Conservation of Moisture
advertisement

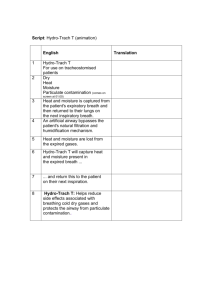
Conservation of Moisture The Moisture Equation • Equation of State • 1st Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation of Energy) • Moisture Equation (Conservation of Moisture) • Continuity Equation (Conservation of Mass) • Equations of Motion (Conservation of Momentum) – Coming to an ATMS 251 lab near you on March 22 Hydrologic Cycle – What can happen to moisture? Moisture Equation • Mathematical representation of what can happen to water in a column of the atmosphere Change of moisture storage in the column Evapotranspiration from ground Precipitation dS I E O P dt Moisture Inflow from atmosphere Moisture Outflow from column Precipitable Water • The vertical integral of the specific humidity for a column of atmosphere • Represents the upper limit to the total precipitation that may fall • Units: m (mm) Average Specific Humidity for the layer 1 N PW qi pi g i 1 Pressure Interval Sum up the number of levels This will yield the precipitable water in units of kg/m2. To get PW in units of meters, divide by the density of water (ρw=1000 kg/m3) PW (m) PW (kg / m 2 ) w http://www.osdpd.noaa.gov/PSB/IMAGES/images/amsua_tpw_des.gif Moisture Advection • Of course, moisture can be transported horizontally and vertically in the atmosphere – Moisture Advection q q q V q u v w x y z http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/guides/mtr/af/adv/gifs/madv1.gif