File
advertisement

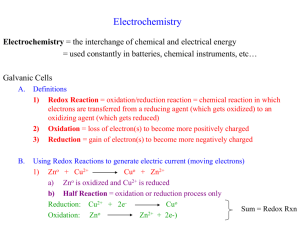
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 12/17 Redox Reactions Leave your completed Precipitates Lab out to be collected. They will be graded in the exhibition category. 1. Make qualitative observations about the pieces of Mg metal at your station 2. Dip them in the bath of CuSO4 3. Record detailed observations in your notebook 4. Use the “Activity Series” on the right – Which metal is more reactive, Copper or Magnesium? 5. What does this remind you of from the Durability Lab? 1 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 12/17 Electroplating 1. Connect your Nickel to the black wire. Turn on your power supply. Quickly dip it in and out of the the blue CuSO4 solution. Wipe /scrub firmly with a paper towel. Repeat. 2. On paper, RECORD your observations. 3. WHAT do you think is happening? WHY? 4. WRITE at least 2 questions that you would like to answer today about what happened in this demo. 5. This technique is called electroplating (coating one metal with another using electricity). WHY might an artist (or chemist) use this technique? Oxidation and Reduction lose oxidation When atoms _________ gain e it is called ___________________. reduction When atoms _________ e- it is called ___________________ . Therefore, - LeO the _____ lion goes LeO GeR GeR Redox Reactions Oxidation and reduction always occur together. Therefore, Redox these types of reactions are abbreviated ________________ reactions. These reactions are often broken up into ____________________. half - reactions Some redox reactions occur ____________________, spontaneously while others require ___________ energy . Half-reaction e- Lost or Gained? Oxidation OR Reduction Electroplating When metals are __________________ oxidized (lose e-), they can __________________ dissolve into solution. The reverse is also possible; when a dissolved metal cation is ________________ reduced (gains e-) they become uncharged ______________ solid metal electricity to coat the surface of one again. Using _________________ metal with another is called ______________________ electroplating . More Easily Oxidized Activity Series Electroplating eCu2+ Cu0 Cu0 Cu0 SO42- Cu2+ e- Cu2+ Cu2+ SO42- Cu2+ SO42- Cu2+ Cu2+ SO42- Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu2+ 2- SO4 Cu2+ cations being reduced (gaining e-) and plating as new solid copper metal onto the nickel coin Cu0(s) SO42- Cu0 metal being oxidized (losing e-) and dissolving into solution ePOWER SUPPLY Electroplating Left Side Front Flap Right Side Front Flap REDUCTION OXIDATION GeR LeO Gaining e- Losing e- Copper cations in the solution are becoming solid and electroplating onto the surface of the Nickel as solid Copper Solid Copper is dissolving into Copper cations Electroplating Left Side Inside Flap Right Side Inside Flap e- travel from the negative terminal and build up on the surface of the Nickel and are absorbed by Cu cations which become solid e- are leaving the piece of Copper because they are drawn to the positive terminal of the power supply. GeR Gaining e- Oxidation Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu0(s) LeO Losing e- Oxidation Cu0(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e-