01. Introduction
advertisement

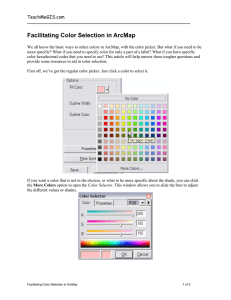
ECE 638: Principles of Digital Color Imaging Systems Jan P. Allebach School of Electrical and Computer Engineering allebach@purdue.edu What is a digital color imaging system? What else besides printers? Digital cameras Flatbed scanners Mobile phones Flat panel displays How do we organize all this? Image capture devices Cameras Scanners Image output devices Interconnection space and processing Personal computers Internet Displays Printers What do we need to study in order to understand digital color imaging systems? Color science Image capture Image display Image printing Image processing Image quality models and assessment Color science topics What is color? Trichromatic model for human vision Opponent channel models for human vision Standard color spaces Models for color imaging devices – Device gamma Color imaging systems calibration Transformation between color spaces – White point – Color space interpolation – Gamut mapping Color appearance models Color management practices Image capture topics Sensors – Technologies – Characteristics and models Scanners – Architecture – Illuminations – Scan bar motion Spatial analysis of scanning and sampling Calibration of image capture devices Descreening Page classification Image display topics Display technologies – – – – Cathode ray tube Liquid crystal Plasma panel E-paper Calibration of image display devices Spatial analysis of image display Color image quantization Image printing topics Printing technologies – Silver halide-based systems – Ink-based systems • Plate-based systems • Inkjet systems – Toner-based systems • Dry electrophotography • Wet electrophotography Colorant-media-light interaction Color trapping Digital halftoning Calibration of printing systems Image quality models and assessment topics Image quality terminology Basic psychophysical methods Image artifact assessment Image quality metrics Image quality rulers What is color? Let’s see what Microsoft has to say about color Click on “More Font Colors…” HSV HSL Crayon Picker CMYK Picker What did we learn? Lots of different ways to talk about color Ordering and naming systems – Crayon picker Coordinate systems – HSV – HLS – CMYK Many questions remain… How were these attributes chosen? – – – – Hue Saturation Lightness Value Which CMYK are we talking about? – Rendering device – Capture device CMYK Cyan (C) Magenta (M) Yellow (Y) Black (K) Which CMYK? – effect of rendering device Monitor HP DJ 970Cse Mac Driver HP DJ 970Cse IPP Driver Which CMYK? – effect of capture device Olympus C3000 Digital Camera Heidelberg Scanner Different color representations Are they all equivalent? How do we get from one to the other? Can we get from one to the other? Even if we can, what do all these numbers mean? Example: capture to capture Given RGB values from one capture device, can we predict RGB values for a second capture device? Olympus C3000 Digital Camera Scanner RGB values (23, 136, 180) RGB values (?, ?, ?) (203, 11, 52) (?, ?, ?) (219, 186, 33) (?, ?, ?) (7, 7, 7) (?, ?,?) Discussion topic What is the basis for the equations that underlie color transformations? So what is color? Color is a sensation experienced by a human being in response to a visual stimulus. What are the key parts of this definition? Color is a sensation experienced by a human being in response to a visual stimulus. Sensation – human being Need to understand something about the human visual system – physiology – perception – psychophysics Relevant courses – EE 595T Psychophysics (Profs. Hong Tan and Zygmunt Pizlo) – PSY606V Vision Seminar (Prof. Zygmunt Pizlo) Visual stimulus Need to understand interaction of illuminant and object Illuminant Viewer Object Why should we care about color? Important aspect of everyday experience New imaging and information technologies provide unprecedented ability to manipulate and use color – Capture devices • digital cameras • scanners – Output devices • CRT and LCD displays • Inkjet and laser printers – Intermediaries • PCs • applications • internet and web Why should we care… Color provides valuable information about the world around us Application areas – – – – manufacturing medicine agriculture environmental Contexts – image analysis for inspection – machine vision for robotics – remote sensing