not more than 5 yrs old, must be available in GL (or MSC) Rights of handicapped students Instructional Objectives… Definition “Are types of executions that the students can perform after being taught in a way that they show that they have learned what was expected.” Norman Gronlund ------------------------------------------------------Purpose Express expectations of what is to be learned in a course Provide a context for what will be learned Course objectives help… The Student Clarify personal goals Measure success Reduce anxiety Improve studying effectiveness The Professor Design relevant classroom material Design relevant assignments Design tests/projects Course Goals and Objectives Teaching Focuses on the professor’s effort, intent “Expose the student to recent research in marine sciences” “Evaluate recent research in marine sciences” or Learning Focuses on the student’s achievement Hierarchy of Learning Goals Institutional Goals “Apply scientific inquiry methods.” College Goals “Think logically and critically.” Program Goals “…basic and applied research.” Course Goals “…apply data collection techniques.” Session Objectives “list steps in the scientific research process.” Complex versus Simple Objectives Write one complex objective for each main topic. Write several simpler objectives within each topic. “Given the data of a job analysis, develop a job description that complies with EEO and ADA guidelines”. “Identify pros and cons of different job analysis methods”. “Discuss EEO and ADA provisions for writing job descriptions”. Write 1-2 simple objectives for each class/assignment. “Provide a definition of job analysis”. “Describe the process of analyzing jobs”. Effective Learning Objectives Express them in terms of observable and measurable behavior Facilitates assessment of learning Objectives should answer these questions: What must students do to show that they have learned. What should students be able to do as a consequence of their learning. Good learning objectives address… What the student is expected to do after learning. (performance) 2. The circumstances under which the student will be able to perform.(condition). 3. The level of acceptable performance. (standard) 1. Basic Elements Using Measurable Action Verbs analyze compare demonstrate discuss identify justify grasp state compute appreciate direct display infer list report synthesize classify contrast derive evaluate integrate understand respond name collaborate define designate know interpret organize solicit explain Levels of Learning Bloom’s Taxonomy Compare Evaluating contrast, critique, justify Adapt, Synthesizing combine, compare, contrast, design, generate Correlate, Analyzing diagram, distinguish, outline, infer Determine, Applying develop, compute, utilize, conduct Classify, Comprehending Knowing Define, explain, discuss, give examples, summarize describe, list, reproduce, enumerate & Let’s Practice! Rewriting Learning Objectives “At the end of this session you will be able to: How to get started… Identify each general topic of your course Write down what you expect the students to be able to do in regard to each topic. These become the list of course objectives Communicate them to students Use them to develop assignments, exams, etc… Make sure you will be able to measure each objective Consider the level at which they should be able to perform. (Bloom’s taxonomy) Rewrite each objective based on outcomes. Dealing with “understand” Always ask yourself… What would students be able to do if they “understood”? Give examples of … Determine the “correct” method to use… Discuss pros and cons… Identify elements in a given case… Apply the correct technique