100807 Respiratory Pharmacology Revised 319KB Jan 14 2015
advertisement

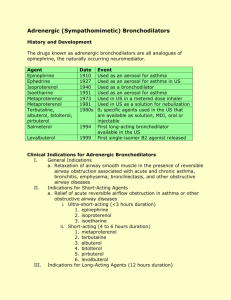
Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System P. Andrews Chemeketa Community College Paramedic Program Fall 07 When do we consider respiratory medications? • Asthma – Decreases pulmonary function – May limit daily activity – Presents with • SOB • Wheezing • Coughing Or, perhaps…… • • • • • • SOB, unknown etiology Allergic reaction Pneumonia Congestive heart failure Emphysema Others…..? Asthma, cont. • Has numerous components! – – – – – Bronchoconstriction Inflammation Edema Mucus hypersecretion And others…. • Usually an allergic reaction Categories of respiratory meds • Bronchodilators • Beta2 specific agonists (short-acting) • Beta2 specific agonists (long-acting) • Methylxanthines • Anticholinergics • Glucocorticoids • Leukotriene antagonists • Mast-cell membrane stabilizer Advantages of Nebulized Meds. • Smaller doses • Onset Rapid • Targeted delivery • Less side effects Disadvantages of Inhaled Meds • Variables in delivery • Usage variables – User – Caregiver • Requires delivery to lungs – Not always adequate depth of respiration Remember This? • • • • Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination Absorption and Distribution • Absorption – Ionized drugs (Ipratropium) • • • • Absorb poorly Won’t distribute well to body Mostly local effect Used for AEROSOL – Non-Ionized drugs (Atropine) • • • • Absorb well Distribute well Systemic Effect Poor Aerosol Drug Quick Review of Receptors – Sympathetic • Adrenergic – Epinephrine or Nor-epinephrine » Primary neurotransmitters – Parasympathetic • Cholinergic – Acetylcholine » Primary neurotransmitter Muscarinic • A drug that stimulates Acetylcholine at Parasympathetic nerve endings. • When drugs refer to muscarinic or antimuscarinic action, – It ONLY acts on Parasympathetic sites! Adrenergic Stimulation • Alpha 1 – Vasoconstriction – Increase Blood Pressure • Beta 1 – Increase Heart Rate – Increase Force of Heartbeat • Beta 2 – Bronchial Smooth Muscle Dilation Adrenergic Bronchodilators • Indication – Obstructive Airway Disease • Asthma, Bronchitis, Emphysema • Mode of Action – Adrenergic Receptors • Alpha 1…vasoconstriction • Beta 1…Increase HR • Beta 2…Bronchodilate (Yeah!) Adrenergic Bronchodilators • Adverse Effects – – – – – – Dizziness, Nausea, Tolerance, Hypokalemia, Tremors H/A Adrenergic Bronchodilators • Nonspecific agonists – Epinephrine (rarely used) • Beta2 Specific agonists – Short acting – Albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil) • 2.5 mg in 3 mL NS – Metaproterenol (Alupent) – Terbutaline (Brethine) Bronchodilators, cont. • Inhaled Beta2 selective (long-acting) – Salmeterol (Serevent) Anticholinergic Bronchodilators • Indication – Bronchoconstriction – Mainly in COPD • Mode of Action – Competes at Muscarinic receptors – Blocks Acetylcholine at smooth muscle – Reduces Mucus Production Anticholinergic Bronchodilators • Adverse Effects – Watch for Cholinergic side effects – More with nebulized form than MDI • Examples – Atrovent (ipratropium) • 0.5 mg in 2.5 mL NS – Combivent (mixed w/ Albuterol) • 0.5 mg Atrovent & 2.5 mg Albuterol in 3 ml NS) – Atropine • 0.5 – 1 mg in 2 – 3 mL of NS – Robinul • Peak effects in 1 – 2 hrs Mucus Controlling Agents • Indication – Excessive , thick secretions – As in COPD and TB • Action – Lower viscosity of mucus Mucus Controlling Agents • Side effects – – – – – Irritation of Airway Bronchospasm Pharyngitis, voice change, laryngitis Chest pain