Respiratory System

Respiratory System
• Lungs
• Air passages
Parts
Functions
• Takes in oxygen
• Removes carbon dioxide
• Body has 4-6 minute supply of oxygen
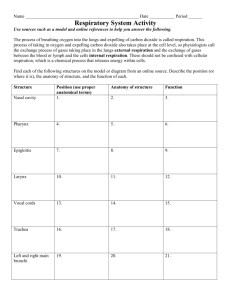
Air Passages
Nose
• 2 nostrils or nares
• Nasal septum
– Divides nose into 2 nasal cavities
• Lined
– With mucous membrane with a rich blood supply
• Functions
– Warms
– Moistens
– Filters
• Cilia
– Tiny hair-like structures that help move dirt trapped in mucous to the esophagus
• Olfactory Receptor
– Receptors for sense of smell
• Lacrimal Ducts
– Tear ducts
– Drain tears from the eye into the nose
Olfactory Receptors
Sinuses
• Cavities in the skull that surround the nasal area
• Connected to nasal cavities by short ducts
• Function
– Warms and moistens air
• Lined with mucous membrane
• Provides resonance for the voice
Pharynx
• Throat
• Lies behind the nasal passages
• 3 sections
– Nasopharynx
– Oropharynx
– Laryngopharynx
Larynx
• Voice box
• Layers of cartilage
– Largest is the thyroid cartilage commonly called the Adam's apple
• Contains
– Vocal chords
• Vibrate on exhaled air to produce sound
• The tongue and lips act on the sound to produce speech
– Epiglottis
• Flap of cartilage that closes the larynx during swallowing and prevents food and liquids from entering the trachea
Trachea
• Windpipe
• Series of “C” shaped cartilage to keep the tube open to the back
• Divide into the right and left bronchi
• Continues to divide into smaller bronchioles
• End in the alveoli
– Air sacs
Alveoli
- One cell thick and surrounded by capillaries
- Look like a cluster of grapes
- Allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Surfactant
- Surfactant
- Reduces surface pressure and prevents alveoli from collapsing
Exchange of Gases
Lungs
• Right lung 3 lobes
• Left lung 2 lobes due to the heart
• Covered by a double layer sac called the pleura
Pleura
Ventilation
• Process of breathing
• Diaphragm
– Muscle of respiration
– Assisted by the intercostal muscles
• Phases of respiration
– Inspiration
• Inhale
– Expiration
• Exhale
Dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
Diaphragm
Process of Respiration
• Controlled by the medulla oblongata in the brain
• An increase in amount of CO
2 in the blood , increases the rate of respiration
• Both involuntary and voluntary process
Stages of Respiration
• External
Respiration
– Exchange of gases between air in the lung and the blood
Internal Respiration
– Exchange of gases between the blood and the cells
Cellular Respiration
– Use of gases to make energy, water and
CO
2
Diseases
• Asthma
– Inflammation of airways with increased mucous production and muscle constriction
– Cause – allergen, exercise, stress, chemical
– S/S - wheezing, coughing, dyspnea, shortness of breath
– Tx bronchodilators, steroids
Nebulizer Inhaler
Bronchitis
• Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchial tubes
• Acute – infection
• Chronic – longtime exposure to smoking
• S/S productive cough, dyspnea, fever, chest pain
• Tx – antibiotics, bronchodilators, oxygen
Emphysema
Emphysema
• Non infectious, chronic respiratory condition when walls of alveoli deteriorate and loss elasticity
• CO
2 remains trapped in the alveoli
• Poor exchange of gases
• S/S dypnea, feeling of suffocation, barrel chest
• TX – No cure
Epistaxis
• Nosebleed
• Congested capillaries bleed
• Due to injury, blowing too hard, hypertension
• TX – pinch nostrils lean forward slightly
Influenza
• Flu
• Viral infection of the lungs
• Spread by respiratory droplet
• S/S - fever, malaise, chills, cough, sore throat, muscle pain
• Tx - symptomatic
Lung Cancer
• Leading cause of death of men and women
• S/S no symptoms in early stages, later cough hemoptysis
• Tx – surgical removal, radiation, chemotherapy
Pneumonia
• Inflammation or infection of the lungs
• Build up of exudates
(fluid) in the alveoli
• S/S cough, chest pain, fever, dyspnea
• Tx – antibiotics, bed rest, fluids, respiratory therapy, pain medication
Rhinitis, Laryngitis, Sinusitis
Tuberculosis
• Infectious lung disease caused by the bacteria
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
• Can be walled off in a tubercle and become dormant
• New strains are drug resistant
• S/S fatigue, fever, night sweats, hemoptysis weight loss, chest pain
• Tx - several drugs over a period of two years