Do Now
advertisement

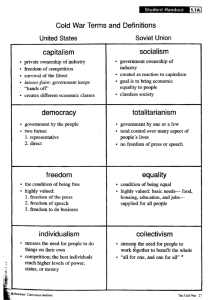
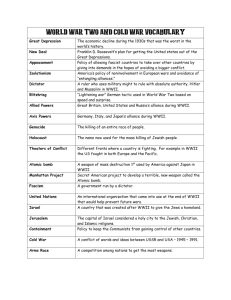
Questions! Write down everything you know about the period of American history referred to as the “Cold War.” What is a cold War? The Cold War Begins Aim: How did post WWII tension lead to the Cold War? Overview The United States and the Soviet Union had cooperated to win WWII. After the war, however, conflicts in ways of thinking led to mutual suspicion, hostility , and eventually to indirect conflict that lasted for over 40 years. This period is referred to as the cold war. In 1948, JournalistWalter Lippman first used the term Cold War, borrowing from a French phrase, to refer to a “constant war of nerves” between the Soviet Union and the United States. I. Superpowers After WWII several powerful nations of the past were devastated. (Which ones?) The Soviet Union and the United States emerged from WWII as the worlds greatest powers. Superpower: Powerful country that plays a dominant economic, political, and military role in the world. II. Post WWII Europe Both Germany and Japan were devastated socially, economically, and physically by the war. In both countries the army was disbanded and trials were held to punish people responsible for war crimes. The victorious allied powers occupied the two countries. III. Division of Europe (1945) Yalta Conference: Before the end of WWII the US, England and Soviet Union met to outline division of Germany after the war. (Stalin first agrees to have free elections in Poland, Bulgaria, Romania but later goes back on his word) Potsdam Conference: Big three formalize the decision to divide Germany into four zones of occupation. Truman walks away from the conference believing the USSR was planning “world domination.” IV. Divided Europe After WWII democratic governments were restored in Western Europe. Eastern Europe was occupied by the armies of the communist Soviet Union. Iron Curtain: Imaginary line that divided Europe after WWII between communist and democratic nations. Soviet goals vs. American goals Soviet Keep Germany weak and divided Eastern Europe under Soviet control Spread Communism World Domination America Germany stronger and united Eastern Europe – Independent Nations Stop spread of Communism Support free peoples resisting subjugation Containment V. Growing Distrust After WWII the Soviet Union was viewed as a threat to security of noncommunist world. Containment: U.S. Foreign policy in which US attempted to limit communist expansion. Full commitment of the American economic, military and political power US Cold War Policies Truman Doctrine 1947 Marshall Plan 1948 Support free peoples $13 billion in aid to resisting subjugation European countries Berlin Airlift Lasted about a year. http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAss etId=7fa4128b-d776-4c5e-bc2b-91ae1ae844a3 Satellite States Countries/States controlled by the Soviets Poland Czech Republic Hungary Romania Bulgaria Activity #1 Cold War Terminology Go Over Definitions! HOMEWORK: Pgs 510-516 Questions: 1 & 4, 5, 6 Democracy Democracy is a form of government by the people in which citizens choose who will govern them through voting. American Perspective: From the American perspective, democracy is the best system of govt. In the US, decisions on everything from who should be president to what to watch on TV are made by majority rule. During much of the Cold War the US frequently violated democratic principles. African Americans could not vote in the south until the 60s and the US govt. supported dictatorships around the world. Soviet Perspective: The Soviets argued the US was hypocritical to promote democracy and capitalism at the same time. True democracy they argue, can only be secured in a system that rewards everyone equally. Equality Equality is the condition of being equal. American Perspective: Equality can be defined in on e of three ways. Equality of opportunity, equality before the law, and equality of condition. Americans argued equality of opportunity and before the law are necessary for a healthy society but equality of condition is not. Many Americans believe that providing guarantees for basic necessities, such as helth care and employment, regardless of a person’s effort or work undermines work ethic and adversely affects society. Soviets Perspective: Soviets argued that equality of condition was essential for a healthy society. They argued that a society must share its material wealth to ensure that no one has an unfair advantage. Capitalism Capitalism is an economic system that stresses the private ownership of industry, freedom of competition, and the acceptance of economic classes. American Perspective: From the American perspective capitalism is an economic system that provides the opportunity for individuals to better themselves through hard work and individual initiative. Soviet Perspective: Soviets believe capitalism is an evil economic system. They argued that the capitalism emphasis on competition breeds selfishness and undermines cooperation and community. They urged workers of the world to overthrow capitalist governments. Individualism Individualism is the belief that people working on their own to reach their highest level of achievement produces the best results for individuals and society. American Perspective: Americans believe that the outcome of people’s lives are determined not by outward circumstances, which can be overcome, but by inner fortitude. They argued that basic human nature is individualistic, competitive, and acquisitive. Soviet Perspective: Soviets believed that a society built upon individualism produces some winners and many losers. Soviets argued that individualism results in a society full of inequality and exploitation where winners take advantage of losers. Collectivism Collectivism is the belief that people working together produce better results for individuals and society than people working on their own. American perspective: Americans believe collectivism violates basic human nature, which they believe is competitive. They argued that by calling for sharing and teamwork collectivism works against human nature and is doomed to failure. It also violated the rights of individuals to own property. Soviet Perspective: Soviets believed cooperation and caring are the finest parts of human nature, and a society based on cooperation among people is possible in spite of humans’ nature. They argued that American emphasis on the individual resulted in exploitation of a large part of society. Fairness=shared ownership of property. In the soviet system every factory and business was owned collectively by all members of society. Socialism Socialism is an economic system that stresses govt. ownership of industry, economic equality, and a classless society. The government stipulates how people work together to produce goods and distributes the profits equally to the workers. American Perspective: Socialism threatens one of Americans’ most basic rights- the right to own and control property. Abe Lincoln “Property is the fruit of labor” Soviet Perspective: The soviets adopted socialism as a response to the evils of the capitalist system. They believed government ownership provided a means by which the wealth of a society could be evenly distributed to all the people. Totalitarianism Totalitarianism: A totalitarian government is one in which a few people have total control over the populace. Freedom of the press, speech, and religion are denied. American Perspective: Americans believe that totalitarianism is equivalent to dictatorship. They believe totalitarianism violates the basic human rights. Soviet perspective: Soviets believed that totalitarianism was required to transform society from an unequal one to one in which wealth was evenly distributed. Freedom Freedom is the condition of being free to express or do whatever one pleases. American Perspective: Soviet Perspective: Activity Defining Cold War Terms