The Crusades: Causes, Events & Effects
advertisement

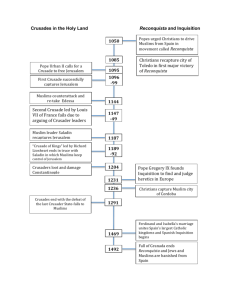
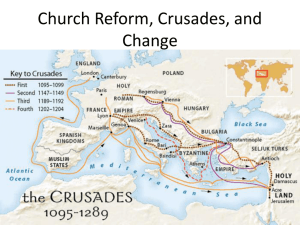
Chapter 10, Lesson 2: The Crusades (Pgs. 327-321) ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why did the Christians begin a series of wars to conquer Palestine? Causes of the Crusades • Seljuk Turks captured Palestine, including Jerusalem, in 1071 - Jerusalem was sacred to Christians, Jews, Muslims - Seljuks made Christian pilgrimages to Jerusalem nearly impossible • European princes, merchants were eager for power, trade opportunities • Seljuks attacked Byzantine Empire • Crusades—military expeditions from Christian Europe to Palestine- first Crusade began in 1096 The First Crusade • In 1096, European armies departed for Byzantine capital Constantinople - lack of supplies, attacks left tens of thousands dead along the way • Christian forces captured Jerusalem in 1099 • Christians divided land into four Crusader statesEdessa, Antioch, Tripoli, and Jerusalem Muslims Return to Power: Saladin’s Rise To Power • Second Crusade (1147–1149) began after Muslims recaptured Edessa - French, German armies marched separately, were defeated by Muslims - rifts among Muslim leaders helped other Crusader states survive • Saladin—Muslim political, military leader in late 1100s - fought with Syrian army to defend Egypt from Crusaders; ruled Egypt - united Muslims to recapture Jerusalem in 1187 The Third Crusade • Pope called for Third Crusade (1189–1192) to recapture Jerusalem - some of Europeʼs most powerful leaders joined the Crusade - Englandʼs King Richard the Lion-Hearted led Crusade • Crusade was successful at first, but failed to recapture Jerusalem • In 1192, Saladin and Richard agreed to a truce- Muslims controlled Jerusalem, Christians allowed to visit Holy Land The Fourth Crusade • Truce didnʼt last; Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) launched • Crusaders attacked Byzantine city of Zara, sacked Constantinople-Europeans put political ally in charge of Byzantine Empire • Pope angered by attacks on Christian cities, but could not stop them • Crusade ended, Byzantine Empire left even weaker Muslims Recapture Palestine: Effects of the Crusades • By 1270, Muslims had driven Crusaders out of Palestine • Crusades didnʼt have permanent effect on Muslims in Palestine-but Christian traders, pilgrims continued efforts in Palestine • Crusaders brought Asian goods to Europe (spices, furs, cloth, rice)-increase in trade helped European towns to grow • Christians became increasingly hostile toward Jews-believed non-Christians were their enemyJews expelled from England, France; many moved to eastern Europe • Muslims allowed Jews, Christians to live in peace in most cases The Reconquista • In 700s, Muslims conquered Iberian Peninsula (Spain, Portugal today) • Muslim unity faltered by 1000; Spanish, Portuguese defeated Muslims-Reconquista—the Christian reconquest of Spain (1000–1492) • King Ferdinand, Queen Isabella unify Spain through religion, military • Inquisition—European court punished those opposed to Christianity- Jews, Muslims tortured, executed for their beliefs Lesson Summary • Christian Europe launched Crusades from 1096 to 1270 to take control of Palestine from muslims. • Under Saladin, Muslims regained much territory lost during the First Crusade. • Crusaders failed to take control of Palestine, but the Reconquista in Spain was successful.