Biology 11: Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Fungi
advertisement

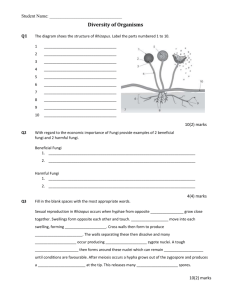
Name: Date: Biology 11: Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Fungi Purpose: To investigate the characteristics of Kingdom Fungi and their place in the development of complexity. Text: 355-361* This is essential reading. 1. Study the diagram below, which shows the timing of some major events in the history of life: a) According to the diagram above, are Fungi most closely related to Animals or Plants? b) Approximately how long ago did the branch of the phylogenetic tree that gave rise to Fungi evolve? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 1 2. Are fungi mainly unicellular of multicellular? ____________________ Name one exception. ____________ Although we may think of them as plants they are heterotrophs and this means that they _________________________________________. Fungi are different from Animals as they secrete ______________________ that break down food outside of their bodies. Fungi can then ______________________ the nutrient molecules. Most are saprotrophic decomposers that break down _________________________________________________. Present Classifications of Fungi There are over 100,000 known species of fungi, but scientists predict that there could be as many as 1.5 million! Fungi are classified based on sexual reproduction structures and molecular evidence. a) Chytrids have flagellated spores and live in fresh water and soil. They are thought to be the earliest fungi lineage. b) Zygomycetes have protective zygosporangia around their spores. Bread mold is an example. c) Glomeromyctes are important symbiotic partners with plants, delivering phosphate and other minerals in exchange for organic nutrients. d) Ascomycetes are characterized by sac-like asci that produce spores. They can range from unicellular yeasts to elaborate morels and include plant pathogens. e) Basidiomycetes have club-shaped spore producing structures called basidia. They are important decomposers of wood, but can also include plant pathogens. Watch the link to see killer fungi! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XuKjBIBBAL8 Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 2 3. If you were to dissect a fungus you would find it is made up of filaments called hyphae and mycelia. What is the difference between a hypha and a mycelium? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________ 4. Describe the difference between the fruiting body and the vegetative body. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 3 _____________________________________________________________________________________ Fungi Explorations a) Basidomycetes Examination -Instructions: 1. Obtain a mushroom. This is one type of Basidomycete fruiting body 2. Draw a diagram to illustrate the macroscopic structure of the mushroom. (1 Mark) Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 4 3. Remove the cap and examine the gills under the dissecting microscope. Do you see any spores? (1 Mark) _________ 4. Use high magnification on light microscope to observe the gills and basidia (clubshaped, spore-bearing structures on the gills) in a prepared slide. Draw and label your observations. (1 Mark) Magnification Power: ______________(1 Mark) Other Observations: Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 5 b) Ascomycete Examination page 357 fig 17.14D and charts in lab. 1. Name and briefly describe 2 multicellular ascomycetes. (1 Mark) Ascospore Ascus ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Examine the prepared slides of the spore containing asci under the light microscope. Label: Ascus and Ascospores (1 Mark) Magnification Power: _____________ (1 Mark) Other Observations: 2. Yeast Examine the yeast sample through a light microscope and draw what you observe. (1 Mark) Magnification Power: _____________ (1 Mark) Other Observations: How is yeast different to other forms of ascomycetes? (1 Mark) _________________________ -How is Yeast different in its dormant and live (or reproducing) stage? (2 Marks) Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 6 _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ -What is the scientific name for yeast? (1 Mark) ______________________________________________ 3. Ascomycete Mutalistic Relationship with Algae (Text 359) -Lichens are a symbiotic relationship between a ________________ and a blue green algae ( ________). (1 Mark) -Label all parts of a lichen in one of the diagrams right. (1 Mark) -What does the Fungi provide in this relationship? And the Algae? (2 Marks) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Examine the various lichens in the lab and comment on their macroscopic structure. (1 Mark) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Zygomycete Examination a) Bread mold is a common zygomycete found in everyday life. -What is the scientific name for Bread Mold? (1 Mark) ________________________________________ Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 7 1. Examine the Bread Mold prepared slide underneath a light microscope. 2. Draw what you observe. Label one sporangium and one sporangiophore. (1 Mark) Magnification Power: _________________ (1 Mark) Other Observations: b) Penicillium (Text 358) -Examine the cheese on display and read the following: -Blue Cheese is cow, sheep or goat milk cheeses that have had Penicillium cultures added to them. This produces an end product that is spotted or veined with blue, blue-gray or blue-green mold and which has a distinctive smell. Some blue cheeses are injected with spores before the curds form and others have spores mixed in with the curds after they form. Blue cheeses are typically aged in a temperature controlled environment, such as a cave. What is the medical significance of Penicillium? (1 Mark) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Fungal Mutualistic Relationship with Plants (Text 359) Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 8 -The mutually beneficial relationship between Fungi and Plants is called __________________. (1 Mark) a) The picture shows a myccorrhizal fungal relationship with a plant. What does the Fungi provide in this relationship? And the Plant? (2 Marks) __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Label the endomyccorrhizae and plant root cells in the diagram below. Indicate with labelled arrows the flow of minerals and water between the two cells. (2 Marks) b) In what other way are fungi essential to the survival of plants? (1 Mark) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Parasitic Fungi Relationships (Text 361) -Name and describe two Fungi that parasitize plants and two that parasitize humans. (2 Marks) ____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 9 Predatory Fungi- View videos of specialized hyphae trapping Nematodes from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v8Y8i5DDsHs&feature “World’s first video on soil nematode trapped Arthobotrys mycoadhesive” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h8PlLHkddpA&feature “Nematode lassoed by a fungus.” -Describe how the Fungi would “eat” their prey after having captured them. (3 Marks) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Fungi Mutalistic Relationships with Leafcutter Ants -Watch the http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dOV0E5FaKoQ “Ancient Farmers of the Amazon” and briefly record what you learn from this video about the roles of the following organisms in the food chain discussed: (3 Marks) a) Ants: ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Fungi: _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Bacteria: ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Biology 11: Kingdom Fungi Page 10