Rash • Considerations – Have suction ready – Anticipate cough Mucus Controlling Agents • Examples – Mucomyst (Acetylcysteine) • COPD, TB • Acetaminophen OD – Pulmozyme • Cystic Fibrosis – Nebulized Saline • Simple yet effective! Inhaled Corticosteroids • Indications – Asthma – Anti-Inflammatory MAINTENANCE – Require Hours to Act! Preventative drug • Mode of Action – Modifies RNA/DNA action in Cells – Complicated Stuff Inhaled Corticosteroids • Adverse Effect – Small incidence with nebulized • Oral doses have high incidence • Considerations – Not valuable in Acute Care – Watch for these in Pt Drug Lists Corticosteroids • Examples – – – – – – Beclovent, Vanceril Azmacort Aerobid Flovent Pulmicort Advair® • fluticasone (steroid) and salmeterol (bronchodialator) Glucocorticoids • Indications – Prophylactic treatment of Asthma – Hayfever Glucocorticoids (cont) • Mode of Action – Lowers release of Histamine in Mast Cells – Lowers release of Inflammatory Response • Prevents Bronchospasm, airway inflammation – Acts in allergic and non-allergic asthma – Not a bronchodilator! • Not for use in acute setting • Controllers, not relievers Glucocorticoids (cont) • Adverse Effects – Include • H/A • Nausea • Diarrhea Cromolyn sodium • Similar to glucocorticoids • Adverse Effects – Only coughing or wheezing Anti-inflammatory Agents, cont. • Corticosteroids - Injected – Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) • Children; 0.25 mg/kg (max dose 125 mg IVP) • Adults; 125 mg IVP – Dexamethasone (Decadron) Nasal Decongestants • Alpha1 agonist – Phenylephrine – Pseudoephedrine – Phenylpropanolamine • Administered as mist or drops • Side Effects – rebound congestion (use greater than 7 days) Antihistamines • Blocks histamine receptors • Common 1st generation – cause sedation – Chlor-Trimeton – Benadryl – Phenergan • Common 2nd generation – does not cause sedation – Seldane – Claritin – Allegra • Caution: thickens bronchial secretions – do not use in Asthma! Cough Suppressants • Antitussive meds – suppress cough stimulus in CNS – Codeine, hydrocodone A couple of ‘odd’ ones Epinephrine Racemic Epinephrine (microNEFRIN) • Class – Bronchodilator (adrenergic agonist) • Action – Affects both beta1 and beta2 receptors sites. Bronchodilation, reduces subglottic edema – Also increases pulse rate and strength – Also Alpha effects, vasoconstriction, Increased BP Epinephrine • Indications – Croup, Epiglottitise • Bronchospasm • Absorption – Absorption occurs following inhalation • Half-life – Unknown Epinephrine • Contraindications – Hypersensitivity • Precautions – Watch for Rebound Worsening – Watch ECG for changes – Increases Myocardial O2 demand • Side effects – Nervousness, restlessness, tremor, arrhythmias, hypertension, tachycardia Epinephrine • Interactions – Beta blockers may negate effects • Route and dosage – Inhalation • One time Only • 1 mg Epinephrine, 1:1000 in 3 mL NS • Considerations – Give ENROUTE – ONLY if patient in Extreme Distress Epi, cont. • May also consider Epi SQ – Patients who can’t cope with aerosol admin. – 0.3 – 0.5 mg SQ, then Neb treatment once patient can move air • Or Infusion; – 1 mg Epinephrine 1:1000 in 250 mL NS (concentration 4 mcg/mL) infuse at 1 mcg/min, titrating to effect Magnesium Sulfate • Not usually admin. in pre-hospital setting • Can be used to treat moderate to severe asthma in patients who respond poorly to beta-agonists • Don’t use in patients with heart blocks, myocardial damage, or hypertension • 2 gm in 100 mL NS, given over 2 – 5 min. Status Asthmaticus •