BUDDHISM
advertisement

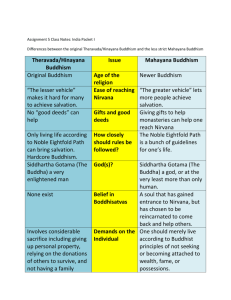
What is Buddhism? Buddhism is a religion to about 300 million people around the world. “Buddhism” comes from the word “budhi". Early Buddhism Siddhartha Gautama, the the founder of Buddhism came from the Kshatriya family, but he gave up his position and inheritance in order to seek salvation. About 534 B.C.E Gautama left his wife, his family, and the comforts of home to lead the existence of a holy man. He brought around the religion known as early Buddhism (a.k.a. Thervada Buddhism) Buddha’s followers The Buddha publicly announced his doctrine for the first time in 528 B.C.E at the deer park of Sarnath, near the Buddhist holy city of Banaras (modern Varanasi), in a sermon delivered to friends who have formerly been his companions in asceticism. The Dharma The dharma is the basic doctrine shared by Buddhists of all sects consisting of the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path What is the First Noble Truth? The first truth is that life is suffering life includes… pain getting old disease death psychological suffering (loneliness frustration, fear, embarrassment, disappointment and anger) It is realistic rather than pessimistic because pessimism is expecting things to be bad. lnstead, Buddhism explains how suffering can be avoided and how we can be truly happy. What is the Second Noble Truth? The second truth is that suffering is caused by desire. We will suffer if we expect other people to conform to our expectation, if we want others to like us, if we do not get something we want,etc. In other words, getting what you want does not guarantee happiness. Rather than constantly struggling to get what you want, try to modify your wanting What is the Third Noble Truth? The third truth is that suffering can be overcome and happiness can be attained; this is known as nirvana. When one achieves Nirvana, they escape the cycle of the otherwise endless reincarnation cycle What is the Fourth Noble Truth? The fourth truth is that the Noble 8-fold Path is the path which leads to the end of suffering. The Eightfold Path In summary, the Noble 8-fold Path demands… Right belief Right resolve Right speech Right behavior Right occupation Right effort Right contemplation And… What are the 5 Precepts? The moral code within Buddhism is the precepts, of which the main five are… Not to kill Not to steal Not to lie Not to be unchaste And to avoid drugs and intoxication What is Karma? Karma is the law that every cause has an effect How can we test the karmic effect of our actions? The answer is summed up by looking at… the intention behind the action effects of the action on oneself the effects on others. What is Wisdom? Buddhism teaches that wisdom should be developed with compassion. At one extreme, you could be a goodhearted fool and at the other extreme, you could attain knowledge without any emotion. True wisdom is not simply believing what we are told but instead experiencing and understanding truth and reality. Wisdom requires an open, objective, unbigoted mind. The Buddhist path requires courage, patience, flexibility and intelligence. What is Compassion? Compassion includes qualities of… sharing readiness to give comfort sympathy concern Caring In Buddhism, we can really understand others, when we can really understand ourselves, through wisdom. Ashoka’s Support The early Buddhism movement benefited from the support of the Mauryan dynasty Ashoka adopted Buddhism about 260 B.C.E. after the war against Kalingans Saddened by the violence by the violence of the war and the suffering of the Kalingans, Ashoka decided to live peacefully Ashoka’s Influence Ashoka… Banned animal sacrifices Gave up his beloved hunting expeditions Eliminated most meat dishes from the tables of his court Ashoka rewarded Buddhists with grants of land He built monasteries and stupas and made pilgrimages to the holy sites of Buddhism Sent missionaries to Bactria and Ceylon Development of Buddhism Early Buddhism, Thervada, did not promise to make life easy for its adherents three new developments in Buddhism Between 3rd century B.C.E and 1st century C.E. thought and practice reduced obligation of believers opened new avenues to salvation brought explosive popularity to the faith. This change became known as Mahayana Buddhism Mahayana Buddhism First, although Buddha did not identify himself as divine, some of his later followers began to worship him as a god. This allowed them to identify themselves closer with their religion. Mahayana Buddhism Second, theologians articulated the notion of bodhisattva (“enlightened being”) Reached perfection and was merited the reward of nirvana, but he intentionally delayed their his to help others who were still struggling Some believe that bodhisattva’s could even perform good deeds on behalf of their less spiritual brethren Bodhisattva’s served as examples of spiritual excellence Mahayana Buddhism Finally, Buddhist monasteries began to except gifts from wealthy individuals They regarded these bequest as acts of generosity that merited salvation In this way, wealthy people could avoid the sacrifices demanded by early Buddhist teachings, and still ensure their salvation. The Spread of Buddhism Mahayana Buddhism flourished partly because of educational institutions that promoted the faith When monasteries were created, they established educational institutions Best known of all was the Buddhist monastery of Nalanda Nalanda soon became so famous as an educational center that foreigners came there to study with the most renowned masters of the Buddhist doctrines Like so, Buddhism was able to spread quickly The Spread of Buddhism Sources http://www.buddhanet.net/e-learning/5minbud.htm Traditions & Encounters: A Global Perspective on the Past Fifth Edition (AP Edition) by Jerry H. Bentley and Herbert F. Ziegler